Adopting Wiki at UCF
- 1. Presented by: Dr. Baiyun Chen John Raible Debbie L. Kirkley
- 2. Agenda Introduction Social Constructivism Diffusion of Innovations Implementation at UCF Wiki Research Lessons Learned/Pilot Study
- 3. University of Central Florida Established, June 1963 One of Florida’s 11 public universities Fall 2007 Enrollment: 48,699 Metropolitan university with 11 regional campuses Located East of Orlando
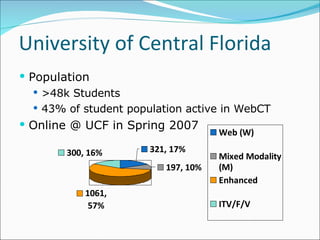
- 4. University of Central Florida Population >48k Students 43% of student population active in WebCT Online @ UCF in Spring 2007
- 5. Web 2.0 and Beyond Web 2.0 is a “World Wide Web technology and web design that aims to facilitate creativity, information sharing, and, most notably, collaboration among users. These concepts have led to the development and evolution of web-based communities and hosted services, such as social-networking sites, wikis, blogs, and folksonomies ” Wikipedia, 2008
- 7. “ Knowledge is the result of social interaction and language usage, and thus is a shared, rather than an individual, experience.” (Dolittle, 1999) Looking at Web 2.0 for pedagogical implications, we concluded that Web 2.0 embodies constructivism theory. Theory Practice Social Constructivism
- 8. Social Constructivism Wheeler, Kelly, & Gale(2005) suggest 'transparent technologies' let the user concentrate more on the learning task by 'seeing through' the technology with which they are interacting. The focus of these technologies is the user, especially in the aspects of content generation and usability.
- 9. Social Constructivism Problem-based learning Learner-centeredness Collaborative learning Social presence Interactivity Support Cognitive tools Active learner
- 10. Social Constructivism Constructivist learning should engage students in meaningful learning: Active and manipulative Constructive and Reflective Intentional Authentic, Challenging and Real World Cooperative, collaborative, and conversational
- 12. -- Process by which an innovation -- is communicated through certain channels -- over time -- among members of a social system . Everett Rogers (1995) Diffusion
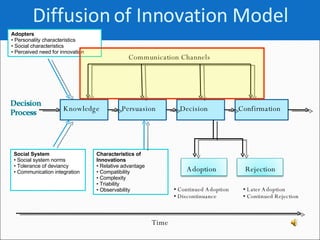
- 13. Diffusion of Innovation Model Communication Channels Characteristics of Innovations Relative advantage Compatibility Complexity Triability Observability Later Adoption Continued Rejection Continued Adoption Discontinuance Time Knowledge Persuasion Decision Confirmation Adoption Rejection Adopters Personality characteristics Social characteristics Perceived need for innovation Social System Social system norms Tolerance of deviancy Communication integration
- 14. Diffusion of Innovation Model Communication Channels Characteristics of Innovations Relative advantage Compatibility Complexity Triability Observability Later Adoption Continued Rejection Continued Adoption Discontinuance Time Knowledge Persuasion Decision Confirmation Adoption Rejection Adopters Personality characteristics Social characteristics Perceived need for innovation Social System Social system norms Tolerance of deviancy Communication integration
- 15. Diffusion of Innovation Model Communication Channels Characteristics of Innovations Relative advantage Compatibility Complexity Triability Observability Later Adoption Continued Rejection Continued Adoption Discontinuance Time Knowledge Persuasion Decision Confirmation Adoption Rejection Adopters Personality characteristics Social characteristics Perceived need for innovation Social System Social system norms Tolerance of deviancy Communication integration
- 16. Knowledge Persuasion Decision Implementation Confirmation Decision Process
- 17. Diffusion of Innovation Source: Rogers, 1995 Time Diffusion Process Early Adopters Take Off Late Adopters Cumulative Adoption
- 18. Diffusion of Innovation Model Communication Channels Characteristics of Innovations Relative advantage Compatibility Complexity Triability Observability Later Adoption Continued Rejection Continued Adoption Discontinuance Time Knowledge Persuasion Decision Confirmation Adoption Rejection Adopters Personality characteristics Social characteristics Perceived need for innovation Social System Social system norms Tolerance of deviancy Communication integration
- 19. Innovators / Leading edge: Experiment frequently with emerging innovations Leaders Adoption Levels of Technology
- 20. Early adopters: Uses advanced features in generally adopted innovations Adoption Levels of Technology
- 21. Early Majority / Mainstream: Uses generally adopted innovations proficiently on a regular basis Not prone to experimentation Adoption Levels of Technology
- 22. Late Majority / Reluctant : Skeptics Try to use generally adopted innovations but have problems using basic features Will use innovations or products only when the majority are using it Adoption Levels of Technology
- 23. Laggards /Avoiders : Love to hang onto the old ways Critical of new ideas Use technology as little as possible Will accept innovation only if it has become mainstream over a period of time Adoption Levels of Technology
- 24. Where do you fall on the adoption curve? Innovator Early Adopter Early Majority/ Mainstream user Late Majority Laggard/Avoider
- 25. Diffusion of Innovation Clip from “Reap The Wild Wind” (1942)
- 26. “ Just lookie at what Steve’s got….” “ Matches? Well, what are they for…” “ Goodness, gracious, …Mr. Tolliver” “ Do another one Steve….” “ Steve, you do get the quaintest things…” “ They’re terrifying!” “ They’ll never be popular, Tolliver, TOO DANGEROUS…”
- 27. According to Everett Rogers, the change agent: develops in others a need for change creates intent to change translates intent into action diagnoses problems stabilizes adoption and prevents discontinuance establishes information-exchange relationships shifts others from reliance on the change agent to self-reliance Change Agents
- 28. Motivations, Incentives, and Support required are different for each stage of adoption After early adopters, support increases dramatically Later stages involve large populations at various levels Differing needs and attitudes Applying Diffusion of Innovation
- 29. Ease of Use Pick-up fruit Low-hanging fruit Top-hanging fruit Implementation
- 30. Implementation Strategy Initial determination by the Instructional Innovations Incubator group Investigation of current research Development of possible strategies for use in higher education Initial testing (piloting)
- 31. Gathering of data Refinement of best practices Application on a programmatic level Ongoing evaluation Implementation Strategy cont.
- 32. Wiki Research Attitude surveys and usage statistics show positive feedback on collaborative benefits In-class research (Atteberry, 2006; Augar, Raitman, & Zhou, 2004; Socialtext, 2007) Systematic studies ( de Pedro et al., 2006a, 2006b; Sajjapanroj, Bonk, Lee, & Lin, 2006)
- 33. Research Question How to implement wiki as an instructional strategy for higher education?
- 34. Research Method Case studies - multiple cases Political Science Education Health Information Data collection Review wiki assignments Interviews Survey
- 35. Pilot Group Provided them with Faculty Instructions Setting up group wikis Inviting students to the groups Included face to face training within our faculty development course Provided them with basic Student Instructions How to access and login How to edit and add pages Provided them with model activities Consulted with faculty for their class needs
- 36. Themes from Interviews Advantages of using a wiki Issues of using a wiki Advice
- 37. Advantages Ease of collaboration Ease of use A channel to the outside community Richer contents
- 38. Issues Technical issues Collaboration issues
- 39. Advice from UCF Faculty Offer training sessions at beginning Clear expectations Wiki as an optional assessment tool
- 40. Conclusions & Future Research Active participation Collaborative benefits Recommendations for wiki strategy Future survey studies