Multi-Dimensional Context-Aware Adaptation of Service Front-ends
- 1. FP7 Serenoa (ICT Call 5) Multi-Dimensional Context-Aware Adaptation of Service Front-ends www.serenoa-fp7.eu On behalf of Serenoa project Jean Vanderdonckt Université catholique de Louvain jean.vanderdonckt@uclouvain.be http://www.slideshare.net/jeanvdd/multidimensional-contextaware-adaptation-of-service-frontends
- 2. Overview • Serenoa is aimed at developing a novel, open platform for enabling the creation of context sensitive service front- ends (SFEs) • Context-sensitive SFE provides a user interface (UI) that – exhibits some capability to be aware of the context • User • Platform • Environment – and to react to changes of this context in a continuous way • Goal: improving people’s satisfaction and performance compared to traditional SFEs based on manually designed UIs
- 3. Computational Framework Domain CADS CARF CARFO – OWL Design Refer. Space Frame. Context + Reference Models (UML) Context of Use Management Advanced Adaptation Algorithms Adaptation Task & Domain Engine Authoring Tool Abstract UI Runtime UI Generation Enabling Concrete UI Technologies Final UI Methodology Adaptation Engine Technology Domain
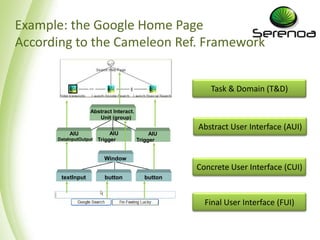
- 4. Example: the Google Home Page According to the Cameleon Ref. Framework Task & Domain (T&D) Abstract Interact. Unit (group) Abstract User Interface (AUI) AIU AIU AIU DataInputOutput Trigger Trigger Window Concrete User Interface (CUI) textInput button button Final User Interface (FUI)
- 5. Cameleon Reference Framework Reification: from high- to lower-level T&D → AUI AUI → CUI: e.g., a GUI, a vocal UI CUI → FUI: e.g., HTML, VB for GUI VoiceXML, X+V for Vocal UI Task & Domain (T&D) Abstraction: from low- to higher-level FUI → CUI: e.g., reverse HTML CUI → AUI: e.g. for changing modality Abstract User Interface (AUI) AUI → T&D: e.g., for recovering task Reflexion: at the same level FUI: e.g. transcoding Concrete User Interface (CUI) CUI: e.g., graceful degradation AUI: e.g., restructuring T&D: e.g., for retasking Final User Interface (FUI)
- 6. Standardization action with W3C • Step 1: W3C Incubator Group on Model- Based User Interface Design – The Cameleon Reference Framework is a reference for expressing the levels of abstraction during user interface development – Recommended in the final report at http://www.w3.org/2005/Incubator/model -based-ui/XGR-mbui-20100504/ (July 2010)
- 7. Standardization action with W3C • Step 2: Serenoa partners join their effort – IDEAL2 (CTIC): http://files.morfeo- project.org/mymobileweb/public/specs/ide al2/ – Maria (ISTI): http://giove.isti.cnr.it/tools/MARIA/home – UsiXML (UCL): www.usixml.eu, www.usixml.org
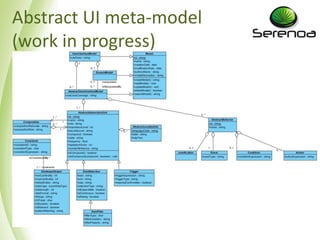
- 8. Standardization action with W3C • Step 3: W3C Charter Group on Model-Based User Interface Design (http://www.w3.org/wiki/Model- Based_User_Interfaces) – Also see http://www.w3.org/2011/mbui/ – Started Feb. 2012, end in Nov. 2013 – Lead by Dave Raggett <dsr@w3.org> • Contents – Introduction to MBUI – Glossary of MBUI terms – Task meta-model – Abstract user interface meta-model
- 10. Abstract UI meta-model (work in progress)
- 11. Next steps • Finalizing the meta-models and interchange formats – UML2.0 Class Diagram and OWL2 Full ontology – XML Schema • Coverage of use cases • Software implementation compliant with the W3C MBUI format • Quill – A Collaborative model-based UI editor using WebSockets – http://www.w3.org/2012/quill/
- 12. Thank you very much! • Some links – http://www.w3.org/2011/01/mbui-wg-charter – http://www.w3.org/wiki/Model- Based_User_Interfaces – http://www.w3.org/2012/quill/ – www.serenoa-fp7.eu
Editor's Notes
- GivenThe context consists of CADS + CARF: it is a generic meta-model that defines context information (in a broad approach)The context of use management includes: pre-processing (sensing and treating information) by instantiating the RMThe adaptation engine takes the instances of the RM given by the Context of Use Management and matches them with the AAA, producing as a result a selection of methods, techniques and strategies to perform and present (respectively) adapted UIThe main open questions that remainHow the runtime UI generation is related with the “Cameleon RF”How the authoring tool and the enabling technologies are involved? (the enabling technologies can be ‘decided’/’inferred’ by the AAA based on information provided by the set: Contex+RM+Context of Use Management)
- GivenThe context consists of CADS + CARF: it is a generic meta-model that defines context information (in a broad approach)The context of use management includes: pre-processing (sensing and treating information) by instantiating the RMThe adaptation engine takes the instances of the RM given by the Context of Use Management and matches them with the AAA, producing as a result a selection of methods, techniques and strategies to perform and present (respectively) adapted UIThe main open questions that remainHow the runtime UI generation is related with the “Cameleon RF”How the authoring tool and the enabling technologies are involved? (the enabling technologies can be ‘decided’/’inferred’ by the AAA based on information provided by the set: Contex+RM+Context of Use Management)
- GivenThe context consists of CADS + CARF: it is a generic meta-model that defines context information (in a broad approach)The context of use management includes: pre-processing (sensing and treating information) by instantiating the RMThe adaptation engine takes the instances of the RM given by the Context of Use Management and matches them with the AAA, producing as a result a selection of methods, techniques and strategies to perform and present (respectively) adapted UIThe main open questions that remainHow the runtime UI generation is related with the “Cameleon RF”How the authoring tool and the enabling technologies are involved? (the enabling technologies can be ‘decided’/’inferred’ by the AAA based on information provided by the set: Contex+RM+Context of Use Management)
- GivenThe context consists of CADS + CARF: it is a generic meta-model that defines context information (in a broad approach)The context of use management includes: pre-processing (sensing and treating information) by instantiating the RMThe adaptation engine takes the instances of the RM given by the Context of Use Management and matches them with the AAA, producing as a result a selection of methods, techniques and strategies to perform and present (respectively) adapted UIThe main open questions that remainHow the runtime UI generation is related with the “Cameleon RF”How the authoring tool and the enabling technologies are involved? (the enabling technologies can be ‘decided’/’inferred’ by the AAA based on information provided by the set: Contex+RM+Context of Use Management)
- GivenThe context consists of CADS + CARF: it is a generic meta-model that defines context information (in a broad approach)The context of use management includes: pre-processing (sensing and treating information) by instantiating the RMThe adaptation engine takes the instances of the RM given by the Context of Use Management and matches them with the AAA, producing as a result a selection of methods, techniques and strategies to perform and present (respectively) adapted UIThe main open questions that remainHow the runtime UI generation is related with the “Cameleon RF”How the authoring tool and the enabling technologies are involved? (the enabling technologies can be ‘decided’/’inferred’ by the AAA based on information provided by the set: Contex+RM+Context of Use Management)
- GivenThe context consists of CADS + CARF: it is a generic meta-model that defines context information (in a broad approach)The context of use management includes: pre-processing (sensing and treating information) by instantiating the RMThe adaptation engine takes the instances of the RM given by the Context of Use Management and matches them with the AAA, producing as a result a selection of methods, techniques and strategies to perform and present (respectively) adapted UIThe main open questions that remainHow the runtime UI generation is related with the “Cameleon RF”How the authoring tool and the enabling technologies are involved? (the enabling technologies can be ‘decided’/’inferred’ by the AAA based on information provided by the set: Contex+RM+Context of Use Management)