A Critical Analysis And Comparison Of Major Mobile Operating Systems And A User Classification Of Each Major OS 2014
- 1. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 ABSTRACT In a fast-paced world, where communication is not taken for granted, the use of mobile devices as one of the main methods of communication is finding direct applications in the society where they can be used as an interface between humans and devices or machines with the eradication of distance and location as a barrier with the goal of making life easier. As technology advances, regular mobile phone has also evolved from being a ‘phone to a smartphone and tablet’ in the past years with millions of features, thanks to the operating systems. This report provides a comprehensive historic overview and introduction to smartphones and operating systems for mobile devices. Also, a compilation of a research on the four currently most popular mobile platforms or operating systems, it consists of a comprehensive comparison of the four heavyweights: Apple's iOS, Google's Android, Microsoft's Windows Phone, and RIM's BlackBerry OS. The report also incorporates a better knowledge of operating systems (OS), their history, usability, functionality, design, applications etc. Furthermore, this report offers a complete insight on mobile devices operating systems and the massive development that has taking place from the time past till date, the smartphone is no more just a device that can be taken casually. It has a zillion more uses now apart from basic ones, and that has contributed to the success of making it not just a mobile phone but also a smartphone. Introduction Background In the past it was never clear that mobile devices would have such an important status in today’s society. But the development of the mobile phone into a smartphone and tablets proves this statement right. This includes transformations, besides the normal functionalities of a phone like text messaging, receiving and making calls. A mobile device’s operating system reflects the user’s lifestyle because it controls the choice of applications, the general features and functionality in the device. However, the mobile market is fragmented amongst the following software platforms or operating systems; WebOS,
- 2. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 BlackBerry OS, Windows phone formerly known as (Windows Mobile OS), Android OS, Meego OS, Bada OS, Symbian OS, iPhone OS, and Tizen OS. Due to the continues advancement in the technology of a mobile phones and devices, each one now needs an operating system in order for it to reach its full capacity in today’s world, however a phone is not smart on till it is powered by an operating system. i.e. phone manufacturers such as Samsung, HTC, LG, SonyEricson etc. Play a role by manufacturing a phone (hardware) with the demand and capability of running this software, which is the OS inside. This simply means that the phone (hardware) is the infrastructure, while an operating system (software) powers the phone. (Cromar. at al. 2010) Currently there are applications like a web browser, which allows you to see web pages the way they were designed to be seen, more also there are applications for sending and receiving email messages just to mention but a few, this makes the mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets more similar to a PC. So not the device itself seems to be the most important thing. It is the also the operating system and the applications on it, which can make the difference in the future. (Steve, et al. 2007) Mobile devices are now part of our lives, most people find it hard to live a day without their mobile devices. With the help of operating systems, smartphones and tablets now plays a major role in our day-to-day activities; this is possible because there are virtually applications for almost everything we do on our computers and more. The operating system (OS) in the mobile devices has become increasingly important in transforming the phone or tablet into a music player, camera, personal assistant, GPS navigator and game console, more also smartphone’s OS delivers the framework to go beyond simply making a call, allowing it to run productively and media playing applications as well as operate on social networks such as Twitter and Facebook. The mobile phone is not just a calling device these days; it has evolved tremendously thanks to the operating systems (OS). (Cromar. at al. 2010) Mobile phones until sometime back, was determined only by the manufacturer it came from, in the past one would go to the store and ask for Nokia or Samsung phone, now things are changing, the thinking of the consumers is moving to a whole new direction. Today, the consumer goes into a store and asks for an android phone, iOS phone or a windows phone. This
- 3. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 is because these devices allow far better productivity and user freedom. Consumers are finally coming to realization that it is the platform that powers them that delivers that particular kind of productivity and not just the manufacturer. However, each one of these operating systems is highly vital in today’s IT world as more and more consumers understands the significance the mobile OS offers, more also many users now understands the differences in the general user experiences as highlighted to be discussed. The idea here is to discuss in detail the four aforementioned OS in other to help consumers and analysts understand the operating systems better, in so doing the advantages and disadvantages, cognitive load, efficiency and integration, customization and user experience friction (UEF) of each one of the OS will be critically analyzed. Keywords: mobile, operating system (OS), device, android, windows phone, and blackberry. Research scope and limitations This research by the author is carried out independently to help consumers, mobile OS developers and applications developers, to comprehensively analyze the general concept of the mobile operating systems paradigm. In order to remain at the foreground of the mobile OS technological developments and it is on this foundation that this research was commissioned. This analysis investigates the four-top prominent mobile devices operating systems that are currently being used in the world, namely Apple iOS, BlackBerry OS, Google Android and Windows Phone. However, the mobile devices market is currently dominated by two mobile OS, Google Android and Apple iOS. By the end of the year 2012 the Android OS had 54.4 percentage and iOS had 32.4 percentage of UK mobile devices sales, collectively that is simply equivalents to just below 87% of UK’s total mobile devices like smartphones and tablets market stake. The mobile OS in the third and fourth place respectively are the Blackberry OS (6.4 percentage) and subsequent by Windows Phone (5.9 percentage). The scope of this research is centered on mainly on mobile computing in the area of mobile devices and mobile operating systems it is structured from the foundation to the most recent
- 4. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 general enhancements and updates i.e. latest software and hardware updates, design, features etc. the research is further based on a selection of the four most popular mobile operating systems, which are Google’s Android OS, Apple’s iOS, Microsoft’s windows phone OS and RIM’s Blackberry OS. This operating system are the four most commonly used and these mobile OS companies owns most if not all of the market shares till date. This research will provide a guideline for mobile OS development and an in-depth comparative analysis of major mobile operating systems. Then consumers model for analyzing and accessing the impacts of mobile OS on mobile devices paradigm then finally, a conceptual technological model for business analysts and developers on mobile devices offering and prospects. This research will seek to critically compare and analyze this aforesaid four most popular mobile OS; this will be carried out by comprehensively looking deep into areas such as the developmental history, design, features, functions, popularities and future prospects. Further each released software and hardware updates from the launch date will be analyzed and discussed with a detailed approach because this is the only texted and released updates for users pending on other future updates and enhancements. And a detailed pros and cons, cognitive load, efficiency and integration, customization and user experience friction (UEF), of each of the four aforementioned operating systems will be comprehensively listed and analyzed. Further questionnaires will be used to analyze consumer’s choices and preferences, these will be carried based on 3 specific areas, which are social, education and business users, this is a limitation because there is delay in responses from the respondent of the questionnaires. There are more than 20 other known mobile operating systems, but this research covers just four of the most popular mobile OS, the four most popular OS was selected to be analyzed compared because, users often find it difficult in making choices in which to buy. Furthermore, there are basic applications that these four operating systems performs effortlessly, but the ways in which the performance takes place varies this areas will be also analyzed in details. Due to time constraint and lack of expertise in developing a prototype application for each one of the four selected operating systems to show a simulation of how the OS handles or runs each basic application, however a prototype for each OS is not added in this research. This is a
- 5. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 potential area of extension for future research on this topic. There are also other known mobile operating systems that can be further researched on in the future and compared such as obuntu OS, Bada OS, Web OS, Tizen OS, Meego OS etc. some of this OS are popular in some parts of the world and have great potentials to go mainstream in the mobile technology market, however this would be a potential research area in the future. Problem statement The use of mobile devices is strongly becoming a part of everyday life, the technology used in these mobile devices are getting more and more sophisticated with each new update as a result of the operating system powering these devices, this means that the operating system plays a vital role as it determined how the device performs every task. There are quite a number of these high-end popular operating systems with each possessing its own uniqueness i.e. pros and cons. However, consumers have constant arguments and many times confused on which is a better choice and suits their needs best. As a result, these researches was developed to address these issue using the four overwhelmingly mobile devices operating systems market share leaders. To address this issue by creating a comprehensive comparison framework and further using three categories of users, which are business, social and education (student) users to classify which one of these four OSs suits best their requirements. Research academic question aim and objectives To assess the report that has been assumed, there are set out aims of this report i.e. precisely what the report aims to accomplish, and then the objectives, which are the tasks that have been acknowledged for how the aims are going to be reached for this report. Academic Question – How does the overall concept, design and functionality of mobile operating systems technology impacts consumer choices and preference? Aims and objectives Aim 1: To compare and contrast the four-main mobile operating system, their general functions, design, applications, popularity, and user experience.
- 6. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 Aim 2: To further appraise the extent to which the mobility, design, applications and functionality of mobile OS impacts the consumer’s preference paradigm towards education, business and social user’s classification. Objectives: 1. Research into the history and development of mobile devices and operating systems with mainstream examples of mobile devices and OS for (smartphones and tablets). 2. Investigating their general concepts, design, features, application and functions (hardware and software). 3. Investigating the four-major mobile operating systems development and availability, popularity worldwide. 4. Examining the use of mobile operating system i.e. social, education and business user classifications. 5. To further analyse the mobile operating system’s advantages and disadvantages, based on user’s preferences of smartphone and tablet usage in relation to mobile tasks. 6. Examining user preferences of mobility and technical features of mobile devices (smartphones and tablets). 7. Investigating some specific areas of the 4 most popular OS such as cognitive load, efficiency and integration, customization and user experience friction (UEF). Discussion of the academic question Mobile devices and operating systems has been a major topic of interest for many years, since mobile phones became part of human existence, as human virtually use phones for many different purposes daily. Mobile phone OS is the technology today, there has always been a great desire to know the processes of how phone transformed into smartphones and tablets with great capabilities, and the roles of operating systems and in making that a continues success. In the course of university education, the skills and knowledge acquired in information technology and particularly within the realm of IT and mobile technologies, have enabled an
- 7. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 ability to understand how mobile devices functions with the operating systems using programming languages. The skills and interest were predominantly in mobile devices and operating systems development; therefore, the decision was made to combine the two together and create an academic question for the final thesis. This would allow a far-reaching research and study on mobile operating systems from a comprehensive standpoint and give the ability to compare popular operating systems. Research Methodology Managing this research in order to achieve the goals and objectives identified in the report, an appropriate research methodology would be carried out to achieve the desired outcome. This is a qualitative research; the main method used will be document review and questionnaires. The document review part will be done based on some comprehensive detailed steps and some identified checklist all in the chapter 3, using academic papers, conference papers, textbooks, journals and other suitable resources. The use of Harvard style referencing format will be employed in all parts of the report where necessary. Furthermore, some questionnaires for insight on how the aforesaid four main mobile OS are impacting general consumer preferences will be also analyzed and discussed with the help of the questionnaires. The correspondents will be classified into three categories such as business, social and education users. Details of how but of this research methods will be employed will be also discussed in detail in the chapter three. However, this research will form the following section of the report, which is the literature review. The next chapter after the literature review is the methodology of this research with justification of the hypothesis and methods. The methods utilized in the research are a mixture of two methodologies, which are qualitative and quantitative. The design of the study is analysis and comparison of the four-main mobile OS by document review. Then Survey questionnaires were created to meaningful information and data obtained will be used to improve the quality of this research in terms of the OS comparison. The sample design of the research is non-probability because of the time limitation and it consists of mobile devices
- 8. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 users. The data collection method here are being documents reviews as stated earlier and questionnaires. The data will then be analyzed using the qualitative and quantitative methodology. The next chapter 4: Is the analyzing of the questionnaires utilized and the results. The findings from the documents reviewed and the results of the questionnaires will be properly analyzed to improve the research. The next chapter 5: will be the presentation of the artifact of the research carried out, which will be framework or guild for comparison of the three key mobile devices OS. Finally, a conclusion of all the researches carried out on mobile devices and the four main operating systems (Android OS, iOS, Windows phone OS, and Blackberry OS) based on different areas of their advantages each of the mobile operating system has over others as suggested by other profound researchers and surveys. All the investigations will be carried out using trustworthy resources. Operating System Definition of Operating System: According to Bhor and Rote et al., 2003. On their journal article ‘operating system’ the three- main definition of the general concept of operating system was defined below: ▪ An Operating system is a program that controls the execution of application programs and acts as an interface between the user of a computer and the mainframe hardware. ▪ A more common definition is that the operating system is the one program running at all times on the computer (usually called the kernel), with all else being applications programs. ▪ An Operating system is concerned with the allocation of resources and services, such as memory, processors, devices and information. The Operating System correspondingly includes programs to manage these resources, such as a traffic controller, a scheduler, memory management module, I/O programs, and a file system. (Bhor and Rote et al., 2003)
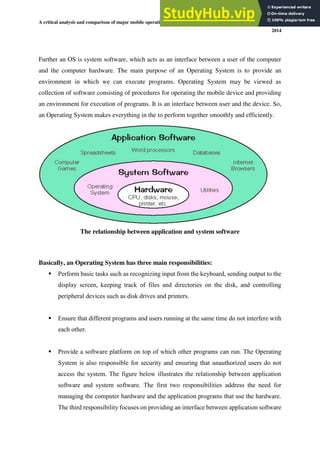
- 9. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 Further an OS is system software, which acts as an interface between a user of the computer and the computer hardware. The main purpose of an Operating System is to provide an environment in which we can execute programs. Operating System may be viewed as collection of software consisting of procedures for operating the mobile device and providing an environment for execution of programs. It is an interface between user and the device. So, an Operating System makes everything in the to perform together smoothly and efficiently. The relationship between application and system software Basically, an Operating System has three main responsibilities: ▪ Perform basic tasks such as recognizing input from the keyboard, sending output to the display screen, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers. ▪ Ensure that different programs and users running at the same time do not interfere with each other. ▪ Provide a software platform on top of which other programs can run. The Operating System is also responsible for security and ensuring that unauthorized users do not access the system. The figure below illustrates the relationship between application software and system software. The first two responsibilities address the need for managing the computer hardware and the application programs that use the hardware. The third responsibility focuses on providing an interface between application software
- 10. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 and hardware so that application software can be efficiently developed. Since the Operating System is already responsible for managing the hardware, it should provide a programming interface for application developers. As a user, we normally interact with the Operating System through a set of commands. The commands are accepted and executed by a part of the Operating System called the command processor or command line interpreter. (Kumar and Kr, 2005) The interface of various devices to an operating system What is a mobile Operating System? According to John Ross the author of ‘The Book of Wireless’ defined mobile operating systems, (2008, page258) “A mobile device such as smartphone or tablet is a small mobile computer with an operating system that controls its features and performances, including the screen layout and the way it sends and receives data and telephone calls”. Basically, a mobile device has the capability of a computer which means that it can be used for data transfers, entertainments like gaming, watching videos, or listening to music etc. in order for it to achieve this capability it has to be powered by one of this operating systems which gives it a PC experience, there are few number of OS, some are generally used and some are
- 11. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 used by professionals in IT. Each OS includes a marginally unique feature set, and also strengths and weaknesses, but they all have the power to essentially carry out the same task. Mac life, Autumn (2007, p.13) gives a clearer understanding on mobile devices such as smartphones and the operating system’s importance “to truly be considered a smartphone or tablet, a device must run a full-fledged operating system that supports a strong complement of applications and it is able to download and run additional applications as needed” in today’s world even low cost phones sports an impressive display of features in them, it is not unusual for free phones to have basic features like camera, Bluetooth compatibility etc. this days. The magic of a mobile device’s such as phones and tablets functionality is powered by its operating system every OS has its own very unique feature compared to other OS. The application that runs on the mobile devices OS and how nice they appear and arrayed plays a significant role on the consumer choices, because users make their choices based on the functionalities of the device, for example some users prefers mobile devices such as smartphones or tablets with physical keyboards to others with touch screen keyboard and not all mobile device’s operating system supports physical keyboards or touch screen, example: IOS supports touch screen keyboards while Android OS supports both. Mac life suggests that in order for a phone to be called a smartphone it has to go beyond basic features like camera, media player etc. more is needed like the capability of running applications and multitasking in order for it to achieve a smartphone status. However not all smartphones are built equally. According to Ken Lo in his article the mobile operating systems compared, 2012, described the mobile device operating systems in a general terms, “The operating system in a mobile devices such as smartphone and tablets is the very basic software, which allows your device to operate. It brings together the hardware chips and components inside your phone so they all work in conjunction with each other”. Further more the operating system in a mobile device provides all of the basic functionality: i.e. the capability to make calls, send and receive text messages, entertainments such as videos, and high graphical games, browse the internet and being able to run applications. The choice of operating system has a massive impact on the look and feel of the mobile device and the applications that it is capable of running in the device generally.
- 12. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 Types of Mobile device OS platforms: According to a White paper on Mobile OS and efforts towards open standards, (2009). The mobile devices such as smartphone and tablets OS can be differentiated based on the existing operating systems used by computers. (Dotcom Infoway. 2009) Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) A Real-Time Operating System, which responds to inputs, immediately and generates results, instantly. This type of system is usually used to control scientific devices and similar small instruments where memory and resources are crucial and constricted. This type of devices have very limited or zero-end user utilities, so more effort goes into making the OS really memory efficient and fast (less coding), so as to minimize the execution time, in turn saving on power as well. E.g.: 8086 etc. (Dotcom Infoway, 2009) Single user, single tasking operation system This type of OS is better version of Real time OS, where one user can do effectively one thing at a time, which means that doing more than one thing at a time is difficult in this type of OS. For instance: The palm OS in palm hand held computer is an example of single-task OS. Single user, multi-tasking operating system
- 13. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 It allows more than one program to run concurrently like printing, scanning, word processing etc. e.g. MS Windows and Apple’s Mac OS. Multi-user operating system It allows two or more users to run programs at the same time. Some OS permit hundreds or even thousands of concurrent users. e.g. UNIX, Android and Main Frame OS. (Dotcom Infoway, 2009) This part presents a study of the mainstream OS for mobile computers. Not all of the existing mobile OS on the market have remained analyzed. However just the highest active and company pushed variants have been chosen based on market analysts’ realistic statistics (and forecasts (Gartner, 2009), (DigiTimes, 2009)). This literature below involves the most popular operating systems for a general overview of the OSs such as: Symbian OS, Tizen OS, Windows phone OS, BlackBerry OS, iOS, Android OS, Firefox OS and Ubuntu OS. General examples of mobile operating systems and classifications A. Manufacturer-built proprietary operating systems ➢ Apple iOS ➢ RIM BlackBerry OS ➢ HP WebOS ➢ Bada from Samsung Electronics B. Third party proprietary operating systems ➢ Microsoft Windows Phone 7 ➢ Microsoft Windows Mobile C. Free & open source operating systems ➢ Android ➢ MeeGo ➢ Symbian
- 14. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 Comparison of the four most popular mobile OS Comparison of the four most popular smartphone operating system’s main characteristics according to (Cromar, et al. and Aviram, et al. 2010) Development Model Available Hardware App store Service providers Special Features Android Open Source, Extendable Multiple Manufacturer s Numerous Configurations Android Marketplace (Large), others All Usu. end-user can Make changes; Growing rapidly Due to openness iOS Closed (Proprietary) Apple only IPhone only The App store (large, only option) Few ITunes integration, iPod BlackBerry (RIM) Closed (proprietary) RIM only Numerous configuration App world (New) All End-to-end encryption Windows phone 7 Closed licensable, minor customizations Multiple manufacturer s Many configurations Windows phone marketplace (New) Few (soon to be all) Brand new, lots of potentials Research methods The methods utilized in the research are a mixture of two methodologies, which are qualitative and quantitative. Which are the two types of research methods used in this chapter to gather data, using both research methods was inevitable as the nature of the research requires both, quantitative method will be used in analyzing the questionnaire aspect while qualitative method will be used in the document review aspect for secondary date gathering. Data collection methods The methods utilized in collection of data in this research is first reviewing past documents or research done by other researchers such as conference proceedings, articles, books, former surveys and others for comparison of the four-major mobile operating systems. The process of analyzing this aforesaid past document helps to compare this OSs by reviewing other documents about the particular research area being the four-major mobile OS, all the work done about the OS’s historic development, past survey, pros and cons, market shares, user
- 15. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 experience and more. Then a survey questionnaire was used to also gather data to understand the importance or impacts of the mobile operating systems on user’s choices i.e. to go deep into users perspectives of the mobile OS and also using three classifications areas (social, education and business) to further categorize the users analyze the questionnaires to improve the research. Document review Document review was used in this research to gather secondary data based on other researches and surveys done by many experts on the field of mobile computing. The use of secondary data research methods for this research is due to the nature of the research which talks about the a comprehensive analysis of the four main or most popular mobile operating system today, this includes software updates, design, features, usability, availability, etc. However most of this secondary data are available on the Internet such as tech websites published or updated constantly by tech experts, further conference papers and also textbooks too on mobile technologies are also key reliable resources in gathering the secondary data by reviewing this aforementioned document. The main analysis will be done in the next chapter with document review checklists. Questionnaires Using questionnaires has been very useful for collecting data in research from high number of people or participant, the adventive of utilizing the questionnaire method are cheap, easy and reliable to conduct. The respondents have time and they respond at there pace and liberty and individual records can be also utilized if required. The target for the questionnaires where basically mobile devices users and the users are classified into three categories: which are education, business and social users. Education is basically students or academic usage of the mobile OS, business users are basically business people who uses there mobile devices OS for mostly business purposes and finally social users which are users which uses the OS mostly and social purposes such as entertainment and social medias. There are well-defined processes for distributing and getting feedbacks from respondents such as face-to-face, post, Internet and telephone (Blaxter, Hughes, and Tight, 2006)
- 16. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 However, the questionnaires where sent via social medias such as Facebook and email participants responded online as this method is robust and can go global and poses a fast response. The purpose of carrying out this method of questionnaires is to improve my research and find out which one of these four major mobile device OS most used and suits which class of users identified or classified as social, education and business user. 129 questionnaires were distributed randomly by the author to participants, which are people of different age, race, background, nationality, location and occupation all of which are using mobile devices OS. Data analysis methods All the data gathered in this research would be analyzed utilizing a combination of qualitative and quantitative methodology of research. The process of data analysis commenced after managing the data collection to ensure that the research is on the correct track and reaffirms the final result. The advantage of the data analysis is to aid the researcher in getting the comparison of the four-major mobile OS. “Furthermore, as mush student research will contain quantitative feature as well as qualitative feature, especially in the fields concerned with practical application of ideas, both types of data are required” (Sharp, Peter, and Howard, 2002). The use of both qualitative and quantitative data analysis is employed to analyze data from the documents reviewed and questionnaires. Quantitative data analysis This data analysis method known as quantitative data analysis is utilized in the research to analyze the data collected using the questionnaire. The process of quantitative data analysis is carried out using a statistical technique, such as the Microsoft excel to aid analyzing and further represent the information. The method is utilized because of its easy, accuracy and precise mode; responses needs to be properly counted and the expected outcome can be statistical or in a graphical form. The relations and interdependence between the statistical outcomes can be seen using the quantitative data analysis. Qualitative data analysis
- 17. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 The Qualitative data analysis is used to analyze all the secondary data in the research. i.e. the document reviewed the vital goal Qualitative data analysis is to authorize the research outcomes to develop from the recurrent, principal themes inherent in raw data, exclusive of the restraints required to use structural hypothetical emphasis. Also qualitative data analysis method is an iterative process. Meaning that data gathering, processing, reporting and analyzing are entangled. Qualitative research involves vital process of going back again to the original field of study to gather extra data (Maree, 2007). The Qualitative data analysis will be used to analyze all the information gotten from the questionnaires respondents; this is done by analysis and justifications. Limitations of the research Every research has its limitations; this research is not an exception to that, however there are many limitations and obstacles identified in the research process from the start to finish, one of which is limited time, time is a limitation as the research should be completed in one semester, more also there are no research assistance this simply means that the researchers have to carry out all task including data gathering alone without an aid and this process is indeed time consuming. Further it was also noticed that some of the respondents are not fast in responding to the questionnaires due to one reason or the other such as being busy with other things, as a result the researcher has to constantly remind and persuade them to respond as soon as possible. However, some of the respondents were negative and unserious and this is time consuming and it significantly affected the data gathering and analysis process. Ethical consideration An ethical issue in all forms of research occurs, tensions always arise between the goals of the research and the vital confidentiality of all the participants. As a result the ethical consideration attempts to prevent harm to the individual participants, employing appropriate ethical principles can stop or reduce any harm, which arises. However, the safety of the participant is critical and also essential. (Orb, Eisenhauer. and Wynaden. 2001) There was an ethical endorsement obtained in the process before the questionnaires were distributed. Conclusion This chapter articulates all the suitable methodologies of the research and necessary techniques involved to gather and analyze data. All the appropriate approaches were properly discussed
- 18. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 for the successful completion of the research. Further the limitations encountered in the studies were also discussed. The following chapter of the research proposes the analysis of the whole data gathered in the research. Fist the document review was done based on some articulated checklists, using reliable resources such as textbooks, conference papers, journals and articles, and they are properly referenced using the approved Harvard referencing format. The checklists are Below: Checklists Types of data Source of data Method of data collection Method of data analysis Classifications of mobile operating system Secondary data (Cromar and Aviram, p7, p8 2010) Document reviewing Content analysis History and development for each OS Secondary data (Woods. 2013) (Chen, et al. 2011) (The Verge, 2013) Document review Content analysis Market shares of each OS Secondary data Document review Content analysis Pros and Cons of each OS Secondary data (Chandos, et al. 2012) Document review Content analysis Comparisons of general features design and functions Secondary data (Cromar, et al. and Aviram, et al. p19, 2010) Document review Content analysis Cognitive load Secondary data (Pfeiffer report. 2013) Document review Content analysis Efficiency and integration Secondary data (Pfeiffer report. 2013) Document review Content analysis Customization Secondary data (Pfeiffer report. 2013) Document review Content analysis
- 19. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 User experience friction (UEF) Secondary data (Pfeiffer report. 2013) Document review Content analysis Prospective future of each OS Secondary data (Pfeiffer report. 2013) Document review Content analysis Investigation into mobile operating system What is a mobile operating system? Based on the past chapter the literature reviews the general meaning, characteristics and features of mobile OS was comprehensively discuss in details to give a clear understanding of the mobile OS, this chapter goes further into the main operating system’s classifications and this classifications will be also discussed in this chapter which will lead to the main focus of the report on the four major mobile OS. The smartphone operating systems come in three different forms: • Proprietary, • Licensable • Open source. Mobile devices manufacturing companies tactically select which operating system model to follow based on their fundamental strengths, (Cromar and Aviram, p7, 2010) 1. Proprietary operating systems are developed internally by smartphone manufacturers that manages the whole device system development, manufacturers such as Apple, RIM, and HP/Palm all take this methodology with their own operating systems individually. Basically “the proprietary approach gives the manufacturer a potential competitive edge over rivals as it allows the manufacturer to differentiate their smartphones from any others. It also allows them to more tightly integrate the function of the OS and the hardware of the phone. All this comes at a high cost, as the software development is time consuming and expensive”. (Cromar and Aviram, p7, 2010) 2. The licensable operating systems allow any manufacturer to use the OS for a device they manufacture. Microsoft makes the most popular of such OS’s with Windows
- 20. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 Mobile and the recent Windows Phone 7, (which is an upgrade) operating systems. The licensable operating systems are largely used with a manufacturer’s unique hardware, though some customization is available. Smartphone manufacturers select a licensable OS because of the reduced costs of developing an operating system, although licensing can also be expensive. The gain is being able to take advantage of an existing ecosystem of the operating system’s users who are accustomed with the OS, and who possibly have invested money into software applications, by buying the apps in the store, that only run on that OS. Moreover, Microsoft provides well-established tools for development of additional software for the OS. “Differentiation is more difficult with this approach though, and mainly comes in the form of unique hardware, or proprietary software applications that the manufacturers develop and then put on the phone with the licensable operating system”. (Cromar and Aviram, p7, 2010) 3. The open source operating systems give the smartphone manufacturer access to an existing operating system that is free, and freely customizable. The most popular open source operating system is the Google’s Android, but others include Symbian OS and MeeGo. Android was released as open source by Google under a license that allows everyone to take the OS and use it in any way, included adding proprietary enhancements, exclusive of contributing those enhancements back to the open source operating system. “This allows smartphone manufacturers to use the Android as a highly developed starting point for their smartphone OS, at no cost, and build off of it. This openness has made Android highly popular among smartphone manufacturers”. (Cromar and Aviram, p8, 2010) A mobile operating system reflects the lifestyle of a smartphone user because it determines the choice of apps, the phone’s functionality and the general usability of any smartphone. The most important software in any smartphone is its operating system (OS). “An operating system manages the hardware and software resources of a smartphone”. Some operating systems platforms cover the complete collection of the software stack. While others may only include the lower levels (typically the kernel and middleware layers) and rely on additional software platforms to provide a user interface framework, or AEE. The well-known smartphone
- 21. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 operating systems are listed below i.e. the mobile market is fragmented amongst the following software platforms OS: 1. Google’s Android OS 2. IPhone OS 3. Windows Mobile or Windows phone OS 4. RIM’s BlackBerry OS 5. Symbian OS 6. Palm’s WebOS 7. Linux OS 8. Tizen OS 9. Meego OS. etc. (Coustan and Strickland, p3, 2008) This chapter of the report investigates the four most popular operating systems in today’s world, which are Google’s android operating system, Apple’s IOS, RIM’s BlackBerry operating system and Microsoft’s Windows Phone operating systems. The mobile technology market has grown in such a way that it is now difficult sometimes for consumers to make choices on which mobile device to buy based on the particular OS powering such device, however the case is quite different when selecting a laptop or PC, ones decision lies principally between 2 OS’s which are Windows OS powered PC or Mac OS X powered PC. But choosing between the multitude mobile devices is trickier due to the range of OS’s to pick from.
- 22. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 COMPARISONS Multitasking Full multitasking Limited Full multitasking No Background Notifications Yes Yes Yes Yes App folder Yes Yes Yes No Tethering Yes Yes TBD No VoIP Yes, with third party app Yes, with third party app TBD Yes, with third party app Gaming Yes Yes Yes Yes Flash support Yes No Yes Yes Number of apps 380,000+ 500,000+ 43,000+ 120,000+ Voice commands Yes Yes Yes Yes Mass storage Yes No Yes Yes Universal search Yes Yes Yes No Music store Google play music ITunes Zune BBM Music Web browser Chrome/Web kit Safari/Webkit Internet explorer /trident Not yet
- 23. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 Copy - paste Yes Yes Yes Yes Pinch and zoom multi-touch Yes Yes Yes Yes Video calling Yes No/Optional Yes Yes Face detector Yes Yes No No Bluetooth Yes Yes Yes Yes 4G network Yes Yes Yes No Market share 2011 Q4 USA 46% 30% 6% 15% Parental control Yes Yes Yes Yes Popular smartphones Samsung S4, HTC one X, Galaxy nexus Iphone5s Iphone4 Nokia Lumia 920 Samsung Omnia LG Optimus 7 Blackberry Torch, Blackberry Q10 User interface Icon and widget base Icon-base Tile-based (Metro UI) Tile-based GPS Navigation Via applications Yes, free GPRS Navigation included. Via applications Via application Application store Play App store Windows phone marketplace App world Developer Android Apple Microsoft RIM View Word, Excel, PowerPoint Attachments Yes Yes Yes Yes Email – Exchange, POP, IMAP Yes Yes Yes Yes Jail breaking and rooting Yes Yes Yes No
- 24. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 Syncing software Yes Yes Yes Yes Video recording Yes Yes Yes Yes Text input On screen software keyboard On screen software keyboard On screen software keyboard On screen or button software keyboard SIM card Size Optional Micro-Simcard Standard Standard SDK Available Yes Yes Yes Yes SDK Language Android (JAVA derivative) COCOA (Objective C) .NET framework (Visual C++, C# etc.) Java ME, Blackberry specific APIs Number of users 800Million 300Million 45Million 60+million Screen display HD Super Amoled HD Retina display HD WLCD HD LCD Device sizes Optional Standard Optional Standard
- 25. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 The future of each of the operating systems: What's next for iOS? In the six years since iOS was unveiled, we've seen the conversation move from "Is this a true smartphone?" to "Can this replace a computer?" That change is a testament not just to the march of technological progress, but also to Apple's ability to reinvent its operating system over the years. The progression of iOS has been a steady drumbeat of new features that often felt inevitable. Apps, multitasking, and even cut, copy, and paste all seemed to have come late to the game compared to the competition, but in each case Apple took its time to ensure that the solution it offered matched its own high standards and was designed for future growth. That has brought us to a point where future feature improvements aren't as dramatically clear as they used to be. (The Verge, 2013) Despite a comprehensive visual overhaul, iOS 7 has done little to address how we interface with our smartphones. Once again it checks a few boxes, tacking on useful features like Control Center and AirDrop, but it essentially offers the same basic home screen and app switching experience that’s been the hallmark of iOS for some time now. Meanwhile, Windows Phone has shown a different way of thinking about how a mobile operating system can work and Google’s sharing features and widget support make Android arguably a more elegant experience than what Apple is offering. To suggest that companies other than Apple are bringing more innovation into the UI space was once a strange thing, but the truth is that we’ve reached the point where iOS is part of the old guard of mobile operating systems at least from a user-experience perspective. With the visual redesign mostly out of the way, Jony Ive is now free to rewrite the book on how we interface with our smartphones. In recent years, Apple hasn’t rushed to market with fresh software ideas, instead preferring to take as much time as it feels necessary before unveiling any big changes. Whatever the future may hold, Apple’s willingness to throw out a tried-and-tested design at least gives us hope that broader changes may be on their way. (The Verge, 2013)
- 26. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 Future of android If you thought Android OS was just for smartphones and tablets, you’re in for a surprise. The use of the OS in other embedded systems and devices such watches, TVs, cameras etc. is growing exponentially, and it’s all because of the many benefits Android has to offer. To put it plainly, the developer community is using Android for embedded projects due to its flexibility, ease of customization, and compatibility. (Techsenser.com, 2013) The prospective future of android OS is very bright as foreseen by tech analysts; some of the futuristic expected technological innovations are described below. Bendable devices (smartphones and tablets): We have been hearing about bendable phones for a few years, but it is only a matter of time before a consumer priced model is released. Samsung is rumored to already be developing the first bendable phone for consumers, and we will probably see it sooner than many expect. Along with bendable screens, we will continue to see innovation in what we consider a mobile device. Google Glass is already changing what it means to have the cutting edge in phone screens; even though Google Glass’s screen is a fraction of the size of a traditional phone screen (it is less than an inch in height) it gives us a more integrated viewing experience than anything else on the market. (Techsenser.com, 2013) Maps will show us the world in real-time: Google’s Maps application will eventually allow us to see far more than just real-time traffic updates. Google is already reporting that there will be an increasing amount of personalization in what Maps shows us as early as this year. In addition, Google’s Street View is going to becoming radically different. Google is already in talks with the owners of cameras in many cities and buildings, and the eventual goal is to give users the ability to see what is going on at a specific store or intersection from anywhere in the world. Wearable and interconnected technology: Google Glass is only the first step in making everything in our lives digitally connected. Digital watches, home security systems, washers/dryers, etc. will eventually all be controlled through
- 27. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 our mobile devices. As these devices become more and more connected, users will be able to exert greater control over their lives. Before too long, all of us will have what equates to a digital personal assistant, who makes sure our homes are heated or cooled before we arrive, and makes sure we get to our appointments on time thanks to real-time traffic data. (Techsenser.com, 2013) Android devices sales have surpassed the hugely successful Apple iPhone in the US. The story is similar worldwide as releases like the Samsung galaxy series of phones, HTC one series, LG etc. are flying off the shelves. A number of analysts expect the Android OS to claim a dominant position in the market over the next few years, however, with new versions of iOS for the iPhone and a big overhaul of the Windows phone and Blackberry platform on the horizon they can’t afford to rest on their laurels. Right now the Android OS is tough to beat and it is a pleasure to use. With the number of big companies throwing their weight behind the platform the future looks very bright indeed for the android system. (Hill, et al. 2011). Blackberry OS. The blackberry platform is going through a transition BlackBerry is aiming to reclaim its spot as an innovator in a world where mobile devices already have the processing power to replace laptops and desktop PCs. Despite a number of glowing reviews for the BB10 and reports of strong initial sales, however, some analysts and technology pundits are skeptical about BlackBerry's chances of mounting a comeback, doubting its ability to sell either enough smartphones or manage to transform the way people work. (Reuters, 2014) "The Street cares about how many units of these (devices) they're going to sell and that is the balancing act," said John Jackson, an industry analyst at consulting firm IDC. Jackson said he can see a future in which the BlackBerry 10 operating system will allow users to control a vast array of devices, but added: "They need to sell devices to keep the lights on while they transform themselves into a next-generation computing platform." BlackBerry's marketing head, Frank Boulben, said the company is moving quickly enough to do just that.
- 28. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 "The vision is going to start to materialize this year," he said. "You will be able to plug the (Z10) device into a docking station at the office and then all you need is a keyboard, a mouse and a screen. Combined with cloud services this would mean you don't need a laptop or a desktop." (Reuters, 2014) The company in recent times professes to do more than just mobile devices, blackberry claims to offer strong enterprise services and says it will propagate its BBM (Blackberry Messenger) to other platforms including Android, windows phone and iOS. It also promotes a form of (limited) compatibility for (some) Android apps on its newer devices platform. Hopping that these moves will once again reassure their customers and attract new one into buying and in numbers that can save the company. (Gassée, et al. 2013) Windows Phone OS There are lots of prospects for the WP OS according to analyst one which is creating awhole new windows ecosystem for all their devices, Windows Phone runs on ARM. Windows RT runs on ARM. Both use the NT core. And Microsoft is working to unify the programming interfaces, frameworks and dev tools across these platforms. Though there isn't (yet) a common Windows Store for Windows Phone and Windows RT, there's no reason this will always be the case. According to the new Microsoft OS division chief Terry Myerson "We really should have one silicon interface for all of our devices. We should have one set of developer APIs on all of our devices. And all of the apps we bring to end users should be available on all of our devices," he said. So this looks to be a future convergence of all the Microsoft devices as we are seeing in the likes of iOS and Android OS i.e. the desktop PCs and mobile devices can share the same apps, interface and more. (Foley et al., 2013) Some of the features and enhancement consumers should be looking forward to in the future are that Microsoft would be lowering the hardware requirements for Windows phone OS, to 512 Mb RAM and 4 GB storage, and are making sure the OS works on existing Android hardware, to make it easier for OEMs to license and use. Microsoft also announced Dual-SIM support for the OS.
- 29. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 Microsoft also announced that it would now be simpler for OEMs to turn a Qualcomm reference design into a Windows Phone heading for shelves. OEMs will be able to get support from the Windows Phone Hardware Partner Portal. Microsoft expects to see white label Windows Phones in the future. Microsoft formally announced the addition of Lenovo, ZTE, Xolo, Karbonn, LG and Foxconn to HTC, Nokia, Samsung and Huawei. (WMPoweruser, 2014) Conclusion One of the key differentiation points between smartphones is the operating system they run. Popular operating systems include Apple’s iOS, Google’s Android and Microsoft’s Windows Phone but other operating systems such as BlackBerry OS, Nokia's Symbian and Samsung’s Bada also exist. For better usability of the key functionalities of each smartphone, the cellphones are evolving to allow easier texting, Web surfing, GPS navigation, and social networking, voice calling etc. while keeping up with the day-to-day activities. Smartphones such as the Android and iPhone- based models are leading the charge in today’s smartphone market. According to the report by Salvador Rodriguez in 2012, Thanks to their computer-like operating systems, the devices can run all types of applications, from Twitter to games, restaurant guides, shopping assistants, and more. The functionality of the smartphone is a great determining factor in choosing the operating system and the smartphone itself. The research gathered on each of the operating system suggest that the Windows and Blackberry phones have a strong focus on business, and therefore they are often considered to have a target audience that is more business focused. However the iPhone an Android phones conversely are much more targeted to casual users and have a much more socially based focus, although business apps can be installed as needed by the user. Based on the research carried out and all the resources gathered, the four operating systems can virtually do the basic things needed for a smartphone to do, they have there strengths and weakness, but the difference is how they handle each task, android can handle many applications running seamlessly at the same time, (multitasking) but the rest of the other OS’s has some limitation in multitasking, the iPhone and windows phone are the simplest in
- 30. A critical analysis and comparison of major mobile operating systems and a user classification of each major OS 2014 usability, of all the operating systems because it is easy to navigate. While the Blackberry has the best email and multimedia messaging system, in the end “Technology drives our society today, and from my point of view, there's always something better or something to improve upon”.