Cns lecture alz and als
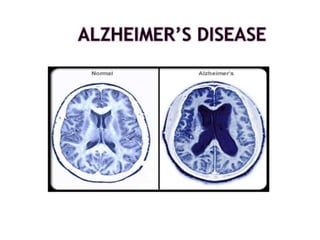
- 3. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, not managing self-care, and behavioural issues.
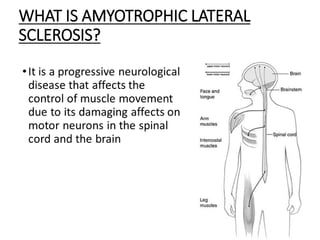
- 10. WHAT IS AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS?
- 11. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a group of rare neurological diseases that mainly involve the nerve cells (neurons) responsible for controlling voluntary muscle movement. Voluntary muscles produce movements like chewing, walking, and talking.
- 12. SIGNIFICANCE OF THE NAME OF THIS DISEASE • A-myo-trophic comes from Greek • “A” = no/negative • “myo” = muscle • “trophic” = nourishment • “No Muscle Nourishment” • Lateral = defines location of the nerve cells that signal and control the muscles • Sclerosis = scarring and hardening in the degenerating region
- 13. OTHER COMMON NAMES FOR THIS DISEASE •Motor neuron disease •Charcot’s disease •Lou Gehrig’s disease Picture from the Neuromuscular website
- 14. NATURE AND CHARACTERISTICS OF ALS Forms: Two types of ALS: • Sporadic – no family history • Familial – family history/background 90% of the known cases are sporadic
- 15. CAUSE OF ALS • Due to a mutation in SOD1, the superoxide radicals are not neutralized • The radicals attack the motor neurons and degrade them • Muscles are not able to be stimulated
- 16. SYMPTOMS OF ALS First signs and symptoms (frequently overlooked) •Twitching and cramping of muscles (especially in hands and feet) •Stiffness •Weakness (especially in hands, arms and legs) •Slurred speech Picture taken from the National Institute of Aging
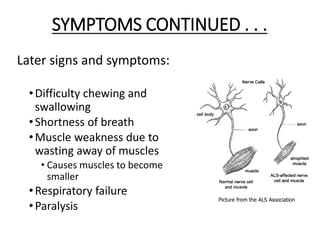
- 17. SYMPTOMS CONTINUED . . . Later signs and symptoms: •Difficulty chewing and swallowing •Shortness of breath •Muscle weakness due to wasting away of muscles • Causes muscles to become smaller •Respiratory failure •Paralysis Picture from the ALS Association
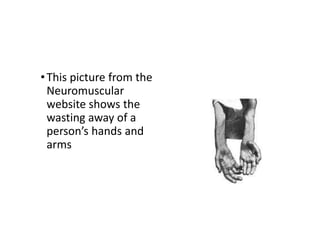
- 18. •This picture from the Neuromuscular website shows the wasting away of a person’s hands and arms
Editor's Notes
- Dementia is a broad category of brain diseases that cause a long-term and often gradual decrease in the ability to think and remember that is severe enough to affect daily functioning.
- Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] also known as superoxide dismutase 1 or SOD1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SOD1 gene, located on chromosome 21. SOD1 is one of three human superoxide dismutases. It is implicated in apoptosis and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.