Tire reinforcements
- 1. TIRE REINFORCEMENTS TE 552 Nonwoven Product Development Neslihan Yagmur
- 2. What is Tire? • A tire is a ring-shaped covering that fits around a wheel's rim to protect it and enable better vehicle performance.
- 3. Duties of Tire • Carry the burden of car • Follow the direction given by the Steering • give very good traction on the road, which keeps cars from sliding • offer a smooth, comfortable ride
- 4. Tire Types • Some examples; – Type P • passenger vehicle tire – Type LT • light truck – Type T • temporary, or spare tire
- 5. Layers of Tire 1) Airtight synthetic rubber liner 2) Carcass ply 3) Beads 4) Sidewall 5) Crown Plies 6) Tread
- 6. 1. Airtight synthetic rubber liner • Keeps air inside the tire • Check your tires' air pressure monthly, as some air loss occurs over time
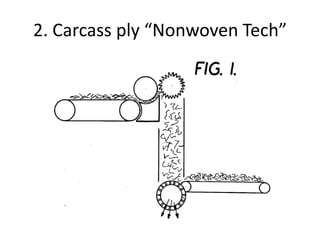
- 7. 2. Carcass ply • The carcass ply is comprised of thin textile fiber cables that are bonded into the rubber • These fiber cables are largely responsible for determining the strength of the tire.
- 8. 2. Carcass ply “Nonwoven Tech”
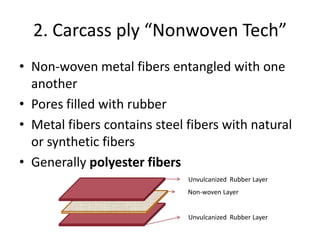
- 9. 2. Carcass ply “Nonwoven Tech” • Non-woven metal fibers entangled with one another • Pores filled with rubber • Metal fibers contains steel fibers with natural or synthetic fibers • Generally polyester fibers Unvulcanized Rubber Layer Unvulcanized Rubber Layer Non-woven Layer
- 10. Materials for Non-woven Ply • Metallic: – Copper – Nickel – Iron – Steel • Fibers: – Polyester – Carbon fiber* – Polyethylene terephthalate*
- 11. 2. Carcass ply “Nonwoven Tech” • Ratio of fiber:rubber; 80:20 • Thickness 1 to 5 mm; – preferably 2-3 mm • Fiber lenght 20-100 (40-60)* mm • Fiber diameter 6-40 denier
- 12. 3. Beads • The beads are responsible for clamping the tire firmly against the rim of the wheel.
- 13. 4. Sidewall • giving the tire its height • protects the tire against impacts with curbs and other objects • contains all the markings which tell you information about the tire; – speed rating – load rating – tire dimensions
- 14. 5. Crown Plies • Crown plies provide the rigid base for the tread • provide centrifugal and lateral rigidity to the tire • allowing the tire to flex sufficiently for a comfortable ride.
- 15. 6. Tread • The tread is designed to provide traction in a variety of conditions. • Good tread design provides also resist to; – wear – Abrasion – heat
- 16. REFERENCES • http://www.tirebuyer.com/education/tire-anatomy-and- construction • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tire • U.S. Patent 3895665 • Rowell, J. D., Tire Tread Seperation, Rowell & Bennett
- 17. THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION