6650812.ppt
- 1. Human Resource Management Strategic Role – Approach
- 2. Management Process Planning Goals and standards Rules and procedures Plans and forecasting. Organizing Tasks Departments Delegating Authority and communication Coordinating
- 3. Management Process Staffing Hiring Recruiting Selecting Performance standards Compensation Evaluating performance Counseling Training and developing
- 4. Management Process Leading Getting the job done Morale Motivation Controlling Setting standards Comparing actual performance to standards Corrective action
- 5. HRM Function Human Resource Management is the process of: acquiring, training, appraising, and compensating employees and attending to their labor relations, health and safety, and fairness concerns.
- 6. HRM People Functions Include: Job analyses Labor needs Recruit Select candidates Orient and train Wages and salaries Incentives and benefits Performance Communicate Train and develop Employee commitment Equal opportunity Health and safety Grievances/labor relations
- 7. HRM is Important to all Managers. Don’t Let These Happen to You! The wrong person High turnover Poor results Useless interviews Court actions Safety citations Salaries appear unfair Poor training Unfair labor practices
- 8. Line & Staff Aspects of HRM Authority distinguishes line from staff as in Making decisions Directing work Giving orders Line Managers Accomplishing goals Staff Managers Assisting and advising line managers
- 9. Line Manager’s HRM Jobs The right person Orientation Training Performance Creativity Working relationships Policies and procedures Labor costs Development Morale Protecting
- 11. Strategy is: the company’s long-term plan for how it will balance its internal strengths and weaknesses with its external opportunities and threats to maintain a competitive advantage. establishing the overall direction and objectives of key areas of human resource management in order to ensure that they not only are consistent but also support the achievement of business goals Strategy, Policy & Administration
- 12. Strategy, Policy & Administration Policy: the development and implementation of detailed procedures, and systems which reflect the strategic framework. Administration: day to day administration of operational activities such as records, payrolls, and benefits programmes
- 14. Strategic Planning Process SWOT analysis - Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats Best strategic plans balance a company’s Strengths and Weaknesses with the Opportunities and Threats the firm faces Basic strategic plans address trends Globalization Technological advances The nature of work The workforce
- 15. HR’s evolving role Protector and Screener Strategic Partner Change Agent
- 16. Strategic HRM Strategic human resource management: linking HRM with strategic goals and objectives to improve business performance and develop organizational cultures, design, people and systems that fosters innovation and flexibility.
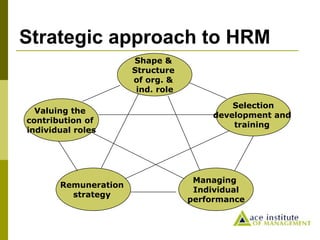
- 17. Strategic approach to HRM Remuneration strategy Valuing the contribution of individual roles Shape & Structure of org. & ind. role Selection development and training Managing Individual performance
- 18. HR STRATEGY Clarify the business strategy Realign the HR functions and key people practices Create needed competencies and behaviors Realization of business strategies and results Evaluate and refine
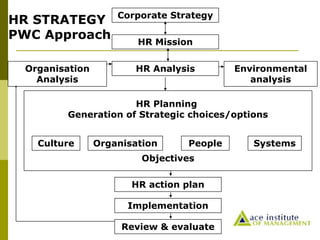
- 19. Corporate Strategy HR Mission Organisation Analysis HR Analysis Environmental analysis Culture Organisation People Systems HR Planning Generation of Strategic choices/options Objectives HR action plan Implementation Review & evaluate HR STRATEGY PWC Approach
- 20. The process by which things get done in the organisation The beliefs, values, norms and style of organisation The structure, jobs, roles and reporting lines of the organisation The skill levels, staff potential and mgmt capability of the organisation Systems Organisation Culture People HR policies & objectives HR Strategy planning
- 21. How HR helps strategy execution Functional strategies should support competitive strategies Value chain analysis Outsourcing Strategy Formulation
- 22. How HR helps form strategy Formation of a company’s strategy = identifying, analyzing and balancing external opportunities and threats with internal strengths and weaknesses Environmental scanning
- 23. HR and technology Basic HR systems demand paperwork 70% of HR’s employees time = paperwork Off the shelf forms from Office Depot/Officemax Online forms Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) HR on the Internet
- 24. HR means performance Can HR have a measurable impact on a company’s bottom line? Better HRM translates into improved employee attitudes and motivation (e.g., working at home) Well run HR programs drive employee commitment