Lange - Industrial Data Space – Digital Sovereignty over Data
- 1. © Fraunhofer INDUSTRIAL DATA SPACE – DIGITAL SOVEREIGNTY OVER DATA Dr. Christoph Lange Fraunhofer IAIS Sankt Augustin b. Bonn Vienna Data Science Group / Taipeh Tech 22 November 2016
- 2. © Fraunhofer 2 INDUSTRIAL DATA SPACE: OVERVIEW Motivation: Digitisation of Industry Strategic Goals Technical Architecture Data Exchange in Industrial Data Space Best Practices: Use Cases and Requirements Partners: Research Project and Industrial Data Space Association
- 3. © Fraunhofer 3 Digitisation of Industry Digitisation Enables Data Driven Business Models … for Example Precision Farming Image sources: wiwo, traction-magazin.de. Quelle: Beecham Research Ltd. (2014). “Precision Farming” Value Creation in the “Ecosystem” “Digital Farming Eco- system” Machine Producer Seed Provider Farmers Wholesale Technology Provider Weather Service
- 4. © Fraunhofer 4 Digitisation of Industry Digitisation is not only Visible in Products, but also in Processes Sources: VILOMA Projekt. Legende: LDL – Logistikdienstleister. OEM – Original Equipment Manufacturer. Production Planning Demand and Capacity Management Stock Management and Range Control Transport Tracking and Control OEMDelivery LDL AssemblyAssembly LDL LDL Risk and Disruption Management user orientedtransparent Intuitiely comprehensible future oriented close to real time
- 5. © Fraunhofer 5 Digitisation of Industry Digitisation is both Driver and Enabler of Innovative Business Models Sources: otto.de (2015), techglam.com (2015), soccerreviews.com (2015), appfullapk.co (2015). Time Hybridity 1 Physical product (running shoe) “classic service” (training monitor) Digital Service (Social Network Integration) 2 3 A core competence of business model innovation is the combination of data in an “ecosystem” or data value chain. Digital offerings follow common architectural principles: • Services are decoupled from physical platforms/products • Architectural layers are decoupled • Products become platforms and vice versa • Ecosystems develop around platforms • Innovation happens via collaboration
- 6. © Fraunhofer 6 Digitisation of Industry As a Consequence of the “Smart Service World”, the Complexity of Service Creation is Increasing. Source: Koren (2010), quoted in Bauernhansl (2014). Image sources: https://en.wikipedia.org (2015), https://www.impulse.de (2015), audi.de (2015), o2.co.uk (2015), computerbild.de (2015). Number of Variants Output per Variant 1850 1913 1955 1980 2000 Ford Model T VW Beetle Production Audi Configurator Mass Production Individualisation “Shareconomy” Complexity Globalisation iPhone 3D Printed Car
- 7. © Fraunhofer 7 Goal and Architecture of the Industrial Data Space Squaring the Circle of Data Management: between Property and Added Value Interoperability Data Exchange “Sharing Economy” Data Centred Services Proprietary Data Data Protection Data Value Digital Sovereignty is the ability of a natural or legal person to exclusively self-determine their use of data assets.
- 8. © Fraunhofer 8 Goal and Architecture of the Industrial Data Space The Industrial Data Space Connects the Internet of Things and Smart Services.
- 9. © Fraunhofer 9 Goal and Architecture of the Industrial Data Space The Three “V” of Big Data – Variety is often Neglected Source: Gesellschaft für Informatik
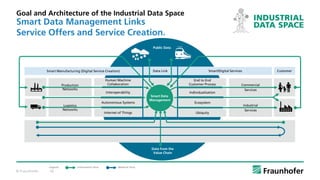
- 10. © Fraunhofer 10 Goal and Architecture of the Industrial Data Space Smart Data Management Links Service Offers and Service Creation. Information flow Public Data Data from the Value Chain Commercial Services Industrial Services Individualisation End to End Customer Process Ecosystem Ubiquity Smart Data Management Interoperability Human Machine Collaboration Autonomous Systems Internet of Things Customer Production Networks Logistics Networks Smart/Digital ServicesData LinkSmart Manufacturing (Digital Service Creation) Material flow.Legend:
- 11. © Fraunhofer 11 Goal and Architecture of the Industrial Data Space Der Industrial Data Space aims at blueprinting a “Network of Trusted Data”. Secure Data exchange Trustworthiness Certified Members Decentralisation Federated Architecture Sovereignty over Data and Services Governance Common Rules of the Game Scalability Network Effects Openness Neutral and User-Driven Ecosystem Platform and Services
- 12. © Fraunhofer One of the essential elements behind digital transformation in industry is the exchange of data and services between industrial companies . Benefit: by networking companies, exchanging data between companies and integrating publicly available data, added value is generated in the form of new products and smart services. This means that new, digital business models are also possible in conventional industries. This guarantees the competitiveness of industrial companies and their independence from IT companies! Data security and trust in secure data exchange are essential prerequisites here. Motivation Why does Industry Need The Industrial Data Space?
- 13. © Fraunhofer www.industrialdataspace.org // 13 APPLICATION DOMAINS OF THE INDUSTRIAL DATA SPACE VERTICAL COOPERATION Material Sciences Energy Business Life Sciences High Performance Supply Chains Traffic Management Exchange of material and material properties over the entire life cycle from product creation through to scrapping Common use of status data for the predictive maintenance of wind power stations Design of a jointly used data platform for the development of medical and pharmaceutical products Exchange of status and quality data for transport goods along the entire supply chain Use of traffic management data for innovative digital services inside the vehicle and for controlling traffic flow
- 14. © Fraunhofer www.industrialdataspace.org // 14 LOCATION IN THE CONTEXT OF “INDUSTRY 4.0” FOCUS ON DATA Retail 4.0 Bank 4.0Insurance 4.0 … Industrie 4.0 Focus on Manufacturing Industry Smart Services Transfer and Networks Real time systems Industrial Data Space Focus on Data Data … The development and promotion of the Industrial Data Space are being conducted in close cooperation with “Plattform Industrie 4.0” initiative.
- 15. © Fraunhofer www.industrialdataspace.org // 15 IDS stands for secure data exchange between companies where the producer of data remains the owner of the data and maintains sovereignty over the use of that data. IDS Assoc. aims to define the conditions and governance for a reference architecture and interfaces aiming at international standards. This standard is actively developed and updated on the basis of use cases. It forms the basis for a number of certified software solutions and business models, the development of which is fostered by the association. INDUSTRIAL DATA SPACE ASSOCIATION SELF-PERCEPTION „
- 16. © Fraunhofer www.industrialdataspace.org // 16 DR. REINHOLD ACHATZ Chairman of the Board of Industrial Data Space e. V. CTO und Head of Corporate Function Technology, Innovation & Sustainability at thyssenkrupp AG MISSION STATEMENT ”Digital transformation and “Industry 4.0” are key success factors for companies in Germany. The association ensures that the specific interests of the industry contribute to the research work. At the same time, companies will have faster access to the results from the Industrial Data Space research project and be able to implement them faster too. DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION ”
- 17. © Fraunhofer 17 Goal and Architecture of the Industrial Data Space Component Reference Architecture internet decentralized data transmission company A IT DB IoT IDS connector company B IT DB IoT IDS connector vocabularies apps IDS connector IDS app store index clearing IDS connector IDS broker registry download optional All Actors (defined roles) are enabled to participate in the IDS by software components The set of all (external) IDS Connectors forms the “Industrial Data Space” Internal IDS Connectors are used to connect, transform and refine back- office data sources.
- 18. © Fraunhofer 18 Goal and Architecture of the Industrial Data Space The Industrial Data Space focuses on the Architecture of Basic and Added Value Services. Automobile Manufacturers Electronics and IT Services Logistics Mechanical & Plant Engineering Pharmaceutical & Medical Supplies Smart Service Scenarios Service and product innovations “Smart Data Services” (alerting, monitoring, data quality etc.) “Basic Data Services” (information fusion, mapping, aggregation etc.) Internet of Things ∙ broad band infrastructure ∙ 5G Real Time Area ∙ sensors, actuators, devices Architecturelevel INDUSTRIAL DATA SPACE
- 19. © Fraunhofer www.industrialdataspace.org // 19 RANGE OF FUNCTIONS BUSINESS MAP OF BASIC SERVICES Industrial Data Space App Store Basic Data Services Provisioning Data Service Management and Use Vocabulary Management Software Curation Data Provenance Reporting Data Transformation Data Curation Data Anonymization Data Service Publication Data Service Search Data Service Request Data Service Subscription Vocabulary Creation Collaborative Vocabulary Maintenance Vocabulary/Schema Matching Knowledge Database Management Software Quality and Security Testing Industrial Data Space Broker Data Source Management Data Source Search Data Exchange Agreement Data Exchange Monitoring Data Source Publication Data Source Maintenance Version Controlling Key Word Search Taxonomy Search Multi-criteria Search »One Click« Agreement Data Source Subscription Transaction Accounting Data Exchange Clearing Data Usage Reporting Industrial Data Space Connector Data Exchange Execution Data Preprocessing Software Injection Remote Software Execution Data Request from Certified Endpoint Usage Information Maintenance (Expiration etc.) Data Mapping (from Source to Target Schema) Secure Data Transmission between Trusted Endpoints Preprocessing Software Deployment and Execution at Trusted Endpoint Data Compliance Monitoring (Usage Restrictions etc.) Remote Attestation Endpoint Authentication
- 20. © Fraunhofer 20 EnterpriseIT Application Container Management Core OS Core IDS Container Inclusion of further IT services (apps) Application Container Management Core OS Core IDS Container Inclusion of further IT services (apps) Data Exchange in the Industrial Data Space Company A requests data from Company B Company B checks the request and sends the data requested Simple Data Exchange with the Connector Company A Company Bencrypted connection Request Authentication Data InternalI nterface Dataquery data forwarding InternalI nterface
- 21. © Fraunhofer 21 Data Exchange in the Industrial Data Space Data Exchange with a Trusted App in the Connector Big Data Analytics App (Trusted) Metatag App Application Container Management Core OS Core IDS Container Application Container Management (Trusted) Core OS (Trusted) Core IDS Container (Trusted) Plant manufacturer A Connec- tivity App encrypted connection Request Authentication Data Plant Dataquery Result Internal Interface Plant operators B, B‘, … Company A requests sensitive data from Company B Company B checks request and sends requested data exclusively to a trusted app Company B can see just the result of the computation/analysis
- 22. © Fraunhofer 22 Data Exchange in the Industrial Data Space Data Exchange by Remote Execution Application Container Management (Trusted) Core OS (Trusted) Core IDS Container (Trusted) Application Container Management (Trusted) Core OS (Trusted) Core IDS Container (Trusted) Plant manufacturer A Plant operator B Connec- tivity App encrypted connection Request Authentication Result Plant Dataquery Result Internal Interface Remotely Executed App (Trusted) App deployment Data Company A requests sensitive data from Company B and deploys a trusted app to the Connector of Company B B forwards data to the trusted app of A running locally Justed the result of computation/analysis leaves B’s Connector
- 23. © Fraunhofer Components Con- nector App Store Voca- bulary Clearing Service Broker Apps Registry 3rd Party Cloud Certification Check point Applicant Certificat‘n Authority Accredidat‘n Agency Process for IDS participation Certification of: Developers, Companies, Components Industrial Data Space Ecosystem Participating Roles with Increasing Set of IDS Features; from Inside to Outside 4 Security Levels 0 1 2 3 SELF- DETERMINATION Data providers control access to their data themselves; define requirements for the consumer. Software Architecture Broker Operator Operator Clearing Operator App Store App Provider Operator IDS Connector Cloud Operator Provider Smart Data Services (IT) Provider Added Value Services Feature set Data provider & consumer
- 24. © Fraunhofer 24 Research Project and Industrial Data Space Association Use Cases of the Companies are bundled to Reference Use Cases Further Reference Use CasesReference Use Case “Production” Reference Use Case “Logistics” Thyssen KOMSAKOMSA Atos Bayer Boehringer Festo Bosch Salzgitter Salzgitter Salzgitter Schaeffler SICKVW
- 25. © Fraunhofer 25 Research Project and Industrial Data Space Association Concept Reference Use Case “Logistics”
- 26. © Fraunhofer 26 Research Project and Industrial Data Space Association First Prototype Reference Use Case “Logistics”
- 27. © Fraunhofer Industrial Data Space Research Project and Association Key Data of the BMBF Project Start: 1 October 2015 Duration : 36 months Budget: 5 M EUR Highlights January 2016: Chartered Association Round-table on EU level CeBIT and Hannover Messe Fraunhofer Consortium 12 Institutes AISEC, FIT, FKIE, FOKUS, IAIS, IAO, IESE, IML, IOSB, IPA, ISST, SIT Industrial Data Space e.V.: 40+ Members from 8 Countries Project Status First Software Demonstrators available 12 active use case projects MoU with OPC Foundation Induced Follow-up Activities Domain specific verticalisation: Materials Data Space, Medical Data Space etc. Internationalisation and Standardisation http://www.industrialdataspace.org
- 28. © Fraunhofer 28 Industrial Data Space Association How you can get Involved • Piloting, applying and testing Industrial Data Space • Early access to software • Implementing requirements in the development of the architecture • Development of Smart Services Use Cases ArchitectureExploitation • Support to help design the reference architecture • Contribution of company- specific know-how Working groups • Participation in working groups • Regular exchange with all member companies • Dealing jointly with problems concerning data exchange • Development of business models in the IDS • Innovation camp • Development of common user models Exchange of information • Transferring the content of the research project • Common events; networking events • Organisation of marketing activities / fairs Standardisation/Certification • Defining and implementing standards • Designing certification measures
- 29. © Fraunhofer 29 Research Project and Industrial Data Space Association Initiative Getting a lot of Public Attention White Paper handed over to German federal research minister Johanna Wanka (CeBIT 2016) EU Commissioner Günther Oettinger visits the exhibit of the Industrial Data Space (Hanover Fair 2016)
- 30. © Fraunhofer 30 Research Project and Industrial Data Space Association After the development of the connector, basic data services (“semantic layer”) will be designed and realised as prototypes. In parallel, the design of further data services (“data apps”) is starting. Broker and AppStore will be realised as special add-on packages based on the Connector. Development Roadmap at a Glance Connector 1 Semantic Layer 2 Broker Core 3 AppStore 4 Data Apps 5 First Prototype on 30 June 2016
- 31. © Fraunhofer 31 Research Project and Industrial Data Space Association Whitepaper https://www.fraunhofer.de/content/dam/zv/en/fields-of- research/industrial-data-space/whitepaper-industrial-data- space-eng.pdf Overview on goals and architecture of the Industrial Data Space Presentation of selected use cases Presentation of the Industrial Data Space Association
- 32. © Fraunhofer // 32 CONTACT Head Office INDUSTRIAL DATA SPACE ASSOCIATION Joseph-von-Fraunhofer-Str. 2-4 44227 Dortmund Germany +49 231 9743 619 info@industrialdataspace.org www.industrialdataspace.org