3.pptx
- 2. Contents • Data communication • Computer network
- 3. Network Types(Geographical Coverage) I) LAN(Local Area Network) Small network, short distance A Room, a floor, a building Limited by no. of computers & distance covered. Has very high speed mainly due to proximity of computer and network devices. Connection speeds can be 10Mbps or 100Mbps or 1000Mpbs also.
- 4. LAN cont’d… Tend to use certain connectivity technologies, primarily Ethernet and Token Ring. Components are Layer 2(switches and bridges) and Layer 1 devices like hubs and repeaters. LANs tend to have fewer problems associated with them, as there is smaller number of systems to deal with. Typically owned, controlled, and managed by a single person or organization. LAN covers 100 meters. Example: Network inside student computer room, or Network inside your home
- 5. 5 II.MAN(Metropolitan Area Network) Metropolitan area network (MAN) is similar to a local area network (LAN) but spans an entire city or campus. MANs are formed by connecting multiple LANs. Thus, MANs are larger than LANs but smaller than wide area networks (WAN). MAN network has lower speed compared to LAN. MAN connection speeds can be 10Mbps or 100Mbps. Example: A network among campuses of Arba Minch university.
- 6. III. WAN(Wide Area Network) Have no geographical boundaries(it covers towns, states and countries). WAN speed varies based on geographical location of the servers. WANs (like the Internet) are not owned by any one organization but rather exist under collective or distributed ownership and management over long distances. Components are Layers 3 devices like Routers, Multi-layer Switches and Technology specific devices like ATM or Frame- relay Switches , etc.
- 7. WANs tend to be less fault tolerant as they consist of large number of systems. WANs have a lower data transfer rate as compared to LANs. Less speed (150 mbps). WANs tend to use technologies like ATM, Frame Relay and X.25 for connectivity over longer distances. Example: Internet is a good example of a WAN
- 8. 8 Network Types (Based on Architecture) 1. Peer to Peer (P2P) network They are more commonly implemented where less than ten computers are involved and where strict security is not necessary. No hierarchy among computers all are equal No administrator responsible for the network Peer-to-peer network is also called workgroup.
- 10. 10 2. Client-Server network These are more suitable for larger networks. A central computer(server) acts as the storage location for files and applications shared on the network. Usually the server is a higher than average performance computer. It controls the network access of the other computers (client).
- 13. Network Types( Based on Topology) Topology refers to the layout of connected devices on a network. The network topology defines the way in which computers, printers, and other devices are connected. A network topology describes the layout of the wire and devices as well as the paths used by data transmissions.
- 14. A network has both a physical and a logical topology. Physical topology shows the physical arrangement of a network, which refers to the actual physical layout of the devices and media. Logical topology refers to the paths that signals travel from one point on the network to another.
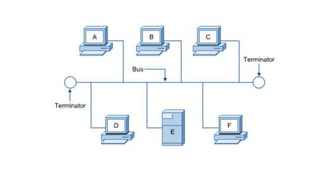
- 15. 1. Bus topology All networked nodes are interconnected, peer to peer, using a single, open-ended cable. Both ends of the bus must be terminated with a terminating resistor(Terminator) to prevent signal bounce. A single cable called a trunk (backbone, segment) is used. It is passive topology in which only one computer can send messages at a time. This topology is rarely used and would only be suitable for a home office or small business with only a few hosts.
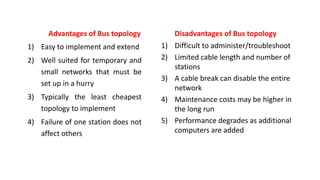
- 17. 1) Easy to implement and extend 2) Well suited for temporary and small networks that must be set up in a hurry 3) Typically the least cheapest topology to implement 4) Failure of one station does not affect others 1) Difficult to administer/troubleshoot 2) Limited cable length and number of stations 3) A cable break can disable the entire network 4) Maintenance costs may be higher in the long run 5) Performance degrades as additional computers are added Disadvantages of Bus topology Advantages of Bus topology
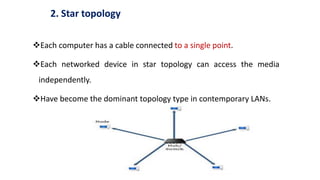
- 18. 2. Star topology Each computer has a cable connected to a single point. Each networked device in star topology can access the media independently. Have become the dominant topology type in contemporary LANs.
- 19. 1) Compared to Bus topology it gives far much better performance 2) Easy to connect new nodes or devices 3) Centralized management. It helps in monitoring the network 4) Failure of one node or link doesn’t affect the rest of network 1) If central device fails whole network goes down 2) The use of hub, a router or a switch as central device increases the overall cost of the network 3) Performance and as well number of nodes which can be added in such topology is depended on capacity of central device. Advantages of star topology Disadvantages of star topology
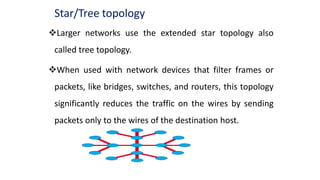
- 20. Star/Tree topology Larger networks use the extended star topology also called tree topology. When used with network devices that filter frames or packets, like bridges, switches, and routers, this topology significantly reduces the traffic on the wires by sending packets only to the wires of the destination host.
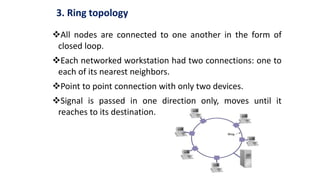
- 21. 3. Ring topology All nodes are connected to one another in the form of closed loop. Each networked workstation had two connections: one to each of its nearest neighbors. Point to point connection with only two devices. Signal is passed in one direction only, moves until it reaches to its destination.
- 22. Token Passing Sending and receiving of data takes place by the help of TOKEN. Token contains a piece of information along with data which is sent by the source computer. This token then passes to next node, which checks if the signal is intended to it. Only the computer who gets the token can send the data.
- 23. 1) Performance is better than that of Bus topology 2) No need for network server to control the connectivity between workstations 3) Additional components do not affect the performance of network. 4) Each computer has equal access to resources 1) Each packet of data must pass through all the computers between source and destination, slower than star topology 2) If one workstation or port goes down, the entire network gets affected 3) Network is highly dependent on the wire which connects different components 4) Expensive and difficult to install Advantages of Ring topology Disadvantages of Ring topology
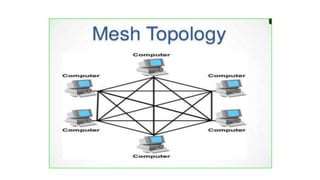
- 24. Here every device has a point to point link to every other device. It is used in WANs to interconnect LANs and for mission critical networks like those used by banks and financial institutions. Advantage: Eliminates traffic problem, Robust/fault tolerant, privacy/security of message. Disadvantage: More cabling required, more I/O ports needed, hard to install and expensive. 4. Mesh topology
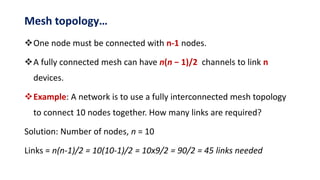
- 26. Mesh topology… One node must be connected with n-1 nodes. A fully connected mesh can have n(n − 1)/2 channels to link n devices. Example: A network is to use a fully interconnected mesh topology to connect 10 nodes together. How many links are required? Solution: Number of nodes, n = 10 Links = n(n-1)/2 = 10(10-1)/2 = 10x9/2 = 90/2 = 45 links needed
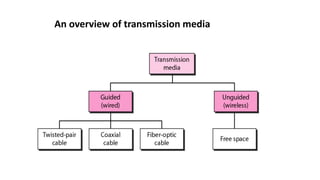
- 29. Transmission Media The transmission medium is the physical path or wireless between transmitter and receiver. So, the characteristics and quality of a data transmission are determined both by the characteristics of the medium and the characteristics of the signal Channel capacity It is the maximum rate at which data can be transmitted over a given communication path, or channel, under given conditions.
- 30. In data communication data are encoded in a form of energy and sent across the transmission medium. Forms of Energy: links can be categorized by the type of energy used for transmission: Electrical Energy is used on wires. Radio Frequency Transmission is used for wireless. Light is used for optical fiber cables.
- 31. An overview of transmission media
- 33. Twisted Pair (TP) Wires are classified in to two parts: I. Shielded twisted pair(STP) II. Unshielded twisted pair(UTP) It is the most commonly-used transmission medium. 1. Twisted Pair (TP) Wires
- 34. Advantages of TP Cheap or less expensive for short distance Easy to install &work with It can be used for both analog and digital transmission Disadvantages of TP Signals cannot travel for long distance without repeaters High error rate if distance is longer than 100m Since it is very thin, it breaks easily
- 35. I. Unshielded Twisted Pair(UTP) Is commonly used for local area networks (LANs). Connect using RJ-45 connectors. Data rates for LANs 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps. Ordinary telephone wire (RJ-11) Cheapest and easiest to install Suffers from external EM interference
- 36. UTP Cable…
- 37. Metal braid or sheathing that reduces interference More expensive than UTP cables Each pair of metals shield with metal foil or braided foil Foil shields:- consists aluminum foil Braided shield:-consists copper braided II. Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
- 38. STP: cables are similar to UTP cables, except there is a metal foil or braided-metal-mesh cover that encases each pair of insulated wires.
- 39. 2. Coaxial cable Similar to cable TV wire Used for cable television, LANs, telephony One wire runs through cable Shielded from interference High attenuation rate makes it expensive over long distance Much less susceptible to interference than twisted pair
- 40. Coaxial Cable…
- 41. Types of coaxial cables 10 Base-2 – ThinNet It uses a lighter and thinner coaxial cable It is a less expensive technology. It allows distances up to 185 meters. 10 Base-5 – ThickNet It can be used in electrically noisy environments which can cause other network types to fail. 10 Base-5 allows distances up to 500 meters.
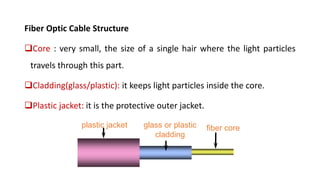
- 42. 3. Fiber Optic Cable Fiber optic cables are made of thinnest strands of glass that enable the transmission of information as light. It carries signals as a light pulses. Has extremely high capacity. Works better under harsh environments.
- 43. Fiber Optic Cable Structure Core : very small, the size of a single hair where the light particles travels through this part. Cladding(glass/plastic): it keeps light particles inside the core. Plastic jacket: it is the protective outer jacket. plastic jacket glass or plastic cladding fiber core
- 46. Unguided Transmission Media/ Wireless Media Data is transmitted through the air LANs use radio waves WANs use microwave signals Easy to setup Difficult to secure
- 47. Radio Wireless transmission of electrical waves over air Each device has a radio transceiver with a specific frequency Includes: AM and FM radios, Cellular phones Wireless LANs (IEEE 802.11) and Bluetooth Microwaves and Satellites Infrared “invisible” light waves (frequency is below red light) Requires line of sight; generally subject to interference from heavy rain, smog, and fog Used in remote control units (e.g. TV)
- 48. Satellite Communications Satellites are special form of microwaves communication that moves around large objects. Earth stations communicate by sending signals to the satellite on an uplink. The satellite then repeats those signals on a downlink It is useful for TV distribution, long-distance telephone transmission and many more.
- 50. Types of Satellite There are different satellites based on how height above from earth such as: 1. Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Occupy region of space from 111 miles (180km) to 1243 miles(2000km) above the earth. 2.Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) It is a satellite that parks in between the low and high flyers 3.Geosynchronous Orbit (GEO) It altitude 22,223 miles (36000km) above the earth
- 51. Thank you!!