Advertising models
- 2. Objectives of this session Are advertising models useful? Some possible ways of modelling advertising messages: AIDA DAGMAR or ‘Hierarchy of Effects’ DRIP VIPS DMP PLC Maslow MECCA or Means-End Chain
- 3. The AIDA Model A ttention Get noticed. I nterest What’s in it for me? Problem solving? D esire ‘ Want’ factor Brand A ction How do I get it?
- 5. The DAGMAR Model ( D efining A dvertising G oals for M easured A dvertising R esults) also known as ‘Hierarchy of Effects’ model
- 7. Ehrenburg Model (1997) Awareness Trial Reinforcement Nudging Let the customer know you exist (Doesn’t have to be just advertising) Curiosity (rather than ‘persuasion’) could lead to trial of product. Provide reassurance in brand. (Role suitable for advertising) Remind – reinforce - repeat purchase.
- 9. The DRIP Model D ifferentiate Be different from the competition R emind Who are we? What do we stand for? I nform What’s new? Features-Benefits P ersuade Why is it right for you?
- 11. David Bernstein’s VIPS checklist To be effective, an advertising message should be checked to see that it has the following qualities: V ISIBILITY I DENTITY P ROMISE S INGLEMINDEDNESS
- 13. The DMP Model (The Decision Making Process)
- 14. The DMP Model (Decision Making Process) 1.Recognition of need Remind or create perception of need? 2.Define parameters of need / solution We’ve got just the solution 3.Search for information Find out what we have to offer 4.Evaluation of alternatives Aren’t we better than the competition? 5.Determining terms of purchase We’re great value for money 6.Purchase It’s so easy to buy 7.Post-purchase evaluation You made the right decision! 8.Re-purchase? You are our valued customer
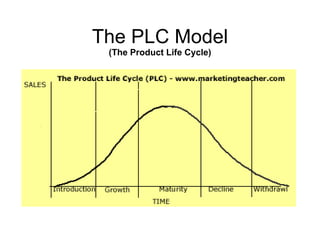
- 16. The PLC Model (The Product Life Cycle)
- 17. The PLC Model Pre-Launch Teaser campaign Introduction Launch campaign Growth Maximise sales Maturity Tactical campaigns Decline / Withdrawal Why advertise?
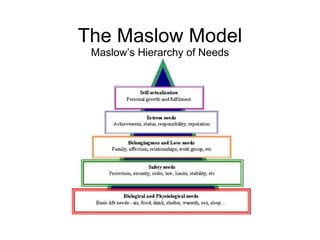
- 21. The Maslow Model Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
- 23. MECCAS M eans- E nd C onceptualisation of C omponents for A dvertising S trategy or Means-End Chain Theory Links product attributes to personally relevant values : Products Attributes / Features Consumer Benefits Leverage Points Memorable ‘hook’ which links benefits to consumer Personal Values What is relevant to this consumer Executional Framework Scenario used to convey message
- 25. Got Milk Means-End Chain Pleasure Fun Excitement Enhanced sexual ability Vitamins Happiness Pleasure Good taste Ingredients Wisdom Comfortable life Healthy bones Calcium Wisdom Self-Respect Healthy Low fat Values Benefits Features
- 26. Conclusion No-one knows why some ads work and others don’t No-one can predict for sure which ads will work and which ones will not Models should act a guide for structuring creativity – not a staightjacket