Addictive and psychotropic drugs
- 2. A psychoactive drug,psychopharmaceutical, or psychotropic is a chemical substance that crosses the blood–brain barrier and acts primarily upon the central nervous system where it affects brain function, resulting in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, and beh avior Psychoactive drugs have therapeutic utility, e.g., as anesthetics, analgesics, or for the treatment of psychiatric disorders INTRODUCTION
- 3. HISTORY Psychotropic drugs have been used from prehistoric times Medicinal use is one of the important facet of psychoactive drug usage in ancient times The chewing of coca leaves, dates back over 8000 years ago has been found by archeologist while studying
- 4. Dr. Timothy Leary , Ralph Metzner, and Richard Alpert (Ram Dass) in the 1960s Dosage – some compounds are beneficial when consumed in small amounts, but harmful in higher doses Set – it is internal attitudes and constitution of a person including their wishes, fears and expectation Setting – it pertains to the surroundings, the place, and the time in which experiences transpire
- 5. Commonly Used Psychotropic Drugs And Its Group Anxiolytics (inhibits anxiety) - Benzodiazepine Euphoriants (induces relaxation) - MDMA , MDA, Indopan Stimulants - amphetamine, caffeine, cocaine, nicotine Depressants - alcoholic beverages (ethanol), opioids, barbiturates, benzodiazepines Hallucinogens - LSD and nitrous oxide
- 6. PSYCHIATRIC MEDICATION Psychiatric medications are psychoactive drugs prescribed for the management of mental and emotional disorders There are six major classes of psychiatric medications : Antidepressant – clinical depression, anxiety, eating disorders Stimulants – attention deficit disorder, suppress the appetite Antipsyhotics – schizophrenia, severe mania Mood stabilizers – bipolar disorder Anxiolytics – anexiety disorder Depressent – hynotics, sedatives, anaesthetics
- 7. ANESTHESIA – It is a class of psychotropic drugs used on patients to block pain and other sensations. Most anesthetics induce unconsciousness, which allows patients to undergo medical procedures like surgery without physical pain or emotional trauma induce unconsciousness, anesthetics affect the GABA and NMDA systems. For example, halothane is a GABA agonist, and ketamine an NMDA receptor antagonist PAIN MANAGEMENT- Psychoactive drugs are often prescribed to manage pain. The subjective experience of pain is primarily regulated by endogenous opiod peptides. Thus, pain can often be managed using psychoactives that operate on this neurotransmitter system, also known as opiod receptor agonist. This class of drugs can be highly addictive, and includes opiate narcotics, like morphine and codeine. USES
- 8. MILITARY Psychotropic drugs have been used in military as non- lethal weapon In World War II 60 million amphetamine pills were used by soldiers Brown-brown, a form of cocaine adulterated with gun powder, has been used in Sierra Leone Civil War Both military and civilian American intelligence officials are know to use psychotropic drugs for there interrogation with captives
- 9. Administration For a substance to be psychotropic it must clear the blood-brain barrier so it can affect neurochemical function. Certain drugs such as alcohol and caffeine are ingested in beverages form. Nicotine and cannabis are often smoked Crystalline drugs like cocaine and methamphetamines are often insufflated (inhaled or ”snorted”) Medicines such as lorazepam is ingested orally in tablet form or capsule form The efficiency of each method of administration varies from drug to drug
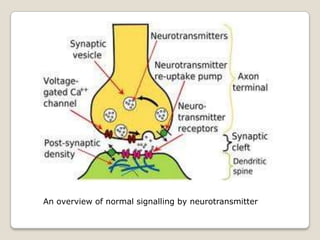
- 10. EFFECTS It affects a person’s neurochemistry, which in turn causes a change in person’s mood, cognition, perception and behaviour. Agonist - Increase the synthesis of one or more neurotransmitter, by reducing it’s reuptake from synapses, or by mimicking the action by binding directly to the postsynaptic receptor. Antagonist – operate by interfering with synthesis or blocking postsynaptic receptors so that neurotransmitters cannot bind to them.
- 11. An overview of normal signalling by neurotransmitter
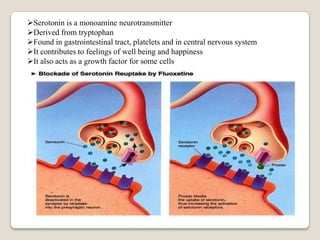
- 12. Serotonin is a monoamine neurotransmitter Derived from tryptophan Found in gastrointestinal tract, platelets and in central nervous system It contributes to feelings of well being and happiness It also acts as a growth factor for some cells
- 13. ADDICTION It is of two types :- Psychological Addiction – by which a user feels compelled to use a drug despite negative physical or societal consequences Physical Dependence – by which a user must use a drug to avoid physically uncomfortable or even medically harmful withdrawal symptoms Drugs that are most likely to cause addiction are drugs that directly stimulate the dopaminergic system, like cocaine and amphetamines Drugs that only indirectly stimulate the dopaminergic system, such as psychedelics, are not as likely to be addictive
- 14. LEGALITY The legality of psychoactive drugs has been controversial The most influential document regarding the legality of psychoactive drugs is the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, an international treaty signed in 1961 as an Act of the United Nations It is signed by 73 nations including United States, USSR, India and United Kingdom It established the legality of each drug and laid out an international agreement to fight addiction to recreational drugs by combatting the sale, trafficking, and use of scheduled drugs In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has authority over all drugs, including psychoactive drugs Psychotropic drugs are only given with a prescription However, certain psychoactive drugs, like alcohol, tobacco, and drugs listed in the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs are subject to criminal laws
- 15. Thank you !!