Angel investor valuation
- 1. Angel Investor Valuation Eagle10 Ventures April 2020 Anjana Vivek
- 2. ... At the start Valuation: Methods Valuation: Focus Startup Valuation: Startup Examples Valuation: Summary To Trigger Thinking … 2 2
- 3. Reflection: You What motivated you to “Invest” as an Angel Investor? 3
- 4. Reflection: You A desire for: • Participating in the start-up ecosystem • Helping an Entrepreneur • Making Money/Name/Fame? • Other ? 4
- 5. Reflection: You TO • Participate in the start-up ecosystem • Help an Entrepreneur • Make Money/Name/Fame? • Something else ? Has this changed in the recent past.. Post lockdown ? 5
- 6. Reflection: You Is it … time to rethink and reset? 6
- 7. “To Trigger Thinking” Best Results when • When Personal Goals are Aligned with Group Goals for Investment 7
- 8. 8 Valuation : Startup At very early stage valuation is often a function of: • Amount of cash burn (with different scenarios of bootstrap and adequate funding) • Stake promoter is willing to give up
- 9. At the Start-up Stage Thoughts and Dreams of the Founders drive the business … Therefore • The Value (Focus) is MORE on the persons behind the venture and less on the business idea and market environment • The tangibles are limited and a valuation exercise attempts to capture the intangibles in numbers (eg. Premium quality may be indicated by a higher price per unit of sales) 9
- 10. At the Start-up Stage Founders may look at how they can tangiblise and demonstrate potential for success … to show value For example • Onboarding respected domain experts/ persons/ brands • Signing on potential customers, even better is getting cash into business from customers i.e. paying customers • Recommendations/referrals from highly regarded persons 10
- 11. At the Start-up Stage • Valuation for an investor is linked to future outcome and expected return on exit from investment • Investment should have potential for high return, which implies – the addressable market should be extraordinarily high PLUS – the founders must have the capability to grow this business PLUS – The founders must (appear to) have the drive and determination to grow this business – IN A POST COVID-19 WORLD: Investors will look at founders who reflect, reset and show resilience 11
- 12. 12 Valuation : Startup At early stage valuation is often a function of: • Amount of cash burn (with different scenarios of bootstrap and adequate funding) • Stake promoter is willing to give up AND factors such as • Value add expected from investor • Expected funds to be raised in future rounds, connecting this to future dilution expected to be made It would help if you can articulate and list what YOU & GROUP bring to the table
- 13. 13 Is valuation a Number? Conditions Post deal Build more tangiblesPrepare Create more value Negotiate/ bargain Before deal Math is ONE Element
- 14. Valuation: Startup to Exit.. Think thru
- 15. Value is connected to type of investor • HNIs, informal and formal angel groups • Seed Funds • Venture Capital • Private Equity • Banks exploring innovative ways to fund SMEs • Strategic Investors • Corporate Funds; (Family) Business Groups, Indian & Global – Directly and/or through a special division or subsidiary – For employees alone or open to public – As intellectual and/or financial capital with other facilities • Government supported funds • Impact Investors • Incubators • Accelerators • Co-Creators • Crowd funding • Online funding platforms 15
- 16. At the start … Valuation: Methods Valuation: Focus Startup Valuation: Startup Examples Valuation: Summary To Trigger Thinking … 16 16
- 17. 17 Valuation methods These can be broadly classified into: • Cost based • Income based • Market based
- 18. 18 Cost based methods There are different ways of arriving at cost: • Book value • Replacement value • Liquidation value NOTE These methods could become relevant when one is considering the accounting, legal and tax impacts of valuation, for eg. –in deals related to M&As, JVs and partnerships etc.. –in cross-border transactions, depending on countries involved
- 19. 19 Income Based methods • Earnings capitalisation method or profit earning capacity value method • Discounted cash flow method (DCF)
- 20. 20 INCOME: Earnings capitalisation method • Also called Profit earnings capacity value (PECV) • Value determined by capitalising earnings at a rate considered suitable • Assumed that the underlying value driver of the company is its future earnings potential • Suitable for fairly established business having predictable revenue and cost models • For example – Profittee Limited is earning post tax profit of Rs. 5 – It is capitalized at 10%. – Value of Profittee Limited is equal to Rs. (5/10%) crores, ie Rs. 50 crores.
- 21. 21 nt t t t r CF Value 1 )1( • CF = cash flow • t = the year and • r = discount rate i.e. the cash flow for each year from year 1 to year n (which is the time period under consideration) is discounted to arrive at the present value of future cash flows from year 1 to n INCOME: Discounted cash flow
- 22. 22 Market based method • Assumption is that other firms in industry are comparable to firm being valued • Standard parameters used like multiples of revenue, EBIDTA, PAT, book value • Other indicative parameters such as revenue per user, net margin per user etc. may also be calculated • At different times, different multiples are popular, for example GMV (gross merchandise value) for e- commerce businesses • Adjustments made for variances from standard firms or deals in the recent past, these can be negative or positive; i.e. premiums and discounts are assigned
- 23. 23 Exercise in Valuation - I ILLUSTRATIVE VALUATION EXERCISE REVENUE FORECAST USD Business Units Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Unit 1 12,00,000 24,00,000 48,00,000 72,00,000 1,08,00,000 Unit 2 12,00,000 24,00,000 48,00,000 57,60,000 69,12,000 Unit 3 8,00,000 16,00,000 32,00,000 38,40,000 46,08,000 Unit 4 8,00,000 16,00,000 32,00,000 38,40,000 46,08,000 Total 40,00,000 80,00,000 1,60,00,000 2,06,40,000 2,69,28,000 Profit margin, year 3 & year 5 respectively 20% 32,00,000 25% 67,32,000 VC Investment USD 20,00,000 Average Revenue Multiple 8 One Year Forward – Average of selected sample cos. Discounts for Liquidity 35% 2.8 Size 35% 2.8 Company 10% 0.8 Total Discount 80% 6.4 Revenue Multiple 1.6 Valuation - Multiple ONE YEAR FORWARD USD 64,00,000 VC Expected Stake 31% While making assumptions for future multiples and expected PAT etc, have a basis for assumptions, as this may be required for negotiations. While you may not necessarily discuss this, you must have this information and justification. for eg. why is the multiple 8 and not 15 etc.
- 24. 24 Exercise in Valuation - I ILLUSTRATIVE VALUATION EXERCISE REVENUE FORECAST USD Business Units Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Unit 1 12,00,000 24,00,000 48,00,000 72,00,000 1,08,00,000 Unit 2 12,00,000 24,00,000 48,00,000 57,60,000 69,12,000 Unit 3 8,00,000 16,00,000 32,00,000 38,40,000 46,08,000 Unit 4 8,00,000 16,00,000 32,00,000 38,40,000 46,08,000 Total 40,00,000 80,00,000 1,60,00,000 2,06,40,000 2,69,28,000 Profit margin, year 3 & year 5 respectively 20% 32,00,000 25% 67,32,000 VC Investment USD 20,00,000 Exit Table Method 3 year time 5 year time Expected Valuation 2,00,00,000 4,00,00,000 Discount Rate applied 50% 50% Present value of expected valuation 59,25,926 52,67,490 % ownership expected by VC Investor 34% 38%
- 25. 25 Exercise in Valuation - II Some parameters used to value Plantation Co. Garden Co. Park Co. Enterprise value/sales 1.4 1.1 1.1 Enterprise value/EBITDA 17.0 15.0 19.0 Enterprise value/free cash flows 20 26 26 Meadows Co. Sales Rs. 200 crores EBIDTA Rs. 14 crores Free cash flow Rs. 10 crores How would you value Meadows Co. based on the market/industry information provided?
- 26. 26 Some parameters used to value Plantation Co. Garden Co. Park Co. Average Enterprise value/sales 1.4 1.1 1.1 1.2 Enterprise value/EBITDA 17.0 15.0 19.0 17.0 Enterprise value/free cash flows 20.0 26.0 26.0 24.0 Application to Meadows Co. Average Value Sales Rs. 200 crores 1.2 Rs. 240 crores EBIDTA Rs. 14 crores 17.0 Rs. 238 crores Free cash flow Rs. 10 crores 24.0 Rs. 240 crores Exercise in Valuation – II: Possible Solution
- 27. 27 Some parameters usedto value Papers Co Docs Co. Prints Co. Enterprise value/sales 2.6 1.9 0.9 Enterprise value/EBITDA 10.0 21.0 4.0 Enterprise value/free cash flows 21.0 30.0 24.0 Application to PenPencil Co. Sales Rs. 300 crores EBIDTA Rs. 15 crores Free cash flow Rs. 7.5 crores Exercise in Valuation - III How would you value PenPencil Co. based on the market/industry information provided?
- 28. 28 Some parameters usedto value Papers Co Docs Co. Prints Co. Average Enterprise value/sales 2.6 1.9 0.9 1.8 Enterprise value/EBITDA 10.0 21.0 4.0 11.7 Enterprise value/free cash flows 21.0 30.0 24.0 25.0 Application to PenPencilCo. Average Value Sales Rs. 300 crores 1.8 Rs. 540 crores EBIDTA Rs. 15 crores 11.7 Rs. 175.5 crores Free cash flow Rs. 7.5 crores 25.0 Rs. 187.5 crores As there is a wide value range, the application of the relative multiples does not look appropriate in this case. What are your thoughts on this? Exercise in Valuation – III: Possible Solution
- 29. At the start Valuation: Methods … Valuation: Focus Startup Valuation: Startup Examples Valuation: Summary To Trigger Thinking … 29 29
- 30. Valuation • At idea and early stage there is limited data, more subjectivity; higher weightage given to – Team – Potential market – Competitive scenario • At next phase, more weightage is given to – Customer traction – Pipeline – Past record of conversion from pipeline etc. – Immediate past performance – Business and financial model 30
- 31. Valuation • Many methods are there, including but not limited to – Multiples of revenue, EBIDTA, user base, etc – Multiples of industry specific value drivers, e.g. GMV (Gross Merchandise Value), revenue per user, net margin per user – Cash flow based, discounted – Exit valuation expected • Financial forecasts are the starting point and required from a regulatory perspective. They are also a key point in the due diligence review, prior to investment • Uncertainties are factored in by way of scenario and sensitivity analysis, probabilities and expectations • Other statutory, accounting and tax implications are to be factored in while arriving at valuation and deal cash flows 31
- 32. Valuation Key Drivers: • Markets: Flavor of season, competitive scenario, industry trends • Team: At helm plus advisors/mentors/board • Cash burn: Or cash needed, look at scenarios of minimum bootstrap and best case • % sharing: Equity promoter is willing to let go 32
- 33. Valuation Other Drivers: • Unbundling of deal issues, such as – Board Membership – Decision making powers – Payment/salary to founders – Assistance in administrative matters (eg. Incubation) – Contribution to execution and participation in key activities such as sales, partner tie-ups – Liquidation preference – Exit clauses • Negotiation and taking control of the situation 33
- 34. Valuation • Deals can sometimes be structured to accommodate valuation perceptions – For eg. linking to future performance – This could become an area of concern when there is a possibility of a “down round” when new investors come into the picture • Understand what could be the – Deal maker issues and – Deal breaker issues 34
- 35. Valuation: Impacted by Quality .. • FOCUS on Quality not just on Quantity … • Illustrative parameter: Revenue Quality – Sales Quantity – Quality of revenue - in terms of product/service/vertical/location etc. – Customer segments addressed – Average revenue per employee – Number of customers, number of high value customers – New customers added – Customers lost – Pipeline customers • Customer acquisition strategy 35
- 36. At the start Valuation: Methods Valuation: Focus Startup … Valuation: Startup Examples Valuation: Summary To Trigger Thinking … 36 36
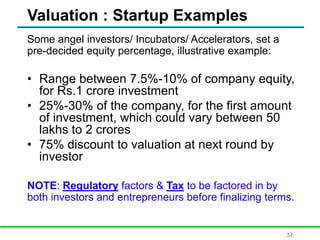
- 37. 37 Valuation : Startup Examples Some angel investors/ Incubators/ Accelerators, set a pre-decided equity percentage, illustrative example: • Range between 7.5%-10% of company equity, for Rs.1 crore investment • 25%-30% of the company, for the first amount of investment, which could vary between 50 lakhs to 2 crores • 75% discount to valuation at next round by investor NOTE: Regulatory factors & Tax to be factored in by both investors and entrepreneurs before finalizing terms.
- 38. 38 Valuation : Startup Examples Names/data changed to maintain confidentiality.. Mentoring: • 1. Edtech Co. 1 year old – Terms: month one meeting (half day), Focus on growth strategy and advisory services for leadership team: 2% equity • 2. Food tech idea stage – Terms: month 2 meetings (2 hour), mentoring on growth strategy, funding strategy and help in fund raising: 5% equity plus 1 % success fee of funds raised • Statutory and tax issues to be addressed while equity is given Incubation by Tech company: • 3. Idea stage: (i) Rs.50 lakhs was committed for 1st year, to be drawn on need basis (ii) Admin/accounting etc. support to be provided (iii) basic sustenance monthly fee of Rs.25,000 per month agreed to for each of 2 founders: 48% equity with Tech Company and balance equally by two founders
- 39. 39 Valuation: Startup Examples 4. Investment in media/entertainment company in 2014! (numbers changed to maintain confidentiality) • HewS closed $10 million valuation from InvestorA • Reading press reports, Investor 2 wanted to participate and asked the promoters to suggest a valuation • HewS Team and InvestorA decided at random: 20% increase in 1 week, leading to valuation of $12 million; • On flight as InvestorA travelled to meet Investor2, he decided he would not just be a messenger, he would value add, so he decided to up valuation to $18 m • During negotiations, Investor2 gave final offer of $15 m • Thus in about 10 days the company valuation went up by 50%, from $10 m to $15 m • Founders ended up with more money than they had planned for and had to think of ways to spend this!
- 40. 40 Valuation: Startup Examples Names/data changed to maintain confidentiality.. Service business: Value add measures: • 5. Two year co. – Rebranded, reclassified domain, pre-funding; on advise that revenue multiple would go up from 3 to 5. • 6. Three year co. – Changed business model to increasing outsourcing of some service delivery aspects. Cost of inputs increased, gross margins reduced, however operational efficiency increased, net profit margins increased and valuation multiples; i.e. revenue and PBT multiples increased. Investor negotiation: • 7. Early stage idea: Jim had high technical knowledge, limited financial knowledge. Investor Z convinced Jim that he could partner and grow the company to high value in 3 years and negotiated for half the business. Jim got into this without understanding how shares could get further diluted in later rounds of funding. At the end, Jim was left with less than 10% of the company he started, however valuation was high.
- 41. 41 Valuation: Dynamic/Volatile Reference: Article published in Livemint November 30th, 2017: SoftBank offers to buy Flipkart shares at up to $10 billion valuation http://www.livemint.com/Companies/QBVZHpX5f43yBKML4HdlFN/S oftBank-offers-to-buy-Flipkart-shares-at-up-to-10-billion.html DO you know what happened later, deal value at exit?
- 42. 42 Valuation: Dynamic/Volatile … “Walmart has wrapped up Flipkart acquisition for $16 billion, a valuation of over $20 billion, which makes it the world's biggest ecommerce deal. Walmart will own around 77 per cent of the Bengaluru-based company in what is also being seen as the largest buyout for the US firm.” https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/industry/services/re tail/softbank-ceo-confirms-walmart-flipkart- deal/articleshow/64093437.cms?from=mdr
- 43. At the start Valuation: Methods Valuation: Focus Startup Valuation: Startup Examples … Valuation: Summary To Trigger Thinking … 43 43
- 44. 44 In Summary: Valuation Process • Use more than one model • Identify current market models relevant to venture • Have a rationale for the models used • Plan long term not short haul • Look at alternate scenarios • Discount for risks, assign probabilities • Arrive at range • Identify deal issues (breaker/maker) for negotiation • Practice before negotiating A valuation range is preferable to a single number
- 45. In Summary • Caution: Look out for concern issues, hidden agendas; evaluate on value-based parameters including but not limited to fund source, governance, ethics and reputation • Keep an eye on the law and statutory regulations; these also impact valuation and deal negotiation • Plan for advisors/CAs/lawyers, due diligence costs and other deal related costs which will add to the price paid or reduce the price received for any transaction • Plan for long term impact of decisions on valuation 45 Thank you