Active Packaging
- 1. welcome Presented by: KRUSHNA YADAV D K ACTIVE PACKAGING
- 2. ACTIVE PACKAGING • Packaging is the technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use • Active packaging Incorporation of certain components into packaging systems that release or absorb substances from or into the packed food or the surrounding environment so as to prolong shelf life and sustain the quality, safety and sensory characteristics of the food.
- 4. Examples of active packaging systems Active packaging system Oxygen scavengers Mechanisms 1. iron based 2. metal/acid 3. metal (e.g. platinum) catalyst 4. Ascorbate metallic salts 5. enzyme based Food application bread, cakes, cooked rice, biscuits, pizza, pasta, cheese, cured meats and fish, coffee, snack foods, dried foods and Beverages.
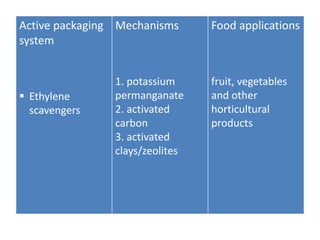
- 5. Active packaging system Ethylene scavengers Mechanisms 1. potassium permanganate 2. activated carbon 3. activated clays/zeolites Food applications fruit, vegetables and other horticultural products
- 6. Active packaging system Ethanol emitters Mechanisms 1. alcohol spray 2. encapsulated ethanol Food applications pizza crusts, cakes, bread, biscuits, fish and bakery
- 9. ACTIVE PACKAGING • Active packaging includes additives or freshness enhancers that are capable of scavenging • Oxygen • Adsorbing carbon dioxide • Moisture • Ethylene or flavour/odour taints • Releasing ethanol, sorbates, antioxidants or other preservatives • Maintaining temperature control.
- 10. Active packaging applications: • Absorbing/scavenging-oxygen, carbon dioxide, moisture, ethylene, flavours, taints, UV light . • Releasing/emitting-ethanol, carbon dioxide, antioxidants,preservatives, sulphur dioxide, flavours, pesticides. • Removing-catalysing food component removal: lactose, cholesterol. • Temperature control-insulating materials, self-heating and self- cooling packaging,microwave susceptors and modifiers, temperature-sensitive packaging. • Microbial control-UV and surface-treated packaging materials.
- 11. Goal of active packaging • The goal of active packaging in conjunction with other food processing and packaging is to enhance preservation of contained food and beverage products. • For example, to optimize the effects of oxygen scavenging, oxygen should first be removed from the product during processing and packaging operations.
- 12. • TRENDS • Reduce the food waste: extend shelf life, monitor food spoilage. • Incorporation of natural active agents into more sustainable packaging material. • CHALLENGES FOR ACTIVE PACKAGING • High cost • Technical limitations: preservation of material properties, integration.
- 13. Conclusion • Active packaging is an emerging and exciting area of food technology that can confer many preservation benefits on a wide range of food products. • The objectives of this technology are to maintain sensory quality and extend the shelf life of foods whilst at the same time maintaining nutritional quality and ensuring microbial safety.