21st century learners
- 2. Information was once at the front of the classroom.
- 3. A. The Folly of Predictions 1970s prediction Improvements in technology will increase the amount of leisure time by the 1990s. Few if any people will work more than a 25-h week. The biggest challenge to be faced in 20 years will be what to do with all of our leisure time.
- 4. Not everyone is a visionary “ Everything that can be invented has been invented.» Charles H. Duell, an official at the US patent office, 1899. "It will be gone by June" Variety, passing judgement on rock 'n roll in 1955. If anything remains more or less unchanged, it will be the role of women.» David Riesman, conservative American social scientist, 1967.
- 5. Signs we live in the 21st Century You have a list of 15 phone numbers to reach your family of three You call your son's mobile to let him know it's time to eat. He texts you back from his bedroom, "What's for dinner?" You chat several times a day with a stranger from South Africa, but you haven't spoken with your next door neighbor yet this year. You hear most of your jokes via Facebook instead of in person You wake up at 2:00 AM to go to the bathroom and check your Facebook on your way back to bed. Your reason for not staying in touch with family is that they are not on Facebook You start tilting your head sideways to smile. :)
- 7. B. Are students less able? •”When I was a student, we were better at spelling, writing and math.” •With the possible exception of spelling this is not true. Curricula is becoming increasing complex. •Students are not the same and curriculum demands have increased.
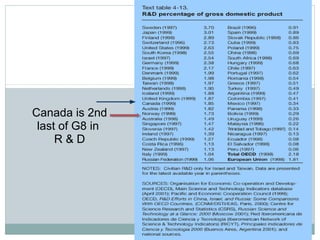
- 9. Canada is 2nd last of G8 in R & D
- 10. D. Profiles of the Learner Students will use engaging technologies in: • collaborative ways • inquiry-based environments • ways that transform knowledge and skills into products, solutions, and new information.
- 11. Today's child "Today's child is bewildered when she enters the 19th century environment that still characterizes the educational establishment where information is scarce but ordered and structured by fragmented, classified patterns, subjects, and schedules." Marshall McLuhan, 1967 What changes have you seen in schools to make knowledge less scarce?
- 13. I am a 21 st Century learner • I will spent 16.5-h watching TV this week. • I will spent 5.5-h on my computer this week. • I game 3.5-h per week. • I spent 2-h reading a book this week. • I listened to Harry Potter on my I-Pad for 5-h this week.
- 14. I will • Read 8 books this year. • Write 42 pages of notes for classes this semester. • Spend 5 to 6-h in class each day. • Work 2-h day. • Sleep 2-h less than my parents did each day. • Read 2300 webpages, 1281 Facebook profiles • Write over 500 pages of email this semester. • Spend 3.5-h a day online. • Listen to musics 2.5-h a day, 2-h on my cellphone.
- 15. I need to be A multitasker • Because I have to be. A decision-maker and problem solver. • In daily life and the world of work. A communicator and collaborator. • Because I live and work in a social environment.
- 16. My Social Life and School • My teacher and parents use email to communicate. • 76% of my teachers have never used WIKIs, blogs and PODcasts. • I text my friends. • I blog • 14% of the week, I get to do something with technology in school. 63% of students don't use technology weekly.
- 17. Teach me to • Think • Create • Analyze • Evaluate • Apply
- 19. 8 Norms of 21st Century Learners 1. They need to be actively engaged. This includes school and their job. 2. Value collaboration above passive learning. 3. A desire to personalize and customize everything they own. 4. Value choice 5. Demand enjoyment at work and school. 6. More likely to research and critique organizations and individuals. 7. Speed is normal, with little patience for turn-around time. 8. Will have challenges in developing their professional identity. Don Tapscott, 2009. Grown-Up Digital, McGraw Hill, Toronto
- 20. E. Teaching Strategies Student Engagement • Problem-based learning • Collaborative work for students and instructors • Emphasis placed on lifelong Learning • Inquiry • Integration of learning and interdisciplinary studies • Simulations Student Choice • Use of technology to present and share students ideas. • Assistive technologies to support student learning. • Students involved in their own assessment.
- 21. Why does every lesson have to entertain students with technology? Students don't need to be entertained, they need to be engaged! • Entertainment is passive • Entertainment is for enjoyment • Entertainment is short- lived • Entertainment is does not require relevance. • Engagement is active • Engagement is for learning • Engagement provides long-term results • Engagement requires relevance and applicability.
- 24. G. Textbooks of the future Digital textbooks • Online assessment as part of the textbook. Students interact with the book. • Textbook linked with online simulations, videos, podcasts and laboratory activities. • Movement away from linear reading - use of pop-ups provide students with choices. • Wikis and blogs allow student interaction during the learning.
- 25. Digital Textbook Project In California Students to use free on-line textbooks. Digital textbooks provide advertising and sponsorship as a possible source of revenue. Advantages • More up-to-date. • Lighter school bags. • Save paper and trees. • Make learning more interactive. • Easier to search. Math and Science Projects 2010. $17 B cut from a $52 B budget. Much of the motivation is seen around cost savings. • Outsourcing of writing. • Compilation and tagging of information. • Linking of information with activities.
- 26. What will be gained and lost Gain • More content and more choices for different types of learners. • Potentially many links for activities. (Labs, WIKIs, blogs, etc.) • Resource development will integrate textbook with pre-existing visual resources. Lost • No philosophy as an underpinning for resource development. • Eclectic resource development means no single format for lab write up or the presentation of work. • Potential for content bound curriculum.
- 27. Choice and Ownership Teachers will look for resources that allow them greater participation in the learning of their students. (A push back against mass uniform delivery and resource models). Students and parents have a expectation that programs are tailored to the child's needs and interests. • Learning any place, any time, and at any pace. (AB Ed 2010-13). Social networking will find stronger links in completing assignments, critiquing the work of students and teachers.
- 28. Opposition to digital books You can't resell digital books legally. Costs of the textbooks are only slightly less, despite a tremendous drop in production prices. Require a digital device - reader, i-Pad, and computers, which require maintenance.
- 29. Reasons for Caution Many e-textbook advantages focus on content (up-to date, possible extensions, other modes for delivering content ie video) rather than the development of skills. • How do students assess evidence as problem solvers? (What evidence supports the conclusion that oil sands development is deleterious to the environment). • How do students communicate and support their ideas? Wikis, blogs, and presentations are linked to social issues. • How do students use the knowledge presented?
- 30. A 1998 study published in the Human Factors & Ergonomics Society journal reported a decline in speed and accuracy, and an increase in fatigue, when reading from a screen rather than paper. American Pediatrics Society has issued cautions about young children using light emitting screens more than 2h a day.
- 32. Conclusions Technological tools have an appeal in providing choice and personalizing learning. The terms technology and innovation are often used as synonyms. There is an assumption that teachers who use more technology are more creative or innovative. Curriculum must focus on skills and attributes and not packages of knowledge.
Editor's Notes
- Many Alberta Schools now allow students to use cell phones in class. The danger is using facebook and not following class. Dean of medicine – checked by students during his speech.
- Study in 1980s looking at Asian students and black students in the USA. Why was there a difference in success rate. Not related to income. Asian students socialized while they worked. (multitasked). Collaborator.
- Changes in medical education.
- 1. 21st century learners, learn by doing. Video games provide choices and immediate feedback. 2. The talking head, a common feature of early videoconferencing does not work. Learners are noisy and group problem-solve. 3. Toyota's SCION division tailors cars to customization. Cell phones and laptop have a variety of cases and decals. 4. Many different schools have arisen, multiple plans for cell phones. Sometimes it gets young employees in trouble - student teacher who indicates this was quite what she paid for in a mentor teacher. 5. Milt Petruk's story, Google work environment with gyms, games rooms etc. 6. Impatience - gets them in trouble. Professors often addressed by their first name and informally.
- This is a view of an ideal situation from a study group on student engagement.
- Simulation – of Specific course Game building exercise… students build their own games… some are specific to content/context and some are just for fun… either way construction of VW or Games is difficult problem-solving exercise that promotes critical thinking in logical domain…