Endocrine system & disorders, gland by gland
- 1. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM • System of ductless glands • Regulates body functions via hormones secreted into the bloodstream. Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 1
- 2. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Major Endocrine Glands: • Hypothalamus • Pituitary Gland • Thyroid Gland • Parathyroid Gland • Thymus • Adrenal Gland Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 2
- 3. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Other organs containing endocrine tissue: • Pancreas • Kidneys • Heart • Digestive Tract • Placenta • Testes • Ovaries • Pineal Gland Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 3
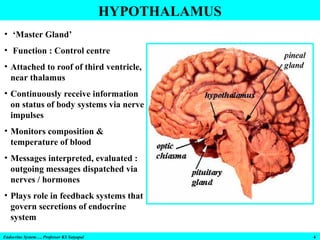
- 4. HYPOTHALAMUS • ‘Master Gland’ • Function : Control centre • Attached to roof of third ventricle, near thalamus • Continuously receive information on status of body systems via nerve impulses • Monitors composition & temperature of blood • Messages interpreted, evaluated : outgoing messages dispatched via nerves / hormones • Plays role in feedback systems that govern secretions of endocrine system Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 4
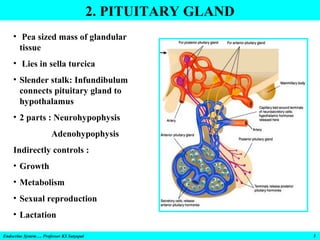
- 5. 2. PITUITARY GLAND • Pea sized mass of glandular tissue • Lies in sella turcica • Slender stalk: Infundibulum connects pituitary gland to hypothalamus • 2 parts : Neurohypophysis Adenohypophysis Indirectly controls : • Growth • Metabolism • Sexual reproduction • Lactation Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 5
- 6. 2. PITUITARY GLAND: PARTS Neurohypophysis Adenohypophysis Small posterior lobe Large anterior lobe Stores hormones Releases hormones Oxytocin Growth hormone (GH) Anti Diuretic hormone (ADH) Thyroid Stimulating hormone (TSH) Adenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Lutenizing hormone (LH) Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH) Prolactin (PRL) Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 7. 2. PITUITARY GLAND: HORMONES HORMONES Stimulates contraction of uterus & contractile cells of breast Prevents excess urine production GH General body growth ACTH Stimulate adrenal cortex to release hormone TSH Controls thyroid gland LH Stimulates sexual & reproductive function FSH Stimulate production of sperm & egg in ovaries & testis MSH Related to skin pigmentation PRL Posterior Pituitary Oxytocin (OC) ADH Anterior Pituitary EFFECTS Initiates milk production in breast Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 8. 3. THYROID GLAND • Located in middle anterior part of neck: below larynx, in front of trachea • “Butterfly” shape • 2 lobes connected by isthmus • ↑ in size : puberty & pregnancy • Rich blood supply: able to deliver high levels of hormones in short period of time • Produces Thyroxin (T4) & Tri-iodothyronine (T3) • Calcitonin : involved in calcium & phosphate homeostasis Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
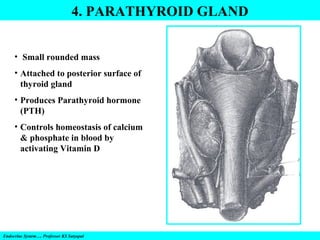
- 9. 4. PARATHYROID GLAND • Small rounded mass • Attached to posterior surface of thyroid gland • Produces Parathyroid hormone (PTH) • Controls homeostasis of calcium & phosphate in blood by activating Vitamin D Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 10. 5. THYMUS • Plays a role in the immune system • Produces thymosin, thymic humaral factor & thymic factor • Responsible for maturation of T-lymphocytes Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
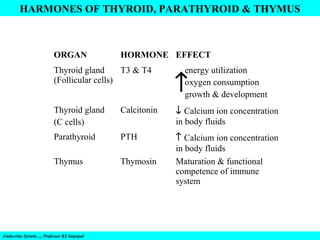
- 11. HARMONES OF THYROID, PARATHYROID & THYMUS ORGAN HORMONE EFFECT Thyroid gland T3 & T4 (Follicular cells) energy utilization oxygen consumption growth & development ↑ Thyroid gland (C cells) Calcitonin ↓ Calcium ion concentration in body fluids Parathyroid PTH Thymus Thymosin ↑ Calcium ion concentration in body fluids Maturation & functional competence of immune system Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 12. 6. ADRENAL GLAND • Located superior to the kidney • Divided into: (i) outer cortex (ii) inner medulla Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 13. 6. ADRENAL GLAND ADRENAL CORTEX ADRENAL MEDULLA Secretes steroid hormones Secretes hormones controlled by ANS Glucocorticoids (metabolism) eg. cortisol Epinephrine (Adrenaline) Mineralocorticoids (homeostasis of ions) eg. Aldosterone Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) Gonadocorticoids (oestrogens & androgens) Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
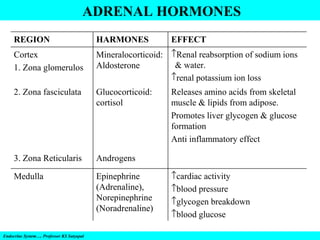
- 14. ADRENAL HORMONES REGION HARMONES Cortex 1. Zona glomerulos Mineralocorticoid: ↑Renal reabsorption of sodium ions & water. Aldosterone ↑renal potassium ion loss 2. Zona fasciculata Glucocorticoid: cortisol 3. Zona Reticularis Androgens Medulla Epinephrine (Adrenaline), Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal EFFECT Releases amino acids from skeletal muscle & lipids from adipose. Promotes liver glycogen & glucose formation Anti inflammatory effect ↑cardiac activity ↑blood pressure ↑glycogen breakdown ↑blood glucose
- 15. 7. PANCREAS • Flattened organ • Lies retroperitoneally & transversly across posterior abdominal wall • Posterior to stomach, between doudenum on right & spleen on left • Classified as exocrine & endocrine Hormones: • Islets of Langerhans secrete: Glucagon, α cells : ↑ blood glucose Insulin, β cells: ↓ blood glucose • Growth harmone inhibiting hormone (GHIH), δ cells : inhibits glucagon & insulin Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 16. HORMONES OF PANCREAS CELLS HARMONE EFFECT Alpha (α) cells Glucagon Glucose synthesis & glycogen breakdown in liver ↑ Blood glucose concentration Beta (β) cells Insulin Stimulation of lipids & glycogen storage & formation ↓ Blood glucose concentration Delta (δ) cells Somatostatin Inhibits secretion of insulin & glucagon Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 17. 12 & 13. TESTES & OVARIES TESTES: • Located within scrotum • Produce testosterone • Stimulates development of male sexual characteristics OVARIES: • Located in pelvic cavity • Produce oestrogen & progesterone • Responsible for development & maintenance of female characteristics & menstrual cycle Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 18. HORMONES OF REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM CELLS HORMONES EFFECT Testes Interstitial cells 1. Testosterone 2. Inhibin 1. Maturation of sperm Male secondary sex characteristics 2. Inhibits secretion of FSH Ovaries Follicle cells 1. Oestrogen 2. Inhibin 1. Follicle maturation Female secondary sex characteristic 2. Inhibits secretion of FSH Corpus Luteum Progesterone Prepare uterus for implantation Prepare breast for secretory function Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 19. OTHER ENDOCRINE TISSUES KIDNEYS: • Renal Erythropoietic factor: erythropoietin HEART: • Atrial Natriuretic factor (ANF) GIT: • Stomach gastrin, enteric gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin, enterocinin, gastric inhibiting hormone PLACENTA: • Human chorionic gonadotropin, oestrogen, progesterone, relaxin Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 20. ENDOCRINE DISORDERS 2 Categories: • Abnormal hormone production • Abnormal cellular sensitivity ACROMEGALY: • Over production of growth hormone after the epiphyseal plates have fused • Bone shape changes • Cartilaginous areas of skeleton enlarge • Broad facial features • Enlarged lower jaw Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 21. ENDOCRINE DISORDERS CRETINISM • Results from thyroid hormone insufficiency in infancy Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 2
- 22. ENDOCRINE DISORDERS GOITER • Enlarged thyroid gland • Results from thyroid hormone hyposecretion • Due to iodine insufficiency Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 23. ENDOCRINE DISORDERS CUSHING’S SYNDROME • Results from hypersecretion of glucocorticoids • Lipid reserves are mobilized • Adipose tissue accumulates in cheeks & base of neck Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 24. PROSTAGLANDINS • Regulators of cell metabolism Pathology: Important in normal physiology of: • Induce Inflammation • Smooth muscle • Promote fever • Blood flow • Intensify pain • Platelet function • Nerve transmission • Immune response • Secretion • Reproduction • Respiration • Fat Metabolism • Inflammation Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal
- 25. FEEDBACK CONTROL OF HORMONE RELEASE • Regulation Eg. Production of releasing substance / inhibiting substance → Release of hormone from pituitary gland → stimulates hormone release by target gland → hormone exert normal effect & influence further release of a releasing or inhibiting substance → inhibit release of hormone from pituitary gland Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal