Actin and myosin
- 1. 100’s of free ppt’s from www.pptpoint.com library
- 2. actin and myosin dr shabeel pn www.hi-dentfinishingschool.blogspot.com
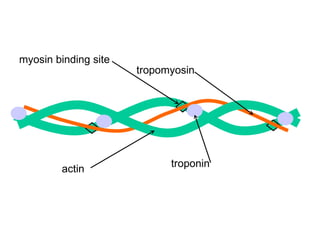
- 3. actin
- 7. actin troponin tropomyosin myosin binding site
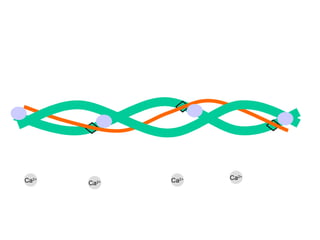
- 9. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+
- 10. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Calcium ions are released from the sarcolemma after stimulation from the T system
- 11. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+
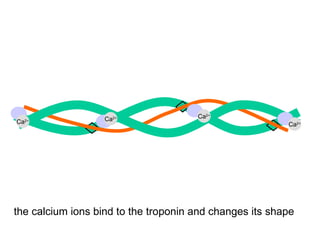
- 12. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ the calcium ions bind to the troponin and changes its shape
- 13. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ the calcium ions bind to the troponin and changes its shape
- 14. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+
- 15. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+
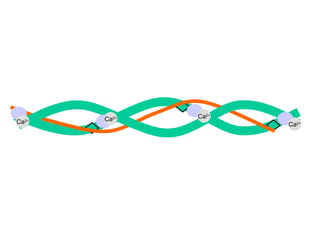
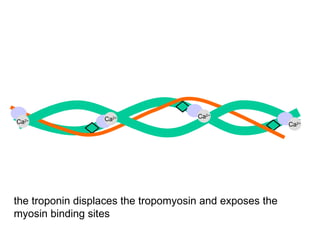
- 16. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ the troponin displaces the tropomyosin and exposes the myosin binding sites
- 17. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+
- 18. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+
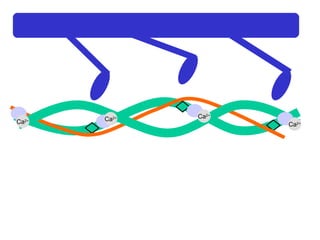
- 19. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ the bulbous heads of the myosin attach to the binding sites on the actin filaments
- 20. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+
- 21. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+
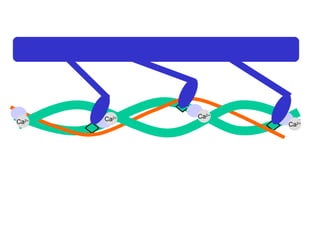
- 22. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ the myosin heads change position to achieve a lower energy state and slide the actin filaments past the stationary myosin
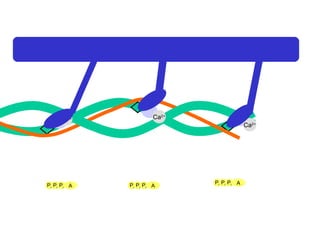
- 23. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i
- 24. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i
- 25. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ ATP binds to the bulbous heads and causes it to become detached A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i
- 26. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ ATP binds to the bulbous heads and causes it to become detached A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i
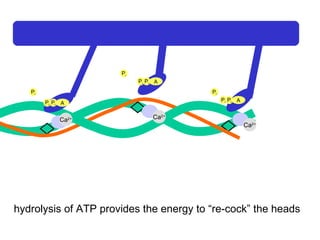
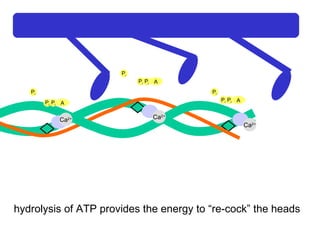
- 27. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i hydrolysis of ATP provides the energy to “re-cock” the heads
- 28. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i hydrolysis of ATP provides the energy to “re-cock” the heads
- 29. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i
- 30. Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i calcium ions are re-absorbed back into the T system
- 31. Ca 2+ A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i calcium ions are re-absorbed back into the T system
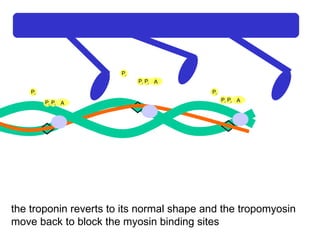
- 32. Ca 2+ A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i the troponin reverts to its normal shape and the tropomyosin move back to block the myosin binding sites
- 33. Ca 2+ A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i the troponin reverts to its normal shape and the tropomyosin move back to block the myosin binding sites
- 34. Ca 2+ A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i the troponin reverts to its normal shape and the tropomyosin move back to block the myosin binding sites
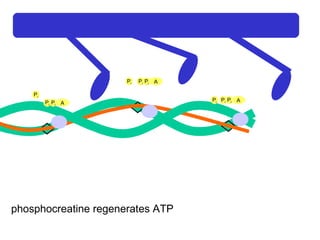
- 35. Ca 2+ A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i phosphocreatine regenerates ATP
- 36. Ca 2+ A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i phosphocreatine regenerates ATP
- 37. Ca 2+ A P i P i P i A P i P i P i A P i P i P i phosphocreatine regenerates ATP