Scrum Refresher
- 1. Scrum Refresher Agile – Process – Values – Responsibilities – Tips along the way 1
- 3. Scrum is one of the flavors Kanban Extreme Programming (XP)
- 4. Agile Self organized cross-functional teams More effective More committed 5
- 5. Motivation ● Autonomy ○ Organizing my own work ● Mastery ○ Becoming better at my work ● Purpose ○ Making a contribution 6
- 6. Scrum Values
- 8. Product backlog ● Product backlog items (PBI) ● Clear acceptance criteria ● Specifications ● Mockups ● Architecture needs ● Sized appropriately ● Should fit in a Sprint – Together with a few more PBI 9
- 9. Product Backlog Item ● Feature Definitions ● Constraints ● Behaviors ● User action or stories ● Bugs/Defects ● Use cases ● Desires ● Non-functional/requirements (max execution time) 10
- 10. User story template As a user I want to see
- 11. Sprint ● No such thing as “Sprint Zero” ● No testing, hardening, release, analysis Sprint ● Pause in between Sprints, Spike for “Testing new ideas” ● Technical Spike – The technical spike is used more often for evaluating the impact new technology has on the current implementation that the team needs experiment a new technology to gain more confident for a desired approach before committing new functionality to a timebox. ○ i.e. “how long it takes to update a customer display to current usage, determining communication requirements, bandwidth, and whether to push or pull the data” ● Functional Spike – A functional spike are used whenever there is significant uncertainty as to how a user might interact with the system. Functional spikes are often best evaluated through some level of prototyping, whether it be user interface mockups, wireframes, page flows, or whatever techniques is best suited to get feedback from the customer or stakeholders., ○ i.e. “Prototype a histogram in the web portal and get some user feedback on presentation size, style, and charting” 12
- 12. Sprint planning ● Top of the product backlog, ready for sprint ● Sprint planning start of sprint ○ Part 1 - What are the requirements? PO required ○ Part 2 - How? PO optional ● All estimates are from the development team 13
- 13. Sprint goal Example: ● Deliver a minimal set of administration features 14
- 14. Sprint backlog Forecast Sprint goal Sprint plan ● Tasks ● Tests ● Estimates 15
- 15. Sprint backlog Each item less than 8h Break down details Adapted by the dev team throughout the Sprint Updated at least daily 16
- 16. Sprint backlog Any time during the Sprint: Update Sprint backlog Detail each task - Decompose 17
- 17. Daily Scrum ● Implement your own technique as long as it is collaborative ● What is your work for the day to meet the Sprint goal? ● Any impediments to reach that goal 18
- 18. Increments ●What? ○ “Potentially Releasable Product Increment” ●When? ○ At least once each Sprint 19
- 19. ● Inspect the increment ● PO gather feedback from stakeholder ● PO makes sure you are on track with regards to goals ● PO is involved ● Member of dev team does demo ● Gather feedback Sprint Review 20
- 20. Sprint Retrospective ● Team retrospect's itself and its behaviors. What worked well? What could be improved? What will we commit to doing in the next Sprint? 21
- 22. Definition of Done Each organization has their own definition "Unit test covers 80% of the code” "No more than 10% critical tickets” The development team conforms to Definition of Done. 23
- 23. Refinement ● Refinement by PO and dev team any time during the Sprint not more than 10% of the Sprint time. 24
- 25. Technical debt ● PO working closely to the team ○ Notice technical debt Technical debt ○ Low quality ○ Slow production Include minor technical debt payment each Sprint 26
- 26. Scrum Roles and Responsibilities 27
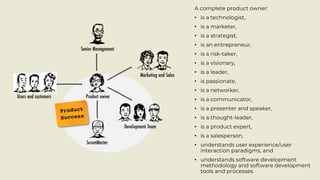
- 28. A complete product owner: • is a technologist, • is a marketer, • is a strategist, • is an entrepreneur, • is a risk-taker, • is a visionary, • is a leader, • is passionate, • is a networker, • is a communicator, • is a presenter and speaker, • is a thought-leader, • is a product expert, • is a salesperson, • understands user experience/user interaction paradigms, and • understands software development methodology and software development tools and processes.
- 29. Scrum Master
- 30. Responsibilities: Scrum Master • Ensures Scrum is understood and enacted • Removing impediments
- 31. Development Team
- 32. Responsibilities: Dev team • Create “Done” increment • In charge of quality of the increment
- 33. Every role has clear accountability ● Scrum implements empiricism in product development ● The scrum artefacts provide transparent information ● The scrum events serve ○ Transparency, ○ Inspection and ○ Adaptation 35
- 34. Nexus Framework Multiple scrum teams (3-9) sharing the same backlog Minimize horizontal dependencies Reorder backlog to reduce dependencies 36
- 35. 😆