1 introduction to e commerce
- 1. E-COMMERCE Department Of Computer Science & IT University of Malakand Presented by Sajid Ullah Khan DilResh 6th Semester 2017 Lecture 1
- 2. COMMERCE Commerce is a division of trade or production which deals with the exchange of goods and services from producer to final consumer.
- 3. E-COMMERCE It is commonly known as electronic marketing. It consist of buying and selling goods and services over an electronic system such as the internet. E-commerce is the purchasing , selling & exchanging goods and services over computer network or internet through which transactions or terms of sale are performed electronically.
- 5. Why we use E-Commerce
- 10. The process of E-commerce
- 11. The process of E-commerce A consumer uses Web browser to connect to the home page of a merchant's Web site on the Internet. The consumer browses the catalog of products featured on the site and selects items to purchase. The selected items are placed in the electronic equivalent of a shopping cart. When the consumer is ready to complete the purchase of selected items, he provides a bill-to and ship-to address for purchase and delivery
- 12. The process of E-commerce When the credit card number is validated and the order is completed at the Commerce Server site, the merchant's site displays a receipt confirming the customer's purchase. The Commerce Server site then forwards the order to a Processing Network for payment processing and fulfilment.
- 13. Features of E-Commerce E-Commerce provides following features Non-Cash Payment: E-Commerce enables use of credit cards, debit cards, smart cards, electronic fund transfer via bank's website and other modes of electronics payment. 24x7 Service availability: E-commerce automates business of enterprises and services provided by them to customers are available anytime, anywhere. Here 24x7 refers to 24 hours of each seven days of a week. Advertising : E-commerce increases the reach of advertising of products and services of businesses. Marketing :It helps in better marketing management of products / services.
- 14. Features of E-Commerce Improved Sales: Using E-Commerce, orders for the products can be generated any time, any where without any human intervention. By this way, dependencies to buy a product reduce at large and sales increases. Support: E-Commerce provides various ways to provide pre sales and post sales assistance to provide better services to customers. Inventory Management: Using E-Commerce, inventory management of products becomes automated. Reports get generated instantly when required. Product inventory management becomes very efficient and easy to maintain. Communication improvement: E-Commerce provides ways for faster, efficient, reliable communication with customers and partners.
- 15. Sr. No. Traditional Commerce E-Commerce 1 Heavy dependency on information exchange from person to person. Information sharing is made easy via electronic communication channels making little dependency on person to person information exchange. 2 Communication/ transaction are done in synchronous way. Manual intervention is required for each communication or transaction. Communication or transaction can be done in asynchronous way. Electronics system automatically handles when to pass communication to required person or do the transactions. 3 It is difficult to establish and maintain standard practices in traditional commerce. A uniform strategy can be easily established and maintain in e-commerce. Traditional Commerce v/s E-Commerce
- 16. Sr. No. Traditional Commerce E-Commerce 4 Communications of business depends upon individual skills. In e-Commerce or Electronic Market, there is no human intervention. 5 Unavailability of a uniform platform as traditional commerce depends heavily on personal communication. E-Commerce website provides user a platform where al l information is available at one place. 6 No uniform platform for information sharing as it depends heavily on personal communication. E-Commerce provides a universal platform to support commercial / business activities across the globe. Traditional Commerce v/s E-Commerce
- 17. Different types of e-commerce I. Business-to-business (B2B) II. Business-to-Consumer (B2C) III. Business-to-government (B2G) IV. Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) V. Government to consumer (G2C) VI. Government-to-business (G2B)
- 18. What is B2B e-commerce? B2B e-commerce is simply defined as ecommerce between companies. About 80% of e-commerce is of this type. Examples: Intel selling microprocessor to Dell Heinz selling ketchup to Mc Donalds
- 19. B2B E-commerce
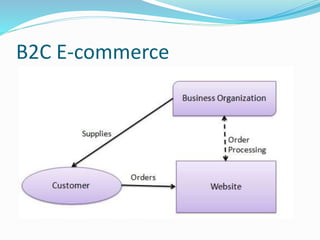
- 20. What is B2C ecommerce? Business-to-consumer e-commerce, or commerce between companies and consumers, involves customers gathering information; purchasing physical goods or receiving products over an electronic network. Example: Dell selling me a laptop
- 21. B2C E-commerce
- 22. What is B2G ecommerce? Business-to-government e-commerce or B2G is generally defined as commerce between companies and the public sector. It refers to the use of the Internet for public procurement, licensing procedures, and other government- related operations Example: Business pay taxes, file reports, or sell goods and services to Govt. agencies.
- 23. B2G E-commerce
- 24. What is C2C ecommerce? Consumer-to-consumer e-commerce or C2C is simply commerce between private individuals or consumers. Example: Mary buying an iPod from Tom on eBay. Me selling a car to my neighbor.
- 25. C2C E-commerce
- 26. G2C E-commerce This Model is also a part of e-governance. The objective of this model is to provide good and effective services to each citizen. The Government provides the following facilities to the citizens through website. Information of all government departments, Different welfare schemes, Different application forms to be used by the citizens.
- 27. G2C E-commerce
- 28. G2B E-commerce Government-to-business (G2B) is a business model that refers to government providing services or information to business organisation. Government uses B2G model website to approach business organizations. Such websites support auctions, tenders and application submission functionalities.
- 29. G2B e-commerce
- 31. Applications of E-Commerce: 1) Online Shopping 2) Online Banking 3) Electronic Bill Payment 4) Electronic ticketing
- 32. Online Shopping: Online shopping is the process consumers go through to purchase products or services over the Internet. Online shopping is a type of electronic commerce used for business-to-business (B2B) and business-to- consumer (B2C) transactions.
- 33. Online Banking: Online banking (or Internet banking) allows customers to conduct financial transactions on a secure website operated by their bank. The common features provided by online-banking fall broadly into several categories: Transactional Non-transactional
- 34. Electronic Bill Payment: Electronic bill presentment and payment (EBPP) is a fairly new technique that allows consumers to view and pay bills electronically. EBPP systems send bills from service providers to individual consumers via the internet.
- 35. Electronic ticketing: An electronic ticket or e-ticket is used to represent the purchase of a seat on a passenger airline, usually through a website or by telephone. This form of airline ticket has rapidly replaced the old multi-layered paper tickets.
- 36. E-Commerce Advantages E-Commerce advantages can be broadly classified in three major categories: Advantages to Organizations Advantages to Consumers Advantages to Society
- 37. E-Commerce Advantages A. Advantages to Organizations Using E-Commerce, organization can expand their market to national and international markets with minimum capital investment. An organization can easily locate more customers, best suppliers and suitable business partners across the globe. E-Commerce helps organization to reduce the cost to create process, distribute, retrieve and manage the paper based information by digitizing the information.
- 38. E-commerce improves the brand image of the company. E-commerce helps organization to provide better customer services. E-Commerce helps to simplify the business processes and make them faster and efficient. E-Commerce reduces paper work a lot. E-Commerce increased the productivity of the organization. It supports "pull" type supply management. In "pull" type supply management, a business process starts when a request comes from a customer and it uses just-in-time manufacturing way.
- 39. Advantages to Customers • 24x7 support. Customer can do transactions for the product or enquiry about any product/services provided by a company any time, any where from any location. Here 24x7 refers to 24 hours of each seven days of a week. E-Commerce application provides user more options and quicker delivery of products. E-Commerce application provides user more options to compare and select the cheaper and better option.
- 40. Advantages to Customers A customer can put review comments about a product and can see what others are buying or see the review comments of other customers before making a final buy. E-Commerce provides option of virtual auctions. Readily available information. A customer can see the relevant detailed information within seconds rather than waiting for days or weeks. E-Commerce increases competition among the organizations and as result organizations provides substantial discounts to customers.
- 41. Advantages to consumers (OR) 1) More products and services: EC provides with more choices; they can select from many vendors and from more products. 2) Cheaper products: EC frequently provides consumers with less expensive products and services by allowing them to shop in many places and conduct quick comparisons. 3) Ubiquity: EC provides consumers to shop or perform other transactions year round, 24 hours a day, from almost any location.
- 42. Advantages to Society Customers need not to travel to shop a product thus less traffic on road and low air pollution. E-Commerce helps reducing cost of products so less affluent people can also afford the products. E-Commerce has enabled access to services and products to rural areas as well which are otherwise not available to them. E-Commerce helps government to deliver public services like health care, education, social services at reduced cost and in improved way.
- 43. ADVANTAGES OF E-COMMERCE Faster buying/selling procedure, as well as easy to find products. Buying/selling 24/7. More reach to customers, there is no theoretical geographic limitations. Low operational costs and better quality of services. No need of physical company set-ups. Easy to start and manage a business. Customers can easily select products from different providers without moving around physically.
- 44. E-Commerce Disadvantages E-Commerce disadvantages can be broadly classified in two major categories: Technical disadvantages Non-Technical disadvantages Technical Disadvantages There can be lack of system security, reliability or standards owing to poor implementation of e-Commerce. Software development industry is still evolving and keeps changing rapidly. In many countries, network bandwidth might cause an issue as there is insufficient telecommunication bandwidth available. Special types of web server or other software might be required by the vendor setting the e-commerce environment apart from network servers.
- 45. Non-Technical Disadvantages Initial cost: The cost of creating / building E-Commerce application in-house may be very high. There could be delay in launching the E-Commerce application due to mistakes, lack of experience. User resistance: User may not trust the site being unknown faceless seller. Such mistrust makes it difficult to make user switch from physical stores to online/virtual stores. Security/ Privacy: Difficult to ensure security or privacy on online transactions. Lack of touch or feel of products during online shopping. E-Commerce applications are still evolving and changing rapidly. Internet access is still not cheaper and is inconvenient to use for many potential customers like one living in remote villages.
- 46. DISADVANTAGES OF E-COMMERCE Unable to examine products personally Not everyone is connected to the Internet There is the possibility of credit card number theft Mechanical failures can cause unpredictable effects on the total processes.
- 47. Disadvantages: 1) Some customers like to feel and touch products. Also, customers are resistant to the change from a real to a virtual store. 2) People do not yet sufficiently trust paperless, faceless transactions. 3) There is an increase amount of fraud on the Internet.
- 49. E-commerce vs. E-business We use the term e-business to refer primarily to the digital enablement of transactions and processes within a firm, involving information systems under the control of the firm. E-commerce include commercial transactions involving an exchange of value across organizational boundaries
- 51. What is e-business E-Business is about using Internet technologies to provide superior customer service streamline business processes, increase sales, and reduce costs. E-Business can be applied to any part of a company's operations, including marketing and sales, purchasing, production, design and engineering etc...,
- 56. E-Marketing E-Marketing is a subset of E- Business that utilises electronic medium to perform marketing activities and achieve desired marketing objectives for an organisation. E-Marketing is a broader term that describes any marketing activity performed via electronic medium. WHAT IS E-MARKETING?
- 57. E-Marketing Reduction in costs through automation and use of electronic media. Faster response to both marketers and the end user. Increased ability to measure and collect data. Opens the possibility to a market of one through personalisation. Increased interactivity ADVANTAGES OF E-MARKETING:
- 58. E-Marketing Dependability on technology. Security, privacy issues. Maintenance costs due to a constantly evolving environment. Higher transparency of pricing and increased price competition. Worldwide competition through globalisation. DISADVANTAGES OF E-MARKETING:
- 59. Difference between E-Business, E-Commerce and E-Marketing. E-Business E-Commerce E-Marketing E-Business is a very broad entity dealing with the entire complex system that comprises a business that uses electronic medium to perform or assist its overall or specialised business activities. E-Commerce is best described in a transactional context. So for example an electronic transaction of funds, information or entertainment falls under the category handled by principles of e-Commerce. Technically e-Commerce is a part of e-Business. E-Marketing is also a part of e-Business that involves electronic medium to achieve marketing objectives. e-Marketing is set on a strategic level in addition to traditional marketing and business strategy.