5. Biodiversity Assessment and the Extractives Sector
- 1. “Insert” then choose “Picture” – select your picture. Right click your picture and “Send to back”. The business of sustainabilityThe business of sustainability © Copyright 2017 by ERM Worldwide Group Limited and/or its affiliates (“ERM”). All Rights Reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, without prior written permission of ERM Biodiversity Assessment and the Extractives Sector MCRB Biodiversity Training David Nicholson Technical Director - Biodiversity
- 2. The business of sustainability ERM Myanmar • ERM has been working in Myanmar for over 25 years. • Office in Yangon with 10 full time staff. • Strong experience in the O&G, Power, Mining and Infrastructure Sectors. • Thorough understanding of local legislation. • Unrivalled experience in EIA / SIA, baseline surveys, due diligence and stakeholder engagement. • Certified under the MONREC Transitional Consultant Registration to undertake ESIAs in Myanmar. 2
- 3. The business of sustainability ERM Project Experience - Highlights • Working on four LNG-to-Power Projects - Total / Siemens; PTT; EMPower; Toyo Thai • ESIAs for a variety of Power Sector Projects – Hydropower, Coal, CCGT, HFO and Wind • Working with all majors for O&G exploration – Shell, Total, PTTEP, Chevron, Woodside, PDC etc • Over 10 projects within International Financing - JBIC, IFC, ADB, AIIB • Supporting investments into three Special Economic Zones - Thilawa; Dawei; Kyaukphyu • Projects in Mining, Agribusiness, Manufacturing, Infrastructure, Tourism, and Safety 3
- 4. The business of sustainability Introduction and Agenda 4 1. Introduction 2. Overview of IFC PS6 3. Biodiversity and the Extractives Sector 4. Defining Residual Impacts 5. Example Mitigations 6. Biodiversity Offsetting 7. Questions and Answers
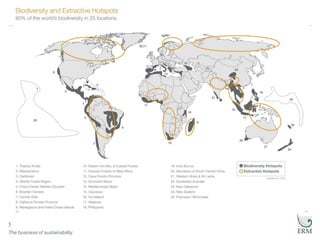
- 5. The business of sustainability 5
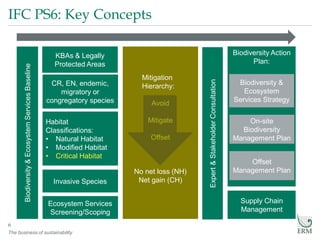
- 6. The business of sustainability Biodiversity Action Plan: IFC PS6: Key Concepts 6 Biodiversity&EcosystemServicesBaseline CR, EN, endemic, migratory or congregatory species KBAs & Legally Protected Areas Habitat Classifications: • Natural Habitat • Modified Habitat • Critical Habitat Invasive Species Mitigation Hierarchy: Avoid Mitigate Offset No net loss (NH) Net gain (CH) Supply Chain Management Offset Management Plan On-site Biodiversity Management Plan Biodiversity & Ecosystem Services Strategy Ecosystem Services Screening/Scoping Expert&StakeholderConsultation
- 7. The business of sustainability Biodiversity Impacts of the Extractives Sector Impacts from the extractives sector can include: - Large spatial habitat loss, often in natural/critical habitats - Impacts to unique biodiversity and potential for new-to- science/endemic species due to underlying geology - Barrier creation, edge effects and fragmentation - Induced clearing due to opening up new areas - Impacts to ecosystem services (water, fisheries etc.) - Induced hunting and poaching - Aquatic ecosystem impacts from water use, discharges and contamination - Introduction of invasive species 7
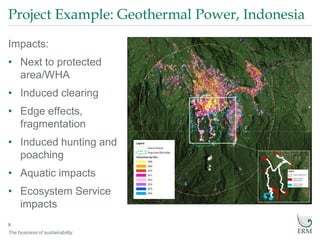
- 8. The business of sustainability Project Example: Geothermal Power, Indonesia 8 Impacts: • Next to protected area/WHA • Induced clearing • Edge effects, fragmentation • Induced hunting and poaching • Aquatic impacts • Ecosystem Service impacts
- 9. The business of sustainability Defining Residual Impacts Residual impacts to biodiversity values require: - Defined metric to determine impacts to habitat types and condition (Habitat Hectares; Averted Loss Metric) - Species impacts defined by population changes (or habitat as a surrogate) - No-net-loss/Net gain calculations require step-by-step assessment of losses and gains (“balance sheet”) - Any residual impacts under IFC PS6 require to be offset 9
- 10. The business of sustainability Project Example Site Species Common Name Habitat Loss Key Residual Impact Offset Description Offset Management Action Summary Monitoring KPI Site Concession Net Gain Manis pentadactyla Chinese Pangolin 32.59ha Habitat loss Hunting and poaching • Management of at least 127ha of forested habitat required. • Population Census • Community Engagement • Patrols and Enforcement • Threat Reduction Campaigns • Wildlife Management Actions • Annual population estimation • Implementation of management actions • Identification of threats and additional management actions Trachypithecus phayrei spp. shanicus Shan State Langur 32.59ha Habitat loss Diplommatina sp. 3 - 235.58ha Habitat loss • Management of at least 1420ha of limestone habitat (or addition of equivalent habitat). • Habitat protection and monitoring • Annual fauna monitoring report 10 • Balance sheet approach used to define residual impacts and achieve no-net-loss/net gain • Supported by comprehensive assessment and management planning framework
- 11. The business of sustainability Key Mitigations for Extractives Sector Key mitigations can include: • Community engagement and empowerment • Community livelihood support • Government capacity building • Access controls • Anti-illegal logging and hunting/poaching measures • On-site rehabilitation/habitat restoration • Invasive species control • Ecosystem service replacement • Translocation of flora/fauna (last resort) 11
- 12. The business of sustainability Project Example: Community Engagement 12 Community engagement objectives: • Raising awareness • Package biodiversity management into livelihood restoration/ alternatives • Manage illegal activities • Empower government • Provide a forum for communities to participate • Update local communities on progress
- 13. The business of sustainability Project Example: Illegal Activity Management Approach should include: - Identify reasons behind illegal activity - Work collaboratively with government - Targeted community programs - Conduct enforcement with Government as a last resort 13
- 14. The business of sustainability Biodiversity Offsetting Biodiversity offset consideration: • Offset goals (no-net-loss/net gain) • Like for like rule • Additionality • Determine offset size (using offset metric) • Ownership of the offset – private, third party or public? • Understanding legal requirements • Understanding ongoing financial obligations • Efficient management, monitoring and validation • Community and stakeholder engagement 14
- 15. The business of sustainability Project Example: STC Group Myanmar Offset design: • 1420ha of limestone habitat & 127ha of forest • Offset size 33,400ha • Species match (e.g. limestone dependent fauna) • 25 year management period • Management committee • Management actions • Financial model • Tender for service provider 15
- 16. The business of sustainability Questions & Answers 16