Age-Related_Eye_Conditions_Presentation.pptx
- 1. Age-Related Eye Conditions A Health Talk by Dr. Damaris Akhigbe (O.D, MNOA)
- 2. AGING IS A BLESSING
- 3. Introduction • The eye is a true wonder of creation and one of the most active organs in the body • Your eyes work actively for 16-18 hours everyday, all your life to ensure optimal vision • - WHO: 1 billion people with vision impairment • - Leading cause of blindness and visual impairment • Eye changes begin from age 40 and there is a need for regular comprehensive eye exams
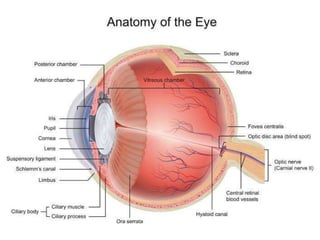
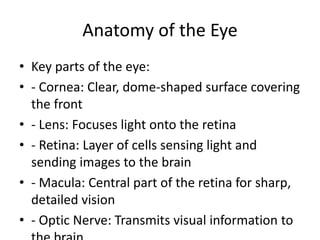
- 5. Anatomy of the Eye • Key parts of the eye: • - Cornea: Clear, dome-shaped surface covering the front • - Lens: Focuses light onto the retina • - Retina: Layer of cells sensing light and sending images to the brain • - Macula: Central part of the retina for sharp, detailed vision • - Optic Nerve: Transmits visual information to
- 6. Common Age-Related Eye Conditions • - Cataracts • - Glaucoma • - Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) • - Diabetic retinopathy • - Presbyopia
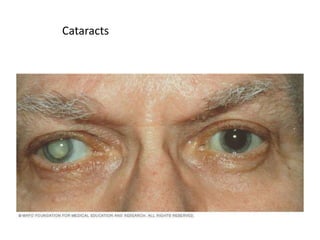
- 7. Cataracts
- 8. Cataracts • Definition: Clouding of the eye's lens • Symptoms: Blurry vision, faded colors, glare, halos, poor night vision • Risk factors: Age, diabetes, smoking, UV exposure, family history • Treatment: Surgery to replace lens • Prevention: Sunglasses, quit smoking, manage diabetes
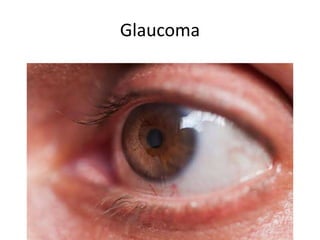
- 9. Glaucoma
- 10. Glaucoma • Definition: Damage to optic nerve often due to high pressure • Symptoms: Often asymptomatic early, peripheral vision loss • Types: Open-angle (common, slow), Angle- closure (sudden, emergency) • Risk factors: Age, family history, high eye pressure, smoking, ethnicity • Treatment: Medications, laser, surgery
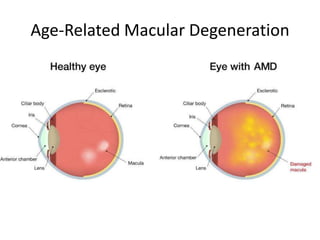
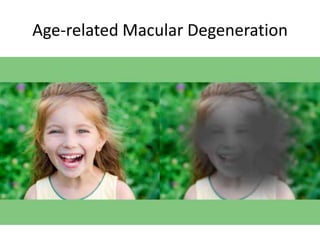
- 12. Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) • Definition: Affects macula, central vision loss • Symptoms: Blurred/reduced central vision, difficulty reading/recognizing faces • Types: Dry (common, slow), Wet (less common, rapid) • Risk factors: Age, smoking, alcohol, family history, high blood pressure, low antioxidants • Treatment: Wet - injections, laser; Dry - lifestyle, supplements • Prevention: Healthy diet, exercise, no smoking
- 15. Diabetic Retinopathy • Definition: Diabetes complication affecting retinal vessels • Symptoms: Often none early, blurry vision, floaters, dark areas, vision loss • Stages: Non-proliferative (early, fluid leaks), Proliferative (advanced, new vessels) • Risk factors: Poor sugar control, duration of diabetes, high blood pressure/cholesterol • Treatment: Laser, injections, surgery • Diabetes management: Control sugar, pressure, cholesterol
- 16. Presbyopia
- 17. Presbyopia • Definition: Age-related loss of close focus • Symptoms: Difficulty reading small print, holding material further away • Risk factors: Age (starts ~40) • Treatment: Reading glasses, bifocals, contacts, surgery • Adaptations: Adequate lighting, larger print, breaks
- 18. The 5 Age-Related eye conditions in order of severity: 1. Glaucoma 2. Diabetic retinopathy 3. Age related macula degeneration 4. Cataracts 5. Presbyopia
- 19. Preventive Measures • Regular eye exams (annually if you are over 40) • Healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, omega-3 (carrots, oranges, tomatoes, spinach, lettuce, fish,e.t.c) • Avoid harmful habits like smoking and alcohol • Manage chronic conditions (diabetes, hypertension) • Protect eyes from UV light (sunglasses, hats)
- 20. Living with Age-Related Eye Conditions
- 21. Living with Age-Related Eye Conditions • Adaptation tips: Magnifying devices, increased contrast/lighting, organize spaces • Resources: Low-vision specialists, rehab services, support groups • Family/community support importance
- 22. Your eyes do a lot for you, what are you doing for your eyes?
- 23. Thank You!