Agricultural Innovation and Social Inclusion
- 1. Agriculture Innovation and Social Inclusion Beatriz da Silveira Pinheiro The 2010 Global Hunger Index Release - Des Moines, October 2010
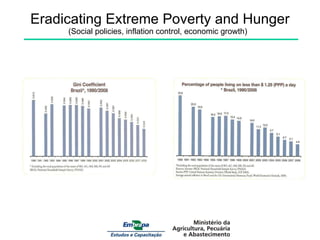
- 2. Eradicating Extreme Poverty and Hunger (Social policies, inflation control, economic growth)
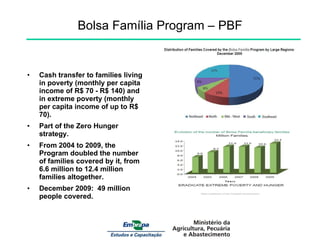
- 3. Bolsa Família Program – PBF Cash transfer to families living in poverty (monthly per capita income of R$ 70 - R$ 140) and in extreme poverty (monthly per capita income of up to R$ 70). Part of the Zero Hunger strategy. From 2004 to 2009, the Program doubled the number of families covered by it, from 6.6 million to 12.4 million families altogether. December 2009: 49 million people covered.
- 4. Decline in Child Mortality Improvements in income distribution, poverty reduction, and schooling of mothers; Changes in fertility patterns, with a significant reduction in the average number of children per woman; Health policies implemented by the Unified Health System –SUS, with emphasis on the health of women and children.
- 5. Harvested Area Growth: 27% = 1.3% / year Production Growth: 145% = 4.8% / year Source: CONAB. *Estimate: October/ 2009 Brazilian Agriculture – Grains (1991-2010*)
- 6. Source: ABIEC, ABEF, UBA and ABIPECS Beef : +73 % (94-08) Pork: + 128% (94-08) Broiler : + 212% (94-08) Brazilian Agriculture – Meat (1994-2008)
- 7. Martha Jr., data from Dieese (2010) Food Basket Real Prices, Jan/1975-Apr/2010
- 8. Innovation in Tropical Agriculture: Soybean Adapted to the Brazilian Savanah 1960 1975 2005 Source: National Company of Food Supply, 2008 2005 Fonte: MAPA 1975 1960
- 9. Agriculture innovation and smallhorder farmer
- 10. Biofortification: breeding micronutrient-rich varieties and post-harvest processing, for the main food staples in Brazil: cassava, sweet potato, rice, common beans, maize, wheat and cowpea. Agriculture innovation and nutritional value of crops
- 11. Ecological and economic zoning Best practices, integrated pest management, biological inputs . No-tillage, Integration of crop, livestock and forest systems. . Image VCP Agriculture innovation and sustainability Ulisses Silva J.A. araújo Filho Image VCP
- 12. Innovation in Agriculture: Economic and Social Impacts Inward development Increased Human Development Index Higher income, education, health, and jobs - Stable food supply - Lower basic food prices Increased agricultural exports trade surpluses, diminished financial vulnerability Novaes, P., unpublished .
- 13. Agriculture Innovation Social Inclusion Nutrition and Health Sustainability Productivity