ppt on Appendicitis by ASHOK BISHNOI LOHAWAT JODHAPUR
- 2. Anatomy &physiology of appendix:-
- 3. The appendix is a slender, worm-shaped pouch, averaging 5-10cm in length, that protrudes from the top of the colon in the lower right abdomen.
- 4. Blood & nerve supply: Blood supply by -Appendix artery from ileocolic artery. Blood return by -Appendix vein -portalal vein Nerve supply by -Sympathetic nerve.
- 5. Definition:“It is inflammation of the vermiform appendix”
- 6. Incidence:- Occurs mainly in 10 to 30 year of age.
- 7. Etiology: Obstruction (accumulated feces in lumen) Tumor Foreign bodies King-King of appendix (Twisting) Swelling of the bowel wall
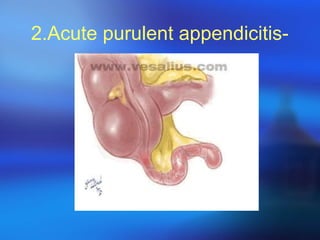
- 8. Types of appendicitis:Four type: 1.Acute simple appendicitis 2.Acute purulent appendicitis 3.Perforation and gangrenous 4.Appendiceal abscess
- 14. Pathophysiology:Due to etiological factor Inflammatory process Increase intra-luminal pressure Severe pain
- 15. Clinical manifestation:Subjective sign & symptoms Epigastric pain spread to right lower quadrant. Malaise Anorexia Vomiting Moderate leukocytosis ( leukocyte in blood) Rebound tenderness Constipation Diarrhea
- 16. Objective sign & symptoms Pain at McBurney’s point.(between umbilical & iliac crest) Rovsing’s sign: (pain in the right lower quadrant upon palpation of the left lower quadrant) Obturator sign: (pain on internal and external rotation of the hip) Psoas sign : (pain on active elevation of the legs) Tachycardia Tachypnoea Low grad fever
- 17. Diagnostic evaluation: History Physical examination WBC count Urinalysis Abdominal x-ray CT Scan USG pregnancy test (women only)
- 18. Management: Medical management Bed rest NPO I/V fluid Antibiotic eg. Antipyretic Antiemetic Analgesic Ampicillin, Sulbactam, Gentamycin
- 19. Surgical management Appendectomy New method laparoscopy appendectomy
- 22. Operation Process: Appendix is divided between clamps and ligated
- 23. a b c
- 25. Nursing management:Pre-operative Pain R/t inflamed appendix. Fluid volume deficit R/T vomiting. Post-operative Risk for infection R/T Perforation. Altered nutrition less then body requirement R/t less intake of food.