Financial Management at J.K. Cement
- 1. J K Cement • A leading grey cement producer in Nimbahera, Rajasthan India the company is also the second largest manufacturer of white cement in India, with an annual capacity of 4,00,000 tones, and valueadded building products, such as wall putty. • J.K. Cement was the first Company to install a captive power plant in the year 1987 at Bamania, Rajasthan. J.K Cement is also the first cement Company to install a waste heat recovery power plant to take care of the need of green power. • J K cement is also the second largest producer of wall putty in the country with an annual installed capacity of 300,000 tones.
- 2. Ratio Analysis (LIQIDITY RATIOS): Year Mar '13 Mar '12 Mar '11 Mar '10 Current Ratio=Curr. A/Curr. L 1.186392 1.19731 1.36792 1.14475 Quick Ratio=(Curr. A-Inv.)/Curr. L 0.7522583 0.83326 0.91699 0.76477 Cash Ratio=(Cash+mkt. Sec)/Curr. L 0.312827 0.06909 0.10547 0.12579 Net Working Capital Ratio 0.7905205 0.81555 0.61425 0.55231 Interval Measure Days 67.477488 27.0231 23.1646 35.2093 Interval Measure Month 2.2492496 0.90077 0.77215 1.17364 Interval Measure Quarter 0.7497499 0.30026 0.25738 0.39121 Interval Measure Half Year 0.3748749 0.15013 0.12869 0.19561
- 3. Ratio Analysis (LIQIDITY RATIOS): • Current ratio for last four years has been average of 1.19 which is good as assets are more than liabilities. For a manufacturing company 2:1 is ideal ratio so still to improve. • Quick Ratio has been kept around 0.8 for last few years at lower than ‘1’ so that the company may really be prospering and paying its current obligation in time if it has been turning over its inventories efficiently. • Interval Measure in 2013 it has been increased to 67 from average of 25 days means it has increased its assets to finance its operation for 67 days without outside help which is a good sign. • Net Working Capital Ratio lower the ratio around 0.7 it shows the higher the ratio, grater ability to meet current liability comparing other firms.
- 4. Ratio Analysis (PROFITABILITY RATIO): Year Mar '13 Mar '12 Mar '11 Mar '10 Gross Profit Ratio=(Sales-COGS)/Sales 1.2469711 1.25461 1.25583 1.23792 Net Profit Ratio=PAT/Net sales 0.0802037 0.06968 0.02712 0.11007 Operating Profit Ratio=Op. Profit/Net Sales 0.1923172 Return of Capital employed = EBIT(1T)/D+E 0.146792003 Return on Investment = EBIT(1-T)/TA 0.204 0.11305 0.2155 0.14212 0.076283 0.140455 0.0822597 0.06799 0.02356 0.09509 Earning Per Share 33.4 25.36 9.16 32.32 Dividend Per Share 21.71 12.68 1.832 19.392 Divident Payout Ratio 0.65 0.5 0.2 0.6 Retantion Ratio 0.35 0.5 0.8 0.4 Return On Equity 0.1891342 0.17947 0.08947 0.20935
- 5. Ratio Analysis (PROFITABILITY RATIO): Gross Margin is high around 59% is an indicator of efficiency with which management is able to produce each unit because they are maintaining the competitive price. Net profit Margin is very low compared to gross. It is because high debt and interest payment. Return on investment has increased in 2012 and 2013 but still 8-9% is not a very good return as a manufacturing firm industry average is 13-14%. Interest burden has been headache for cement industry. Dividend pay-out ratio is kept high in 2011 in crises company retained most of the earning part else more than half has been paid. Shareholders are getting good return around 17+% from last 2 years.
- 6. Ratio Analysis (ACTIVITY RATIO): Year Mar '13 Mar '12 Mar '11 Mar '10 Inventory Turnover Ratio 6.9496609 6.98087 8.65921 9.99015 Days of inventory Holding 51.8010886 51.5694 41.5742 36.0354 9 8 4 8 Raw Material Turnover Ratio 1.52097159 1.45256 1.57588 1.71060 7 5 6 9 WIP turnover Ratio 14.5341 7.82888 9.38512 20.5850644 6 1 1
- 7. Ratio Analysis (ACTIVITY RATIO): Inventory turnover ratio has been decreasing from last four years for 2013 it is almost 7 times a year which is somewhat less the industry average of 8.5 accordingly inventory holding period has also increased which needs improvement, but other reason can be they have increased their production in consecutive years. Raw material turnover ratio & WIP turnover Ratio are constant over the few years that mean their production process has been working at desirable expectation but selling is less compared to production. However WIP turnover Ratio has been increased phenomenally that can be the reason of less sells compared to fast production.
- 8. Ratio Analysis (LEVERAGE RATIOS & VALUE RATIOS): LEVERAGE RATIOS Debt Equity Ratio=TD/equity Fixed Asset Ratio= Fixed A./CE Interest Coverage Ratio=EBIT/Int. Debt to capital Ratio = D/E+D Debt to asset =TD/Total Asset VALUE RATIO Price To Earn Ratio Market to Book Ratio Tobin's Q Mar '13 Mar '12 Mar '11 Mar '10 0.6726739 0.70591 0.94289 0.75563 0.8485436 1.00092 0.96149 1.01288 3.4360606 2.97991 1.53878 5.39032 0.4021548 0.4138 0.4853 0.43041 0.4021548 0.4138 0.48531 0.43041 Mar '13 Mar '12 Mar '11 Mar '10 7.9041916 6.66404 15.2347 5.5229 7.6051446 6.41149 5.95309 8.01874 0.65021337 0.45306 0.35900 0.52518 1 9 2 3
- 9. Ratio Analysis (LEVERAGE RATIOS): Debt to Equity Ratio compared to cement industry d/e ratio is kept at 0.8 which can be called very well; in case of urgency company can raise loan, same in case of Debt to Capital Ratio. Interest converge ratio is 3.4 rupee last year which is also good firm is able to meet the Interest obligations. (VALUE RATIOS): • M/B ratio is always 6+ over the time. A company with a very high share price relative to its asset value, on the other hand, is likely to be one that has been earning a very high return on its assets. • Q ratio < 1 over the time means the stock is undervalued. • P/E Ratio is 7 in 2013; Investors in the stock are willing to pay 7rp for every 1rp of earnings that the company generates. However, this is a far too simplistic way of viewing the P/E because it fails to take into account the company's growth prospects.
- 10. IPO The company, a leading grey cement producer in Northern India, had entered the capital market in 2005 with a public issue shares at a price band of Rs 145 to Rs 155. The issue opened on February 21 and close on February 24, 2005 and subscribed 1.8 times. At the issue price of Rs 148, the company mobilized Rs 296 crore. Stock started trading in BSE on 14 Sept, 2005. Opened at 151 Rp and gave the around % return to investors. In two years of listing price highest went up to 191Rp in May, 2006. and came back to 149 Rp after two year. Today’s price of stock 187.25.
- 11. Share price J.K.Cement ₹ 400.00 ₹ 350.00 ₹ 300.00 ₹ 250.00 ₹ 200.00 ₹ 150.00 ₹ 100.00 ₹ 50.00 ₹ 0.00 Beta = 0.56 All Time High: 24dec,2012 (375) BSE 25000 20000 15000 10000 5000 0 All time low: 2 March,2009 (35.35)
- 14. SUBSTANTIAL GROTH SUBSTANTIALGROTH Year Growth = (ROCE + D/E(ROCE-i(1-T)))* RR Mar '13 Mar '12 Mar '11 Mar '10 6.62% 8.97% 7.16% 8.37%
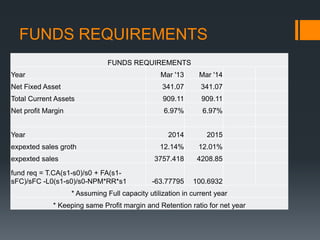
- 15. FUNDS REQUIREMENTS FUNDS REQUIREMENTS Year Mar '13 Mar '14 Net Fixed Asset 341.07 341.07 Total Current Assets 909.11 909.11 Net profit Margin 6.97% 6.97% 2014 2015 12.14% 12.01% 3757.418 4208.85 -63.77795 100.6932 Year expexted sales groth expexted sales fund req = T.CA(s1-s0)/s0 + FA(s1sFC)/sFC -L0(s1-s0)/s0-NPM*RR*s1 * Assuming Full capacity utilization in current year * Keeping same Profit margin and Retention ratio for net year
- 16. COST OF CAPITAL COST OF CAPITAL Current cost of capital Rf beta Market return Cost of equity (Ke)(as per CAPM) 7%(taken) 0.564736(calculated) 13.13%(calculated) 10.51406% cost of debt(Kd)(after tax) 8.38% Cost of capital= ke*e/d+e + kd*d/d+e 9.66% Change in debt/Equity ratio d/e ratio Cost of capital= ke*e/d+e + kd*d/d+e -10.00% 10% 0.6054065 0.739941 41.34% 39.31%