5.-ROCKS.pptx
- 2. • Avoid making unnecessary noise. • If you have questions, raise your hand. • No cell phones. • Be active and attentive to our discussion. • Violating the rules above 3 times, all of you will have a punishment. CLASSROOM RULES
- 3. • Differentiate rocks according to their type. • Classify rocks into the three main types: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary, based on their characteristics and formation processes. LEARNING OBJECTIVES
- 4. • Aggregate of various types of minerals or individual grains of the same kind of mineral. • Most consist of several minerals What is ROCK?
- 5. • How many minerals can you see in this picture? What is ROCK? Granite
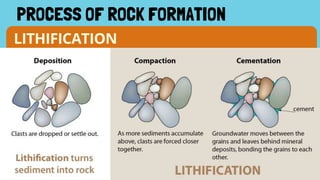
- 7. Rocks are formed through LITHIFICATION PROCESS OF ROCK FORMATION There are 3 ways for lithification to occur • COMPACTION • CEMENTATION • RECRYSTALLIZATION
- 8. COMPACTION PROCESS OF ROCK FORMATION The consolidation of the sediments due to the intense pressing of weight making the them lose the porosity.
- 9. CEMENTATION PROCESS OF ROCK FORMATION Dissolved minerals crystallize and glue sediments together. Happen when ions of ground water precipitates.
- 10. LITHIFICATION PROCESS OF ROCK FORMATION
- 11. RECRYSTALLIZATION PROCESS OF ROCK FORMATION Unstable minerals recrystallize into stable minerals that causes grains to bind together
- 12. THREE MAJOR TYPES OF ROCKS TYPES OF ROCKS • Sedimentary Rocks • Metamorphic Rocks • Igneous Rocks
- 13. IGNEOUS ROCKS TYPES OF ROCKS • Molten rock material that cools and solidify. • Can be classified as Extrusive and Intrusive.
- 14. IGNEOUS ROCKS TYPES OF ROCKS • Extrusive igneous rocks • A volcanic material (lava) that cools down in the surface. • Characterized by fine grained crystals due to fast cooling.
- 15. IGNEOUS ROCKS TYPES OF ROCKS • Intrusive igneous rocks • Also known as plutonic rock. A volcanic material that cools and solidifies underneath or under the surface.
- 16. IGNEOUS ROCKS TYPES OF ROCKS • Intrusive igneous rocks • Characterize by coarse grained crystall due to slow process of cooling.
- 17. COMPOSITION CLASSIFICATION OF IGNEOUS ROCKS • FELSIC • the light-colored (felsic) minerals feldspar and silica in the form of quartz. These have more silica as a proportion of their overall chemical formula.
- 18. COMPOSITION CLASSIFICATION OF IGNEOUS ROCKS • INTERMEDIATE • composition between felsic and mafic. Contains roughly equal amounts of light and dark minerals.
- 19. COMPOSITION CLASSIFICATION OF IGNEOUS ROCKS • MAFIC • It is mostly made of dark minerals like pyroxene and olivine, which are rich in iron and magnesium and relatively poor in silica.
- 20. COMPOSITION CLASSIFICATION OF IGNEOUS ROCKS • ULTRAMAFIC • the extremely mafic rocks composed of mostly olivine and some pyroxene which have even more magnesium and iron and even less silica.
- 21. • ULTRAMAFIC (Coarse grained) • APHANITIC (Fine grained) • PORPHYRITIC (Large crystalls in a large matrix) • VESICULAR (Bubbly or frothy) TEXTURE CLASSIFICATION OF IGNEOUS ROCKS
- 22. • GLASSY • PYROCLASTIC (Fragmental) TEXTURE CLASSIFICATION OF IGNEOUS ROCKS
- 23. SEDIMENTARY ROCKS TYPES OF ROCKS • Formed through accumulation of sediments, pre-existing rocks or part of the living organisms
- 24. SEDIMENTARY ROCKS CLASSIFICATION OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS • Formed through accumulation of clast such as the little broken parts of shells and rocks. • CLASTIC
- 25. SEDIMENTARY ROCKS • Formed via the evaporation of water and the precipitation of ions over time. • CHEMICAL CLASSIFICATION OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
- 26. SEDIMENTARY ROCKS • Formed via accumulation of the materials from the living organisms . • ORGANIC CLASSIFICATION OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
- 27. METAMORPHIC ROCKS TYPES OF ROCKS • Formed from the pre-existing rocks (igneous or sedimentary). Metamorphic rocks form when rocks are subjected to high heat, high pressure, hot mineral-rich fluids or, more commonly, some combination of these factors.
- 28. METAMORPHIC ROCKS TYPES OF ROCKS • METAMORPHISM it is the process of putting the rock under high heat and pressure without melting that causes the geologic texture to change.
- 29. TWO TYPES OF METAMORPHISM
- 30. TWO TYPES OF METAMORPHISM • REGIONAL METAMORPHISM • These rocks were typically exposed to tectonic forces and associated high pressures and temperatures. Usually deformed and foliated
- 31. TWO TYPES OF METAMORPHISM • CONTACT METAMORPHISM • Also called thermal metamorphism by which the country rock that surrounds a hot magma intrusion is metamorphosed by the high heat flow coming from the intrusion.
- 32. Using Venn Diagram, compare and contrast the three types of rocks. ACTIVITY (1/2 CROSSWISE)
- 33. Search for examples (at least 5 for each type) of the rocks. STUDY ABOUT ROCK CYCLE FOR RECITATION Assignment (short B-paper)
- 34. ROCK CYCLE
- 35. Based on the diagram shown and the video, explain the rock cycle. ACTIVITY (1/2 CROSSWISE)