Arrhythmia :ECG-Bradycardia_20120909_中區
- 3. Normal sinus rhythm HR: 87bpm, PR interval: 150ms
- 4. Normal sinus rhythm • Heart rate: 60~100bpm • A P wave before every QRS complex • Normal P axis (upright in lead II) • PR interval >0.12 second
- 5. HR: 61bpm, PR: 128ms Ectopic atrial rhythm
- 6. Rhythm evaluation on ECG • Rate – Regularity • P wave ? • P wave morphology • P wave axis – Normal P wave axis: upright in lead II • PR interval (P & QRS relationship) – Normal PR interval: 120~200ms – Constant
- 7. Bradycardia • Bradycardia: heart rate < 60bpm • May be a normal physiological phenomenon or result from a cardiac or non-cardiac disorder – During sleeping – Athletes • Symptoms: – Dizziness, near syncope, syncope, ischemic chest pain, and hypoxic seizures
- 8. Pathological etiologies of bradycardia • Medication – B-blocker – Ca channel blocker – Digoxin – Class IA, IC, III • Myocardial infarction • Inflammation/infection – Myocarditis – Infectivce endocarditis – Lyme disease • Metabolic effect – Electrolytes – Hypothyroidism – Hypothermia • Autoimmune diseases – SLE • Surgery • Degeneration – Sick sinus syndrome
- 9. Bradyarrhythmia • Sinus node dysfunction – Symptomatic sinus bradycardia – Sinus pause/sinus arrest – Sino-atrial exit block – Tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome • AV block • Junctional/ventricular escape rhythm • Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response
- 10. Marked sinus bradycardia • May be symptomatic if heart rate < 45bpm • Usually related to – Increased vagal tone – Medication: b-blocker, Ca channel blocker – Sick sinus syndrome (SA node dysfunction)
- 11. Marked sinus bradycardia HR: 42bpm, PR: 184ms
- 12. Sinus pause/arrest • Transient cessation of impulse formation at the sinoatrial node • A prolonged pause without P activity • The pause is unrelated to the length of the P-P cycle
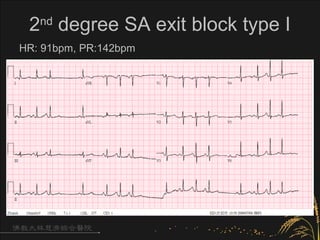
- 14. SA exit block • A transient failure of sinus impulse conduction to the atrial myocardium • SA exit block –1st degree SA block –2nd degree SA block • Type I: group beating, shortened PP interval • Type II: the pause length was two times of PP interval –3rd degree SA block: escape rhythm
- 15. SA exit block
- 16. 2nd degree SA exit block type I HR: 91bpm, PR:142bpm
- 17. 2nd degree SA exit block type II
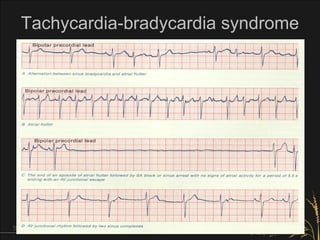
- 18. Tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome • Common in sick sinus syndrome (sinus node dysfunction) • Paroxysmal atrial tachyarrhythmia followed by sinus bradycardia, sinus pause or escape rhythm
- 20. EPS to evaluate sinus node function • Sinus node recovery time (SNRT) – SNRT < 1500 ms – cSNRT (SNRT - BCL) < 550 ms – SNRT/NSR < 150%
- 21. EPS to evaluate SA conduction • Sinoatrial conduction time (SACT) –45~125ms
- 22. Atrio-ventricular block • First degree AV block • Second degree AV block –Mobitz type I –Mobitz type II –Advance AV block: 2:1, 3:1, 4:1,… AV block • Three degree (Complete) AV block
- 23. 1st Degree AV block • Simple prolongation of PR interval (> 0.2 seconds) • No dropped QRS complexes • All P waves are conducted
- 24. 1st degree AV block HR: 57bpm, PR: 350ms
- 25. 2nd degree Mobitz type I AV block (Wenckebach phenomenon) • PR interval progressively increases before dropped QRS • Intermittent dropping of the QRS • RR interval may progressively decrease • Grouping of QRS
- 26. 2nd degree Mobitz type I AV block (Wenckebach phenomenon) HR: 44bpm, PR: 292ms
- 27. 2nd degree Mobitz type II AV block • Fixed PR interval before dropped QRS complex
- 28. 2nd degree Mobitz type II AV block HR: 59bpm, PR: 136ms
- 29. 2:1 AV block • QRS complex dropped in every other beat • Constant PR interval • Mobitz type I or II
- 30. 2:1 AV block HR: 41bpm, PR: 192ms
- 31. HR: 40bpm, PR: 186ms 2: 1 AV block
- 32. Three degree (Complete) AV block • Complete interruption of atrial conduction • Independent atrial and ventricular rhythms (AV dissociation) • Regular PP and RR interval • Atrial rate > ventricular rate • P wave march through the QRS complexes
- 33. Three degree (Complete) AV block HR: 43bpm
- 34. HR: 45bpm Complete AV block
- 35. HR: 67bpm, PR: 207ms Non-conducted APC
- 36. Escape rhythm • When the ventricles are not stimulated as a result of automaticity or conduction problems • Marked sinus bradycardia, sinus pause, complete AV block • Junctional vs. ventricular escape rhythm –Junctional: narrow, rate: 40~60bpm –Ventricular: wide, rate: 20~40bpm
- 38. Sinus bradycardia with junctional escape rhythm HR: 50bpm
- 39. Complete AV block with ventricular escape rhythm HR: 27bpm
- 40. Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response • Atrial rate in Af: 350~700bpm • The ventricular rate depends on the AV conduction ability • Impaired AV conduction
- 41. Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response HR: 48bpm
- 42. Af with regular RR interval Af with complete AV block and junctional escape rhythm
- 43. 感恩聆聽 !
Editor's Notes
- * ESC Rate For elderly with EHRA 1 (IA) Rhythm For EHRA 2 after rate control (IB) For AF+HF (IIaB) Difficult group: long history of AF, older age, more severe associated CVD, other associated medical conditions, and enlarged LA size. Could be ultimate goal, if so, continue rate control Usefulness and benefit are lacking Opportunity exists early in the course CHF rate: no different in AFFIRM, RACE, or AF-CHF AFFIRM post hoc: deleterious effect of antiarrhythmics (mortality increase of 49%) may offset the benefit of sinus rhythm (53% reduction in mortality) RACE analysis: underlying heart Dz effect prognosis more AF-CHF: no