Do You Know The 11g Plan?
- 1. Do you know the 11g Plan? Mahesh Vallampati
- 2. About the Speaker Mahesh Vallampati Senior Practice Manager at SmartDog Services Senior Sales Consulting Manager at Hotsos. Director of IT Database Services at a company in Houston Worked at Oracle for nine years Published in Oracle magazine
- 3. Agenda Plan Table V$SQL_PLAN and Related Views DBMS_XPLAN Key Performance Takeaways
- 5. Plan Table When Oracle parses a query, it creates a plan to execute the query The plan is a set of row source operations Row source operations are specific data access and join/sort method’s Oracle is going to execute to fulfill the request done by the query Some of the row source operations are Index Scan’s (Unique, Range, Skip etc.) Table Access (By Index Rowid, Full Table Scan’s) Joins (Nested Loops, Hash, Sort-Merge) Sort Operations
- 6. Explain Plan Example - I select empno, ename, sal, deptno from emp where empno = 7654 ; ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |Id | Operation | Name |Rows|Bytes|Cost (%CPU)|Time | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0| SELECT STATEMENT | | 1| 17| 1 (0)|00:00:01 | | 1| TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1| 17| 1 (0)|00:00:01 | |* 2| INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | EMP_EMPNO_PK | 1| | 0 (0)|00:00:01 | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 2 - access("EMPNO"=7654)
- 7. Explain Plan Example - II select ename from emp where comm is not null; -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 4 | 32 | 4 (0)| 00:00:01 | |* 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| EMP | 4 | 32 | 4 (0)| 00:00:01 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 1 - filter("COMM" IS NOT NULL)
- 8. How to read an indented, ordered Oracle execution plan… An execution plan line represents a row source operation (RSO) An indented RSO is the child of the first prior less-indented RSO A child RSO must complete before its parent can Order of execution RSOs begin in top-down order at step 0 RSOs complete only after their children complete
- 9. Plan Table The typical name for a plan table is PLAN_TABLE , but you may use any name you wish Create the plan table by running utlxplan.sql , located in $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin Create one per instance or one per schema
- 10. Explain Plan Examples select empno, ename, sal, deptno from emp where empno = 7654 ; ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |Id | Operation | Name |Rows|Bytes|Cost (%CPU)|Time | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0| SELECT STATEMENT | | 1| 17| 1 (0)|00:00:01 | | 1| TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1| 17| 1 (0)|00:00:01 | |* 2| INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | EMP_EMPNO_PK | 1| | 0 (0)|00:00:01 | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 2 - access("EMPNO"=7654)
- 11. Divide and Conquer for Bigger Plans select d.dname, e.ename, s.grade, e.sal from dept d, emp e, salgrade s where d.deptno = e.deptno and e.sal between s.losal and s.hisal ; -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | PID | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 28 | 7 | | 1 | 0 | NESTED LOOPS | | 1 | 28 | 7 | | 2 | 1 | MERGE JOIN | | 1 | 17 | 6 | | 3 | 2 | SORT JOIN | | 13 | 117 | 2 | |* 4 | 3 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 13 | 117 | 2 | | 5 | 4 | INDEX FULL SCAN | EMP_SAL | 14 | | 1 | |* 6 | 2 | FILTER | | | | | |* 7 | 6 | SORT JOIN | | | | | | 8 | 7 | TABLE ACCESS FULL | SALGRADE | 5 | 40 | 2 | | 9 | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID | DEPT | 1 | 11 | 1 | |* 10 | 9 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | DEPT_DEPTNO_PK | 1 | | | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 4 - filter("E"."DEPTNO" IS NOT NULL) 6 - filter("E"."SAL"<="S"."HISAL") 7 - access("E"."SAL">="S"."LOSAL") filter("E"."SAL">="S"."LOSAL") 10 - access("D"."DEPTNO"="E"."DEPTNO")
- 12. Plan Table Evolution The Plan Table Contains the information about the forecasted row source operations for the execution of the SQL statements The changes in the PLAN_TABLE across versions. Introduced in 9i Access Predicates Filter Predicates 9i to 10.1 Projection Time QBlock_name Plan_id Object_Alias Depth 10.1 to 10.2 other_xml 10.2 to 11g No Changes
- 13. DBMS_XPLAN
- 14. DBMS_XPLAN Introduced in 9iR2 Easy way of viewing the output of the EXPLAIN PLAN command in several, predefined formats 10g has some enhanced functionality We will use the DISPLAY function of DBMS_XPLAN available in 9iR2, 10g and 11g
- 15. DBMS_XPLAN Ensure that you are using the right version of the PLAN_TABLE DBMS_XPLAN Version incompatibilities may cause some issues Where is plan table and DBMS_XPLAN? Plan Table - $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/utlxplan.sql DBMS_XPLAN - $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/dbmsxpln.sql
- 16. Using DBMS_XPLAN EXPLAIN PLAN SET STATEMENT_ID = 'abc' FOR select object_type, count(1) from dba_objects where owner= 'SCOTT' group by object_type;
- 17. DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY Options Format parameter for this function choices are BASIC – Just displays the minimum information in the plan TYPICAL – Displays the relevant information in the plan and predicate information (PX information if applicable) SERIAL – Like typical, but no parallel execution information even if applicable ALL – All of typical including projections, alias, etc.
- 18. DBMS_XPLAN. DISPLAY Examples SELECT * FROM TABLE(dbms_xplan.display('PLAN_TABLE', 'abc','BASIC')); SELECT * FROM TABLE(dbms_xplan.display('PLAN_TABLE', ‘abc','TYPICAL')); SELECT * FROM TABLE(dbms_xplan.display('PLAN_TABLE', 'abc','ALL')); These are display formats for DBMS_XPLAN
- 20. DBMS_XPLAN Package - # of Procedures and Functions
- 21. Recap DBMS_XPLAN has been around since 9.2 It is an elegant way of looking at EXPLAIN PLAN outputs The “TYPICAL” option of DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY is most useful because it ties predicate information (access and filters) back to the predicted row source operation lines in the explained plan 11g introduced XML as an output option for plans
- 23. V$SQL and Related views View Name Description V$SQL The SQL Statement that is being executed and its non-plan details V$SQL_PLAN Contains the execution plan information for each child cursor loaded in the library cache V$SQL_PLAN_STATISTICS* Provides execution statistics at the row source level for each child cursor V$SQL_PLAN_STATISTICS_ALL*(Merges V$SQL_PLAN_STATISTICS with V$SQL_AREA) Contains memory usage statistics for row sources that use SQL memory (sort or hash-join)
- 24. V$SQL – New Columns in 11g Column Data Type Comment TYPECHECK_MEM NUMBER ??? IS_BIND_SENSITIVE VARCHAR2(1) Indicates whether the cursor is bind sensitive (Y) or not (N). A query is considered bind-sensitive if the optimizer peeked at one of its bind variable values when computing predicate selectivities and where a change in a bind variable value may cause the optimizer to generate a different plan. IS_BIND_AWARE VARCHAR2(1) Indicates whether the cursor is bind aware (Y) or not (N). A query is considered bind-aware if it has been marked to use extended cursor sharing. The query would already have been marked as bind-sensitive. IS_SHAREABLE VARCHAR2(1) Indicates whether the cursor can be shared (Y) or not (N) SQL_PATCH VARCHAR2(30) SQL patch used for this statement, if any SQL_PLAN_BASELINE VARCHAR2(30) SQL plan baseline used for this statement, if any
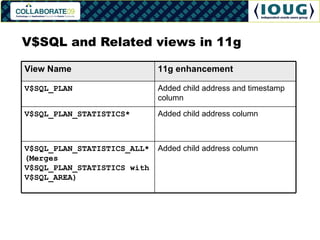
- 25. V$SQL and Related views in 11g View Name 11g enhancement V$SQL_PLAN Added child address and timestamp column V$SQL_PLAN_STATISTICS* Added child address column V$SQL_PLAN_STATISTICS_ALL*(Merges V$SQL_PLAN_STATISTICS with V$SQL_AREA) Added child address column
- 26. Viewing V$SQL_PLAN Data DBMS_XPLAN has made it easier to look at the data underlying the V$SQL_PLAN and V$SQL_PLAN_STATISTICS data Available starting 10g Lets you view the run time plan or the execution plan of a SQL Statement Also, lets you view the execution statistics for a run of the SQL Statement or all prior runs
- 28. New in 11g
- 30. SQL Plan Baselines DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_SQL_PLAN_BASELINE takes in three arguments. SQL_HANDLE SQL_HANDLE from dba_sql_plan_baselines PLAN_NAME Name of the plan FORMAT BASIC, TYPICAL, ALL Init.ora paramter optimizer_capture_sql_plan_baselines = true FUNCTION DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_SQL_PLAN_BASELINE RETURNS DBMS_XPLAN_TYPE_TABLE Argument Name Type In/Out Default? ------------------------------ ----------------------- ------ -------- SQL_HANDLE VARCHAR2 IN DEFAULT PLAN_NAME VARCHAR2 IN DEFAULT FORMAT VARCHAR2 IN DEFAULT
- 31. SQL Plan Baselines select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_sql_plan_baseline('SYS_SQL_8bab62f0bc1db3bc')) PLAN_TABLE_OUTPUT ---------------------------------------------------------------- SQL handle: SYS_SQL_8bab62f0bc1db3bc SQL text: select /*+ full(t1) */ * from t1 where c1 = 1 ----------------------------------------------------------------
- 32. SQL Plan Baselines Plan name: SYS_SQL_PLAN_bc1db3bc750635c2 Enabled: YES Fixed: NO Accepted: YES Origin: MANUAL-LOAD ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 1420382924 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 9 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| T1 | 1 | 9 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 | |* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | T1_N1 | 1 | | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): 2 - access("C1"=1)
- 33. SQL Plan Baselines Plan name: SYS_SQL_PLAN_bc1db3bcdbd90e8e Enabled: YES Fixed: NO Accepted: YES Origin: AUTO-CAPTURE -------------------------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 3617692013 -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 9 | 59 (6)| 00:00:01 | |* 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| T1 | 1 | 9 | 59 (6)| 00:00:01 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 1 - filter("C1"=1)
- 34. Plan Output in XML Format
- 35. DBMS_XPLAN.BUILD_PLAN_XML dbms_xplan.build_plan_xml( table_name IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT 'PLAN_TABLE', statement_id IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, plan_id IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, format IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT 'TYPICAL', filter_preds IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, plan_tag IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT 'plan', report_ref IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL)
- 36. Example Output EXPLAIN PLAN SET STATEMENT_ID = 'abc' FOR select object_type, count(1) from dba_objects where owner= 'SCOTT' group by object_type; The SQL Statement SELECT dbms_xplan.build_plan_xml(statement_id => 'abc') AS XPLAN FROM dual; accomplishes this .
- 37. Still the good stuff…
- 38. Access Predicates / Filter Predicates
- 39. Access and Filter Predicates select attribute1 from bom where item_id=11 and org_id=2 and designator is null; The Explain plan shows -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 196 | 10584 | 142 (1)| 00:00:02 | |* 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| BOM | 196 | 10584 | 142 (1)| 00:00:02 | |* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | BOM_N1 | 11961 | | 31 (0)| 00:00:01 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 1 - filter("DESIGNATOR" IS NULL) 2 - access("ITEM_ID"=11 AND "ORG_ID"=2) The Stat Lines Show STAT #4 id=1 cnt=4889 pid=0 pos=1 obj=70702 op='TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID BOM (cr=787 pr=150 pw=0 time=194697 us)' STAT #4 id=2 cnt=11961 pid=1 pos=1 obj=70704 op='INDEX RANGE SCAN BOM_N1 (cr=357 pr=37 pw=0 time=91948 us)'
- 40. Access and Filter Predicates select attribute1 from bom where item_id=11 and org_id=2 and designator is null -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 196 | 10584 | 4 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| BOM | 196 | 10584 | 4 (0)| 00:00:01 | |* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | BOM_U1 | 1 | | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 2 - access("ITEM_ID"=11 AND "ORG_ID"=2 AND "DESIGNATOR" IS NULL) STAT Lines STAT #12 id=1 cnt=4889 pid=0 pos=1 obj=70702 op='TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID BOM (cr=713 pr=0 pw=0 time=50184 us)' STAT #12 id=2 cnt=4889 pid=1 pos=1 obj=72016 op='INDEX RANGE SCAN BOM_U1 (cr=339 pr=0 pw=0 time=19590 us)'
- 41. Takeaway Look for row source operation that are filtering a lot of rows When a row source operation is filtering a lot of rows, it is accessing those rows and then applying the filter to discard rows that do not match the predicate qualifier Evaluate indexes to access the data and not filter it
- 42. Query Blocks
- 43. Query Blocks Useful when trouble shooting Nested SQL Statements Complex SQL Statements Inline Views Sub-Queries Repeated Visits to Table 10g allows you to name Query Blocks QB_NAME Hint e.g. /*+ QB_NAME(dept_subquery) */ When people write complex SQL statements, require them to name Query Blocks Query Blocks Add clarity to execution and explain plans
- 44. Example SELECT /*+ QB_NAME(outer) */ e.ename , e.sal FROM ( SELECT /*+ QB_NAME(inline_view) */ * FROM emp e WHERE e.sal > 300 AND e.deptno IN ( SELECT /*+ QB_NAME(dept_subquery) */ d.deptno FROM dept d WHERE d.dname IN ('SALES','ACCOUNTING') ) ) e;
- 45. Query Block with DBMS_XPLAN SQL> SELECT plan_table_output 2 FROM TABLE(DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY('PLAN_TABLE','qb_name','ALL')); PLAN_TABLE_OUTPUT ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 844388907 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 7 | 182 | 6 (17)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | MERGE JOIN | | 7 | 182 | 6 (17)| 00:00:01 | |* 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| DEPT | 2 | 26 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 3 | INDEX FULL SCAN | PK_DEPT | 4 | | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | |* 4 | SORT JOIN | | 14 | 182 | 4 (25)| 00:00:01 | |* 5 | TABLE ACCESS FULL | EMP | 14 | 182 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Query Block Name / Object Alias (identified by operation id): ------------------------------------------------------------- 1 - SEL$B9DAFA34 2 - SEL$B9DAFA34 / D@DEPT_SUBQUERY 3 - SEL$B9DAFA34 / D@DEPT_SUBQUERY 5 - SEL$B9DAFA34 / E@INLINE_VIEW
- 47. DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_AWR DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_AWR takes in four arguments. SQL_ID The SQL_ID of the statement in AWR PLAN_HASH_VALUE The Plan Hash value if available DB_ID The Database Id FORMAT Format Options.
- 48. Need Data From… dba_hist_sql_plan dba_hist_sqltext v_$database SELECT * FROM TABLE (dbms_xplan.display_awr('24033vh7b098h'));
- 50. DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_SQLSET FUNCTION DISPLAY_SQLSET RETURNS DBMS_XPLAN_TYPE_TABLE Argument Name Type In/Out Default? ------------------------------ ----------------------- ------ -------- SQLSET_NAME VARCHAR2 IN SQL_ID VARCHAR2 IN PLAN_HASH_VALUE NUMBER(38) IN DEFAULT FORMAT VARCHAR2 IN DEFAULT SQLSET_OWNER VARCHAR2 IN DEFAULT Need to license Diagnostic Pack Tuning Pack
- 51. DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_SQLSET For example, a SQL Tuning set named ‘MY_TUNING_SET’ for the sql statement with the sql_id 'g1pz63cqh5qbf', the following will displays all the execution plans. An example: SELECT * FROM table (DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_SQLSET('MY_TUNING_SET,'g1pz63cqh5qbf'));
- 53. DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_CURSOR FUNCTION DISPLAY_CURSOR RETURNS DBMS_XPLAN_TYPE_TABLE Argument Name Type In/Out Default? ----------------- ------------- ------ -------- SQL_ID VARCHAR2 IN DEFAULT CURSOR_CHILD_NO NUMBER(38) IN DEFAULT FORMAT VARCHAR2 IN DEFAULT SQL_ID SQL_ID From V$SQL CURSOR_CHILD_NO CHILD_NUMBER in V$SQL
- 54. Obtaining SQL_ID and Cursor Child Num. SELECT sql_id, child_number, sql_text FROM v$sql WHERE LOWER(sql_text) LIKE ‘ <begin sql statement string>%'
- 55. FORMAT BASIC, TYPICAL, SERIAL, ALL To view the execution plans alone Viewing Stats about the plan Introduced in 10g R1 Enhanced in 10g R2 Set STATISTICS_LEVEL=ALL at the session level OR Set the GATHER_PLAN_STATISTICS hint
- 56. Viewing the execution plan in V$SQL SELECT plan_table_output FROM TABLE(DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_CURSOR('3a3dz5yva4vnf',0,'ALL'));
- 57. Viewing the Run Time Stats of the Execution Plan SELECT plan_table_output FROM TABLE(DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_CURSOR('3a3dz5yva4vnf',0,‘<Various Options>')); IOSTATS MEMSTATS ALLSTATS IOSTATS LAST MEMSTATS LAST ALLSTATS LAST
- 58. Demo Demo.sql
- 59. Q & Q U E S T I O N S A N S W E R S