2.1 Cells
- 2. Common Cell Traits Cell membrane •outer covering of cell •made of one or more layers of linked molecules Cytoplasm •inside every cell •gelatin-like •contains hereditary material that controls the life of the cell
- 3. comparing cells nerve cells can be 1m long human egg cell is no bigger than the dot on this i human red blood cells is 1/10 the size of a human egg cell bacterium are even smaller - 8000 can fit inside a human egg cell
- 5. cell types PROKARYOTIC CELLS no membrane bound structures EUKARYOTIC CELLS membrane-bound structures
- 7. cell wall found in plants, algae, fungi, most bacteria tough, rigid outer coverings that protect the cell and give it shapeplant cell walls are mainly made of cellulose....which is? what makes the cell walls rigid? Pectin and lignin!
- 9. cell membrane protective layer around all cells if a cell has a cell wall, then the cell membrane is inside of it what does it do? regulate interactions between the cell and the environment water can move into and out of cell through the cell membrane food particles and some molecules enter and waste products leave through the cell membrane
- 12. cytoplasm gelatinlike substance that fills cells which is constantly moving contains a framework called the cytoskeleton - this helps maintain or change the shape of the cell cytoskeleton helps some cells move cytoskeleton is made up of thin, hollow tubes of protein and thin, solid protein fibers
- 15. organelles contained within the cytoplasm What do organelles do? ★process energy ★manufacture substances needed by the cell ★move materials ★act as storage sites ★are surrounded by membranes ★nucleus is usually the largest organelle
- 16. nucleus is surrounded by a membrane directs all cell activities DELI MANAGER materials enter andleave through the membrane contains instructions for everything in the cell, which are found on DNA a nucleolus is also within the nucleus
- 18. energy-processing organelles cells need energy to: ✤process food ✤make new substances ✤eliminate wastes ✤communicate with each other
- 19. PLANTS ๏food is made in green organelles called chloroplasts ๏contain green pigment chlorophyll ๏chlorophyll captures light energy that is used to make glucose
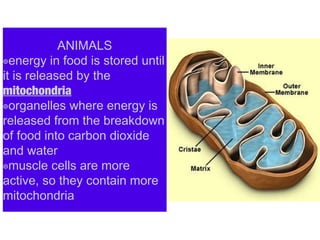
- 20. ANIMALS ๏energy in food is stored until it is released by the mitochondria ๏organelles where energy is released from the breakdown of food into carbon dioxide and water ๏muscle cells are more active, so they contain more mitochondria
- 21. manufacturing organelles proteins take part in nearly every cell activity Proteins: •part of cell membrane •needed for chemical reactions that take place in the cytoplasm •are produced on small structures called ribosomes
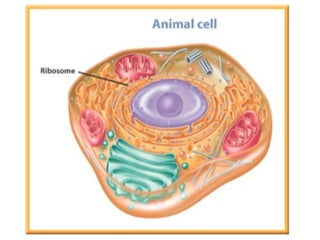
- 22. ribosomesconsidered an organelle, but they do not have a membrane some float freely in cytoplasm, some attach to the endoplasmicreticulum made in the nucleolus receive directions from DNA on how, when, and in what order to make specific proteins
- 24. processing, transporting, and storing organelles endoplasmic reticulum (ER) extends from the nucleus to the cell membrane a series of folded membranes materials can be processed and moved around inside of the cell rough vs. smooth smooth ER process other cellular substances such as lipids that store energy Rough ER make proteins that are moved out of the cell or used within the cell
- 26. golgi bodies proteins are made and sent to the Golgi bodies Golgi bodies sort proteins and other cellular substances and package them into membrane-bound structures called vesicles vesicles deliver cellular substances to areas inside the cell Refrigerator - cells have membrane-bound spaces called vacuoles for temporary storage of materials (water, waste products, food, and other cellular materials)
- 28. recycling organelles active cells break down and recycle substances lysosomes contain digestive chemicals that help break down food molecules, cell wastes, and worn-out parts lysosome membrane keeps the chemicals from leaking into the cell when a cell dies a lysosome’s membrane disintegrates, releasing digestive chemicals that quickly breakdown the cell’s contents