INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION USING PLC
- 2. CONTENTS • AUTOMATION • TYPES OF AUTOMATION • INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION • DEVELOPMENT OF CONTROL SYSTEM • WHAT IS PLC • WHY PLC? • COMPONENTS OF PLC • PLC OPERATION • PLC PROGRAMMING • APPLICATIONS • ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES • CONCLUSION
- 3. AUTOMATION Automation is basically the delegation of human control functions to technical equipment aimed towards achieving: Higher productivity. Superior quality of end product. Efficient usage of energy and raw materials. Improved safety in working conditions etc.
- 4. TYPES OF AUTOMATION Building automation Example: lifts, smoke detectors Office automation Example: printers, cctv cameras Scientific automation Example: rocket launching Light automation Example: street solar lightening Industrial automation Example: automated bottle filling stations , steel factories etc
- 5. INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION The use of Computerized or robotic devices to complete manufacturing tasks. PLANT FIELD INSTRUMENT CONTROL SYSTEM HARDWARE CONTROL SOFTWARE CONTROL
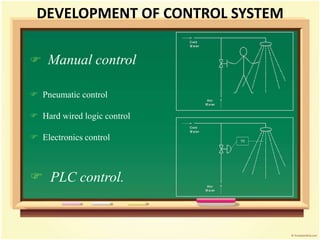
- 6. DEVELOPMENT OF CONTROL SYSTEM Manual control Pneumatic control Hard wired logic control Electronics control PLC control.
- 7. PLC(PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLER) Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is an industrial computer that monitors inputs, makes decisions based on its program and controls outputs to automate a process or machine. The automation of many different processes, such as controlling machines or factory assembly lines, is done through the use of small computers called a programmable logic controllers (PLCs).
- 8. WHY PLC? To reduce human efforts . To get maximum efficiency from machine and control them with human logic . To reduce complex circuitry of entire system . To eliminate the high costs associated with inflexible, relay-controlled systems.
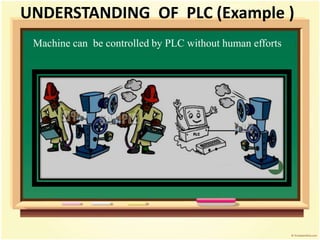
- 9. UNDERSTANDING OF PLC (Example ) Machine can be controlled by PLC without human efforts
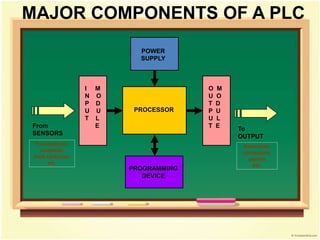
- 10. MAJOR COMPONENTS OF A PLC PROCESSOR POWER SUPPLY I M N O P D U U T L E O M U O T D P U U L T E PROGRAMMING DEVICE From SENSORS Pushbuttons, contacts, limit switches, etc. To OUTPUT Solenoids, contactors, alarms etc.
- 11. PLC INPUT OUTPUT PUSH BUTTONS 1. INPUT MODULES accepts and converts signals from sensors into a logic signal Ex. : Switches, Pushbuttons. 2. OUTPUT MODULES that convert control instructions a signal that can be used by actuators. Ex. : lamps, alarm. COMPONENTS (INPUT /OUTPUT)
- 12. 3. CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT(CPU) It is the brain of PLC and governs the activities of the entire PLC systems The CPU consists of following blocks : Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Internal memory of CPU Internal timers ,counters and Flags . The various operations performed are : Scanning I/O bus traffic control, Program execution, Peripheral and External device communication, Data handling and self diagnostics. PROCESSOR 4. MEMORY is the component that stores information, programs and data in a PLC. COMPONENTS (CPU ,MEMORY) Types of memories used in PLCs are read only memory (ROM) and random access memory (RAM).
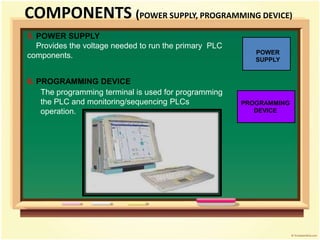
- 13. 5. POWER SUPPLY Provides the voltage needed to run the primary PLC components. POWER SUPPLY 6. PROGRAMMING DEVICE The programming terminal is used for programming the PLC and monitoring/sequencing PLCs operation. PROGRAMMING DEVICE COMPONENTS (POWER SUPPLY, PROGRAMMING DEVICE)
- 14. CHECK INPUT STATUS First the PLC takes a look at each I/O to determine if it is on or off. EXECUTE PROGRAM Next the PLC executes the program one instruction at a time. UPDATE OUTPUT STATUS Finally the PLC updates the status of the outputs .It updates the outputs based on which inputs were on during the first step. PLC OPERATION
- 15. Ladder logic is a programming language used to develop software for PLC used in industrial control applications. RUNGES RAIL RAIL PLC PROGRAMMING
- 16. ELEMENTS OF LADDER LOGIC NORMALLY OPEN NORMALLY CLOSED (CONTACT) (CONTACT) COILS
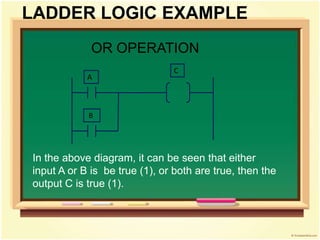
- 17. LADDER LOGIC EXAMPLE OR OPERATION A B C In the above diagram, it can be seen that either input A or B is be true (1), or both are true, then the output C is true (1).
- 18. Manufacturing / Machining Food / Beverage Textile Industry Travel Industry Aerospace Printing Industry AREAS OF APPLICATION
- 19. Replacing Human Operators Dangerous Environments Beyond Human Capabilities Fast Easily programmed and have an easily understood programming language. Improves Productivity Improves Quality ADVANTAGES
- 20. PLC Devices Are Proprietary Initial Costs Are High There's Too Much Work Required In Connecting Wires Unemployment Rate Increases DISADVANTAGES
- 21. The PLC have in recent years experienced an unprecedented growth as universal element in industrial automation . It can be effectively used in applications ranging from simple control like replacing a small number of relays to complex automation problems. Today the PLCs are used for control & automation job in a single machine & it increases up to full automation of manufacturing / testing process in a factory. CONCLUSION