Agriculture sector in india
- 1. AGRICULTURE SECTOR IN AH18118-L SAI TEJA AH18 090-G SRIGANDH AH18152-P MAHESH AH18146-P SRIKANTH AH18080-G PRUDHVI AH18113-K ANIL AH18109-RAVI KRISHNA PRESENTATION BY:
- 2. INTRODUCTION Agriculture is the backbone of the Indian economy Around 58% population of India depends on Agriculture India ranks second worldwide in farm output. India is the leading producer of Jute, pulses. Second largest producer of wheat, paddy, fruits, vegetables.
- 3. Agriculture accounts for 18% of the total exports earning and provide raw material to a large number of industries. Contributes 23% to GDP. High production of arable land(55% or 182.3 million hectares) Provide food to 1 billion people. Produces 51 major Crops. Contributes to 1/6th of the export earning KEY FACTS
- 4. •A major portion of National income comes from Agriculture •Agriculture provides raw materials to industries. •Agriculture creates employment opportunities. •Agriculture plays a crucial role in our international trade. •Agriculture creates infrastructural facilities. •Agriculture feeds the large population of our country. IMPORTANCE OF AGRICULTURE
- 5. MAJOR CROPS OF INDIA If we consider the varieties of crop grown from Kashmir to Kanyakumari and western coast of Gujarat to extreme north eastern states of Arunachal Pradesh, there would be hundreds of crops. We group all these crops into four broad types. Types of Crops Food grains Commer cial Crops Plantatio n Crops Horticult ure Major Crops Rice, Wheat, Maize, Millets, Pulses and Oil seeds Cotton, Jute, Sugarcan e, Tobacco and Oilseeds Tea, Coffee, Coconut and Rubber Fruits and Vegetable s
- 6. ROLE OF AGRICULTURE SECTOR IN INDIAN ECONOMY
- 7. Indian is an agriculture based country, where more than 50% of population is depend on agriculture. This structures the main source of income. The commitment of agribusiness in the national income in India is all the more, subsequently, it is said that agriculture in India is a backbone for Indian Economy. The contribution of agriculture in the initial two decades towards the total national output is between 48% and 60%. In the year 2001-2002, this contribution declined to just around 26%. ROLE OF AGRICULTURE SECTOR IN INDIAN ECONOMY
- 8. The aggregate Share of Agriculture and Allied Sectors, Including agribusiness, domesticated animals, and ranger service and fishery sub segments as far as rate of GDP is 13.9 percent during 2013- 14 at 2004-05 prices. Agricultural exports constitute a fifth of the total exports of the country. In perspective of the overwhelming position of the Agricultural Sector, gathering and support of Agricultural Statistics expect incredible significance ROLE OF AGRICULTURE SECTOR IN INDIAN ECONOMY
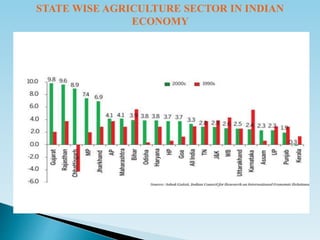
- 9. STATE WISE AGRICULTURE SECTOR IN INDIAN ECONOMY
- 11. AGRICULTURE INDUSTARY CONTRIBUTIN TO GDP
- 14. We all know that the agriculture sector is the backbone and crucial in our Indian economy which provides the basic ingredients to mankind and providing raw material for rapid industrialization sector development. No doubt that the besides manufacturing sectors, Agriculture sector provides great employment opportunities for rural people/youth on a large scale for their livelihood and also provides an entrepreneurship. AGRICULTURE SECTOR CONTRIBUTION TO GDP
- 15. Which share in national income. Provide raw materials to industries. Market for industrial products. The Indian economy is estimated to register a GDP growth rate of 7.1 per cent in 2016-17. The radical measures initiated in November 2016 in the form of demonetization of Rs. 1000 and Rs. 500 currency notes, the Indian economy is likely to experience a slowdown in the growth rate in Agriculture and allied sectors.
- 16. INDIAN EXPORTS OF AGRICULTURE PRODUCTS
- 17. PROBLEMS IN AGRICULTURE SECTOR •Lack of credit facilities. •Lack of fertilizers. •Lack of proper agriculture research. •Small and uneconomic holdings. •Inadequate irrigation facilities. •Defective marketing facilities. •Soil erosion. •Pests and plant diseases. •Very high dependency on monsoons.
- 18. MILE STONES IN AGRICULTURE DEVELOPMENT
- 19. WHAT’S ON INDIANS MENU
- 20. New Innovative Agriculture Business Ideas in 2017 Rice Cultivation Vegetable Farming Groundnut Cultivation Fruits Plantation Mushroom Farming Herbs and Flower Farming Pig Farming Air Fresheners and Perfumes
- 22. Rainbow revolution means the ‘Food Chain Revolution’ to put a check on destroying food grains, vegetables and fruits. It is around development of all primary sector products. RAINBOW REVOLUTION 1. Green revolution – Agriculture (food grains production) 2. White revolution – Milk 3. Blue revolution – Fish 4. Yellow revolution – Oilseeds 5. Golden Revolution- Fruits/apple 6. Black revolution – Petroleum 7. Silver revolution – eggs 8. Round revolution – potato 9. Red Revolution – Meats/Tomato 10. Grey revolution – Fertilizers 11.Pink revolution – Shrip 12.Brown Revolution - Leather
- 23. Green revolution means the tremendous hike in the agricultural production and productivity during the mid of 1960’s. It is also known as the New Agricultural Strategy comprises IADP, IAAP and HYVP. 1. Intensive Agricultural District Programme (IADP) : The objective of this programme was to increase the production of food grains. 2. Intensive Agricultural Area Programme (IAAP) : Introduced in 1964-65 aims for the intensive development of major crops such as wheat, paddy, millets, cotton , sugar cane, potato, pulse etc. 3. High Yielding Varieties Programme (HYVP) was launched in 1966. Aims at the introduction of high yielding verities of seeds. GREEN REVOLUTION
- 24. 1.Hike in agricultural production and productivity. 2. Increase in food production 3. Boost the production of cereals. 4. Fall in poverty. 5. More employment is created 6. More irrigational facilities developed. 7. More infrastructure is created. 8. More land is added to agriculture 9. Better distribution of land. 10. More reasearch on agriculture IMPACT OF GREEN REVOLUTION POSTIVE IMPACT
- 25. 1. Increase in both inter-regional and intra-regional inequalities. 2. Environmental degradation took place 3. Reduction in employment elasticity 4. Increase in personal inequality 5. Traditional knowledge was lost. 6. Ground water level down. 7. Health problems due to excess of mosquitoes 8. Irrigation of fields without proper drainage IMPACT OF GREEN REVOLUTION NEGATIVE IMPACT
- 26. KISAN CREDIT CARD GRAMIN BHANDARAN YOJANA LIVE STOCK INSURANCE SCHEME RASHTRIYA KRISHI VIKAS YOJANA BIJU KRISHAK KALYAN YOJANA PRADHAN MANTRI FASAL BIMA YOJANA PRADHAN MANTRI SANSAD ADARSH GRAM YOJANA SOIL HEALTH CARD SCHEME
- 27. PRADHAN MANTRI KRISHI SINCHAI YOJANA DEEN DAYAL UPADHYAYA GRAM JYOTHI YOJANA BHAVANTAR BHUGTAN YOJANA OPERATION GREEN GOBAR-DHAN YOJANA KUSUM SCHEME ATAL BHUJAL YOJANA PRADHAN MANTRI KISAN SAMPADA YOJANA
- 28. Scheme is a credit scheme introduced in August 1998 by Indian banks. This model scheme was prepared by the NABARD on the recommendations of R.V.GUPTA committee to provide term loans and agricultural needs.
- 29. This scheme was introduced in March 2007. Under this Gramin Bhandaran Yojana or Rural Godown Scheme, government provides supports to an individual, a farmer if they build or renovate rural godowns.
- 30. The scheme is implemented in all the districts of the Country from 21.05.2014. Insurance to cattle and attaining quantitative improvement in livestock and their products. Animals covered are Goat, Sheep, Pigs, Rabbit, Yak and Mithun etc.
- 31. This scheme was introduced in October 2014. Objective is to provide insurance cover to rabi and kharif crops and financial support to formers in case of damage of crops.
- 32. This scheme was introduced in July 2015. Budget : 2600 crore. Government of India is committed to accord high priority to water conservation and its management.
- 33. This scheme was introduced in February 2015. Government plans to issue soil cards to farmers which will carry crop- wise recommendations of nutrients and fertilizers required for the individual forms to help farmers to improve productivity.
- 34. This scheme was introduced in February 2018. Ministry of Drinking Water & Sanitation has launched the GOBAR DHAN scheme. The scheme aims to positively impact village cleanliness and generate wealth and energy from cattle and organic waste.
- 35. Agribusiness is the business of agricultural production. It includes agrichemicals, breeding , crop production (farming and contract farming),farm machinery and seed supply, as well as marketing and retail sales. All agents of the food and fiber value chain and those institutions that influence it are part of the agribusiness system. AGRIBUSINESS
- 36. STEPS TAKEN BY THE GOVERNMENT Crop Insurance Policy Easy availability of capital or investment input Introducing the MSP policy Subsidy in using capital intensive technology Land reforms Institutional credit increased PDS & TPDS
- 37. Agriculture Education Provide adequate diesel, electricity and water at subsidized rates Encourage crop rotation Multi crop farming Encourage cooperative farming Relaxed credit terms IMPROVING THE SECTOR
- 39. If we look at the challenges faced by Indian agriculture, we can broadly group them into two categories. One category belongs to the problems that have been long standing. Second category of problems is new and has been emerging from the prevailing agricultural practices, system, changing climate and economy. •Stagnation in Production of Major Crops: Production of some of the major staple food crops like rice and wheat has been stagnating for quite some time. This is a situation which is worrying our agricultural scientists, planners and policy makers. f this trend continues, there would be a huge gap between the demand of ever growing population and the production
- 40. •High cost of Farm Inputs: Over the years rates of farm inputs have increased manifold. Farm inputs include fertilizer, insecticide, pesticides, HYV seeds, farm labour cost etc. Such an increase puts low and medium land holding farmers at a disadvantage. • Soil Exhaustion: On one hand green revolution has played a positive role in reducing hunger from India. One of which is Soil exhaustion. Soil exhaustion means loss of nutrients in the soil from farming the same cropoverand overagain. This usually happens in the rain forest.
- 41. • Depletion of Fresh Ground Water: The second major negative consequence of green revolution is depletion of fresh ground water. You would remember that areas where green revolution was successful, it was due to the use of chemical fertilizers and irrigation. Most of the irrigation in dry areas of Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh was carried out by excessive use of ground water.
- 43. •Agri machinery India is the largest manufacturer of tractors in the world. Power tillers are gaining popularity especially for lowland flooded rice fields and hilly terrains. Manually operated tools, animal-operated machines, and mechanical - or electrical - operated machinery are some examples, which are slowly increasing in demand. Innovation and technology in the Indian agricultural machinery industry can take the industry to greater heights, keeping pricing in mind. Opportunities to agriculture sector in india
- 44. •Cold chain sector Due to India being an agricultural-based economy, wastage is a concern and so the government with the help of U.S. technology is developing the cold chain sector. Therein lies an opportunity for those looking to invest in this sector with improved storage and transportation techniques. Opportunities to agriculture sector in india
- 45. Poultry sector There is high demand for poultry and this poses as a great target for consumers due to their increasing income rates. This sector prides itself in being one of the largest producers of eggs and poultry meat. Innovation and advancement by foreign companies can further boost sector production and raise industry standards. Opportunities to agriculture sector in india
- 46. •Food processing sector India has an abundant supply of food yet only a small portion of these foods is processed. Nevertheless, this industry is still one of the highest in the country. Advanced methods of food processing are still to be introduced into this country. Though some top global players such as Nestle and PepsiCo have presence in India, there is still huge potential in the Indian food processing and packaging industry. Opportunities to agriculture sector in india