8.docx
- 1. 88 | F I E L D S T U D Y 1 L E A R N I N G E P I S O D E 8 SPARK Your Interest Formal education begins in school. Schools are institutions established to design total learning activities appropriate for each learner in each grade level. Thus, schools have recommended curriculum which is the enhanced K to 12 curriculum. The recommended curriculum was translated into written curriculum like books, modules, teacher’s guides and lesson plans which are the basis of the taught curriculum. A teacher who implements the curricula needs support materials (support curriculum) to enhance teaching and learning so that the written and the taught curricula can be assessed (assessed curriculum) in order to determine if learning took place (learned curriculum). However, there are so many activities that happen in schools but are not deliberately planned. This refers to the hidden curriculum. A classroom teacher plans, implements and evaluates school learning activities by preparing a miniscule curriculum called a lesson plan or learning plan. The teacher then puts life to a lesson plan by using it as a guide in the teaching-learning process where different strategies can be used to achieve the learning objectives or outcomes. There are many styles of writing a lesson plan, but the necessary parts or elements such as (a) Learning Outcomes (b) Subject Matter (c) Teaching Learning Strategies, and (d) Evaluation or Assessment should always be included. All of these elements should be aligned so that at the end of the teaching-learning episode, learning will be achieved with the classroom teacher as a guide. TARGET Your Intended Learning Outcome At the end of this Episode, I must be able to: identify the different curricula that prevail in the school setting; describe how the teacher manages the school curriculum by planning, implementing lessons through different strategies and assessment of learning outcomes; and analyze if the teacher aligns the objectives to subject matter, to teaching strategies and assessment. FIELD STUDY 1 Learning Episode Close Encounter with the School Curriculum FS 1 8
- 2. 89 | F I E L D S T U D Y 1 L E A R N I N G E P I S O D E 8 REVISIT the Learning Essentials School Curriculum: What is this about? From a broad perspective, curriculum is defined as the learning process and outcomes as in lifelong learning. However, school curriculum in this course limits such definition of total learning outcomes to confine to a specific learning space called school. Schools are formal institutions of learning where the two major stakeholders are the learners and the teachers. Basic education in the Philippines is under the Department of Education or DepEd and the recommended curriculum is the K-12 or Enhanced Basic Education Curricula of 2013. All basic education schools offering kindergarten (K) elementary (Grades 1 to 6) and Secondary (Grades 7-10, Junior High School and Grades 11 to 12, Senior High School) adhere to this national curriculum as a guide in the implementation of the formal education for K to 12. What are the salient features of the K to 12 Curriculum? Here are the features. It is a curriculum that: 1. Strengthens the early childhood education with the use of the mother tongue. 2. Makes the curriculum relevant to the learners. The use of contextualized lessons and addition of issues like disaster preparedness, climate change and information and communication technology (ICT) are included in the curriculum. Thus, in-depth knowledge, skills and values, attitude through continuity and consistency across every level and subject. 3. Build skills in literacy. With the use of Mother Tongue as the main language in studying and learning tools from K to Grade 3, learners will become ready for higher level skills. 4. Ensures unified and seamless learning. The curriculum is designed in a spiral progression where the students learn first the basic concepts, while they study the complex ones in the next grade level. The progression of topics matches with the developmental and cognitive skill. This process strengthens the mastery and retention. 5. Gears up for the future. It is expected that those who finish basic education in Grade 12 will be ready for college or tech voc careers. Their choice of careers will be defined when they go to Grade 11 and 12. 6. Nurtures a fully developed youth. Beyond the K to 12 graduate the learner will be ready to embark on different career paths for a lifetime. You will recall that a school curriculum is of many types for the Kindergarten to Grade 12 in the country. The enhanced curriculum K to 12 curriculum is the Recommended Curriculum. It is to be used nationwide as mandated by the Republic Act 10533. When the curriculum writers began to write the content and competency standards of the K to 12 Curriculum it became a Written Curriculum. It reflects the substance of RA 10533 or the Enhanced Basic Education Act of 2013. In the teacher’ s class it is the lesson plan. A lesson plan is a written curriculum in miniscule. What has been written in the lesson plan has to be implemented. It is putting life to the written curriculum, which is referred to as the Taught Curriculum. The guidance of the teacher is very crucial.
- 3. 90 | F I E L D S T U D Y 1 L E A R N I N G E P I S O D E 8 A curriculum that has been planned, and taught needs materials, objects gadgets, laboratory and many more that will help the teacher implement the curriculum. That is referred to as the Supported Curriculum. In order to find out if the teacher has succeeded in implementing the lesson plan, an assessment shall be made. It can be done in the middle or end of the lesson. The curriculum is now called the Assessed Curriculum. The result of the assessment when successful is termed as Learned Curriculum. Learned Curriculum whether small or big indicates accomplishment of learning outcomes. However, there are unplanned curriculum in schools. These are not written, nor deliberately taught but they influence earning. These include peer influence, the media, school environment, the culture and tradition, natural calamities and many more. This curriculum is called Hidden Curriculum or Implicit Curriculum. So, what will be the roles and responsibilities of the teacher in the relations with the school curriculum, specifically in the K to 12 or the enhanced curriculum for basic education? Teachers then should be multi-talented professionals who: Know and understand the curriculum as enumerated above; Write the curriculum to be taught; Plan the curriculum to be implemented; Initiate the curriculum which is being introduced; Innovate the curriculum to make it current and updated; Implement the curriculum that has been written and planned; and Evaluation the written, planned and learned curriculum.
- 4. 91 | F I E L D S T U D Y 1 L E A R N I N G E P I S O D E 8 OBSERVE, ANALYZE, REFLECT Curricula in the School Setting It’s time to look around. Discover what curriculum is operating in the school setting. Recall the types of curriculum mentioned earlier. Can you spot where these are found? Let’s do a hunting game! OBSERVE Resource Teacher: Teacher’s Signature School_________________________ Grade/Year Level: Subject Area: Date___________________________ 1. Locate where you can find the following curriculum in the school setting. Secure a copy, make observations of the process and record your information in the matrix below. Describe your observations. Type of Curriculum Where Found Description 1. Recommended Curriculum (K to 12 Guidelines) 2. Written Curriculum (Teacher’s Lesson Plan) 3. Taught Curriculum (Teaching Learning Process) 4. Supported Curriculum (Subject Textbook) 5. Assessed Curriculum (Assessment Process) 6. Learned Curriculum (Achieved Learning Outcomes) 7. Hidden Curriculum (Media) ACTIVITY 8.1
- 5. 92 | F I E L D S T U D Y 1 L E A R N I N G E P I S O D E 8 ANALYZE Which of the seven types of curriculum in the school setting is easy to find? Why? Which is difficult to observe? Why? Are these all found in the school setting? How do curricula relate to one another? Draw a diagram to show the relationship of one curriculum to the other.
- 6. 93 | F I E L D S T U D Y 1 L E A R N I N G E P I S O D E 8 REFLECT Make a reflection on the diagram that you have drawn.
- 7. 94 | F I E L D S T U D Y 1 L E A R N I N G E P I S O D E 8 The Miniscule School Curriculum: The Lesson, A Closer Look Resource Teacher: Teacher’s Signature School_________________________ Grade/Year Level: Subject Area: Date___________________________ OBSERVE The activity requires a full lesson observation from Motivation to assessment. Procedure: 1. Secure permit to observe one complete lesson in a particular subject, in a particular grade/year level. 2. Keep a close watch on the different components of the miniscule curriculum: The Lesson 3. Follow the three major components of a curriculum (Planning, Implementing, Evaluating/Assessing). Observe and record your observation. Observe and Record Observation on the Following Aspects Major Curriculum Components Key Guide for Observation (Carefully look for Indicators/behavior of the teacher along the key points. Write your observation and description in your notebook.) A. Planning 1. Borrow the teacher’s lesson plan for the day. What major parts do you see? Request a copy for use. Answer the following questions. a. What are the lesson objectives/learning outcomes? b. What are included in the subject matter? c. What procedure or method will the teacher use to implement the plan? d. Will the teacher assess or evaluate the lesson? How will this be done? B. Implementing Now, it’s time to observe how the teacher implemented the prepared lesson plan. Observe closely the procedure. a. How did the teacher begin the lesson? b. What procedure or steps were followed? c. How did the teacher engage the learners? d. Was the teacher a guide at the side? e. Were the learners on task? /Or were they participating in the class activity? f. Was the lesson finished within the class period? C. Evaluating/Assessing Did the learning occur in the lesson taught? Here you make observations to find evidence of learning. a. Were the objectives as learned outcome achieved? b. How did the teacher assess/evaluate it? c. What evidence was shown? Get pieces of evidence. ACTIVITY 8.2
- 8. 95 | F I E L D S T U D Y 1 L E A R N I N G E P I S O D E 8 ANALYZE Write a paragraph based on the data you gathered using these key questions. 1. How does the teacher whom you observed compare to the ideal characteristics or competencies of global quality teachers? ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Was the lesson implemented as planned? Describe: ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Can you describe the disposition of the teacher after the lesson was taught? Happy and eager? Satisfied and contented? Disappointed and exhausted? ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Can you describe the majority of students’ reactions after the lesson was taught? Confused? Happy and eager? Contented? No reactions at all. ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ REFLECT Based on your observations and tasks in Activity 2 how will you prepare your lesson plan? Make a short paragraph on the topic.
- 9. 96 | F I E L D S T U D Y 1 L E A R N I N G E P I S O D E 8 Constructive Alignment of the Components of A Lesson Plan Resource Teacher: Teacher’s Signature School_________________________ Grade/Year Level: Subject Area: Date___________________________ OBSERVE Using the diagram below fill up the components part of the Lesson Plan. I. Title of the Lesson: ________________________________________ II. Subject Area: _____________________________________________ III. Grade Level: _____________________________________________ ACTIVITY 8.3 Outcomes Teaching Method Assessment Fill this up Fill this up Fill this up
- 10. 97 | F I E L D S T U D Y 1 L E A R N I N G E P I S O D E 8 ANALYZE Answer the following questions based on the diagram. 1. Are the three components constructively aligned? Explain. ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Will the outcomes be achieved with the teaching method used? Why? ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What component would tell if the outcomes have been achieved? ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ REFLECT What lessons have you learned in developing or writing the lesson plan? What value will it give to the teacher if the three components are aligned?
- 11. 98 | F I E L D S T U D Y 1 L E A R N I N G E P I S O D E 8 SHOW Your Learning Artifacts Learning Artifacts for Activity 1-3 Present the Artifact for activity 1, 2, and 3. Activity 1: Artifact 1. Present an evidence for each kind of curriculum operating in the school setting. This can be in pictures, realia, documents or others. Activity 2: Artifact 1. Present a sample curriculum in a form of a Lesson Plan. Activity 3: Artifact 1. Present a matrix to show the constructive alignment of the three components of the lesson plan. a. Example Lesson Title: ______________________________________ Subject Area: _____________________________________ Grade Level: _____________________________________ Learning Outcomes Teaching Methods Evaluation
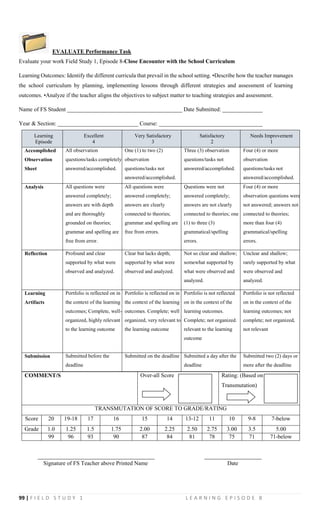
- 12. 99 | F I E L D S T U D Y 1 L E A R N I N G E P I S O D E 8 EVALUATE Performance Task Evaluate your work Field Study 1, Episode 8-Close Encounter with the School Curriculum Learning Outcomes: Identify the different curricula that prevail in the school setting. •Describe how the teacher manages the school curriculum by planning, implementing lessons through different strategies and assessment of learning outcomes. •Analyze if the teacher aligns the objectives to subject matter to teaching strategies and assessment. Name of FS Student ________________________________________ Date Submitted: ______________ Year & Section: ____________________________ Course: ____________________________________ Learning Episode Excellent 4 Very Satisfactory 3 Satisfactory 2 Needs Improvement 1 Accomplished Observation Sheet All observation questions/tasks completely answered/accomplished. One (1) to two (2) observation questions/tasks not answered/accomplished. Three (3) observation questions/tasks not answered/accomplished. Four (4) or more observation questions/tasks not answered/accomplished. Analysis All questions were answered completely; answers are with depth and are thoroughly grounded on theories; grammar and spelling are free from error. All questions were answered completely; answers are clearly connected to theories; grammar and spelling are free from errors. Questions were not answered completely; answers are not clearly connected to theories; one (1) to three (3) grammatical/spelling errors. Four (4) or more observation questions were not answered; answers not connected to theories; more than four (4) grammatical/spelling errors. Reflection Profound and clear supported by what were observed and analyzed. Clear but lacks depth; supported by what were observed and analyzed. Not so clear and shallow; somewhat supported by what were observed and analyzed. Unclear and shallow; rarely supported by what were observed and analyzed. Learning Artifacts Portfolio is reflected on in the context of the learning outcomes; Complete, well- organized, highly relevant to the learning outcome Portfolio is reflected on in the context of the learning outcomes. Complete; well organized, very relevant to the learning outcome Portfolio is not reflected on in the context of the learning outcomes. Complete; not organized. relevant to the learning outcome Portfolio is not reflected on in the context of the learning outcomes; not complete; not organized, not relevant Submission Submitted before the deadline Submitted on the deadline Submitted a day after the deadline Submitted two (2) days or more after the deadline COMMENT/S Over-all Score Rating: (Based on Transmutation) TRANSMUTATION OF SCORE TO GRADE/RATING Score 20 19-18 17 16 15 14 13-12 11 10 9-8 7-below Grade 1.0 1.25 1.5 1.75 2.00 2.25 2.50 2.75 3.00 3.5 5.00 99 96 93 90 87 84 81 78 75 71 71-below _____________________________________________ ______________________ Signature of FS Teacher above Printed Name Date
- 13. 100 | F I E L D S T U D Y 1 L E A R N I N G E P I S O D E 8 LINK Theory to Practice Choose the correct answer from the options given. 1. When we say school curriculum it refers only to the K to 12 curriculum. A. This statement is true. B. This statement is not true. C. This statement is half true. D. This statement is silly. 2. A professional teacher should posses the following skills to address the need for a curriculum EXCEPT one. Which one is NOT? A. Knower of the curriculum. B. Believer of the curriculum. C. Implementer of the curriculum. D. Writer of the curriculum. 3. The influence of multimedia, peers, community tradition, advancement of technology, though not deliberately taught in the lesson, will influence the curriculum. This is referred to as _________. A. Written curriculum. B. Recommended curriculum C. Implemented curriculum. D. Hidden curriculum. 4. Which two components of the lesson plan (as a miniscule curriculum) should be aligned? I. Outcomes and Assessment. II. Assessment and Teaching Methods. III. Outcomes and Teaching Methods. A. I only B. II only. C. III only. D. I, II and III. 5. What is the most important reason why there should be constructive alignment of the components of the curriculum? A. For ease of correcting by the school principal. B. To assure that each component contributes to the attainment of the learning outcomes. C. As a required template when starting to write a lesson plan. D. As a model of other lesson plans written and published.