An introduction to agile leadership
- 2. We build teams that excel Working at all levels of the organization: strategic, teams, individual skills
- 4. Leadership at the center
- 5. Leadership in agile? What we want? ● Autonomous teams ● Self organized teams ● Servant leaders: ○ Scrum Masters ○ Product owners? ● Predictability in their behaviours
- 6. Leadership in agile? What we want? ● Autonomous teams ● Self organized teams ● Servant leaders: ○ Scrum Masters ○ Product owners? ● Predictability in their behaviours What we sometimes get? ● Chaos ● Frustration ● Under performance ● Burntout (personal and team) ● No consistency
- 7. Example: What are the expectations? What are the expectations for each: ● The Product Owner ● Scrum Master ● The Team ● The Stakeholders ● The Agile Coach
- 8. Leadership A bird's eye view
- 9. Experiment time! A taste of leadership... ● 8 volunteers! ● 7 grab a sheet of paper and close your eyes! (Follow my instructions!) ● 1 is going to be my right hand.
- 11. Experiment time! Another taste of leadership. ● Split in teams of 4 - 5 people!
- 12. Some questions: Comment with your groups: ● Who is a leader? ● What makes a good leader? ● Is it something you are born with? ● Is a boss a “de facto” leader? ● Can there be more than one leader in team or group? ● Is someone who uses coercion or force a leader? ● Are we all leaders?
- 14. A definition Leadership is a process of social influence, which maximizes the efforts of others, towards the achievement of a goal.
- 15. Core theories of leadership
- 16. Leadership as Traits Assumptions: ● People are born with inherited traits. ● Some traits are particularly suited to leadership. ● People who make good leaders have the right (or sufficient) combination of traits.
- 17. Leadership as Behaviours Assumptions: ● Leaders can be made, rather than are born. ● Successful leadership is based in definable, learnable behavior.
- 18. Leadership as Contingency Assumptions: ● The leader's ability to lead is contingent upon various situational factors, including the leader's preferred style, the capabilities and behaviors of followers and also various other situational factors.
- 19. Leadership as Power Assumptions: ● Power is the ability to get others to change their behavior even if they do not wish to do so.
- 20. Daniel Goleman Daniel Goleman: Author, psychologist, and science journalist. Wrote the bestseller Emotional Intelligence and has received numerous awards including: ● Career Achievement award for journalism from the American Psychological Association ● Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in recognition of his efforts to communicate the behavioral sciences to the public ● Klingenstein Educational Leadership Award ● Harvard Business Review McKinsey Award winner for his December 2013 article “The Focused Leader”
- 22. The 6 leadership styles
- 23. The 6 leadership styles 1. Share some examples of this leadership styles that you have seen. 2. Discuss with your group: ● Which one is the best? ● Which one is your dominant style? ● Which one is your weakest style? ● Which style do you think a leader in agile needs?
- 24. The 6 leadership styles
- 25. There is no silver bullet Great leaders know how to use each one of them depending on the context.
- 26. How leadership influences results? Comment with your groups: ● What is the link between team results and leadership?
- 28. How leadership influences results? Team climate: ● About 30% of the impact in the organizational performance comes from having a healthy team climate ● Team climate is a combination of motivation, behaviour and leadership styles (clarity, commitment, rewards, etc.) ● Leaders can shape that climate by using different leadership styles (about 70% impact)
- 29. How leadership influences results
- 33. Unilateral control mindset Values: ● Be right ● Act rational ● Don’t lose ● Minimize expression of negative feelings Assumptions: ● I understand the situation; those who disagree, don’t ● I am right; those who disagree are wrong ● I have pure motives; those who disagree have questionable motives ● My feelings and behaviours are justified ● I am not contributing to the problem
- 34. Unilateral control mindset Behaviours: 1. I state my views without asking for others views and vice versa 2. Withhold relevant information 3. I speak in general terms and don’t agree in what important words mean 4. I keep my reasoning private; don’t ask others about their reasoning 5. Focus on positions, not interests 6. Act on untested assumptions and inferences as if they were true 7. Control de conversation 8. Avoid, ease into, or save face in difficult issues
- 35. Unilateral control mindset Results: 1. Lower performance, longer implementation, increased costs, less innovation 2. Lower commitments, decreased trust, reduced learning, greater defensiveness, etc. 3. Reduced motivation, decreased satisfaction, increased stress, limited development opportunities, etc.
- 38. Common learning mindset Values: ● Transparency ● Curiosity ● Informed choice ● Accountability ● Compassion Assumptions: ● I have information; so do other people ● Each of us sees things others don’t ● People may disagree with me and still have pure motives ● Differences are opportunities for learning ● I may be contributing to the problem
- 39. Common learning mindset Behaviours: 1. I state views and ask genuine questions 2. Share all relevant information 3. Use specific examples and agree on what important words mean 4. Explain reasoning and intent 5. Focus on interest, not positions 6. Test assumptions and inferences 7. Jointly design next steps 8. Discuss undiscussable issues
- 40. Common learning mindset Results: 1. Higher quality, lower implementation time, decreased costs, more innovation 2. Greater commitments, increased trust, increased learning, less defensiveness, productive conflict, appropriate dependencies on others, etc. 3. Increased motivation, increased satisfaction, decreased stress, enriched development opportunities, etc.
- 41. Which one fits best?
- 42. Experiment time!! Which one are you? 1. Grab two post-it notes. 2. Write what is your mindset on one. 3. Write what the proportion between mindsets that you see around you is. For examples, 50% - 50%. 4. Swap your post-its with someone else.
- 44. Leadership at the center
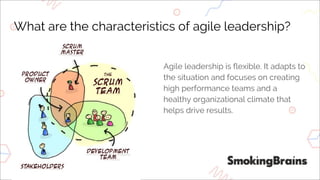
- 45. What are the characteristics of agile leadership? Agile leadership is flexible. It adapts to the situation and focuses on creating high performance teams and a healthy organizational climate that helps drive results.
- 46. Quick recap Leadership is essential if we want a successful agile organization. It is not a one size fits all… The context is important therefore adapting styles and plan to the person, is key. The relationship between leadership and team results. We saw two models that can help us understand what is at the core of agile leadership. ● Unilateral Control mindset ● Common learning mindset
- 48. Thanks ;) Follow us at @teamsthatexcel