Atlas scrub nurse
- 1. RESPONSIBILITIES OF A SCRUB NURSE ATLAS HOSPITAL, RUWI
- 4. Introduction to Perioperative Nursing **** All patients consider their surgery a major thing **** Phases of Perioperative Care Pre Operative - begins with the patient’s decision to have surgery, ends with entry into the operating room Intra Operative - begins with entry into the operating room and ends with admission to the recovery room Post Operative - begins with admission to recovery room, and ends with discharge from care
- 5. Pre-Operative Responsibilities of Operating Room Nurse: Patient Assessment Physical Problems Emotional Aspects Understanding of surgery/consent Legal requirements for chart completion Read and interpret lab results Peri-Operative Teaching
- 6. Intra-Operative Provide for quiet environment during induction Assist during intubation Observe aseptic technique Safe operation of equipment (lasers, electrosurgery unit) Position patient safely - CV, nervous, respiratory system Document events, patient care given, Provide all supplies, equipment, to team during surgery Provide for a safe transfer to recovery room
- 7. Peri-Operative Standards of Care … Pre-operative skin prep shall be done without abrading, cutting or irritating the patient’s skin Patient privacy shall be provided at all times Any pre-operative drainage tubes shall be placed without tissue trauma and be completed utilizing sterile techniques when indicated All IV infusions shall be monitored to maintain the appropriate flow rate and type of solution and remain patent without signs of inflammation or swelling The patient shall be provided emotional and educational support to reduce pre-operative anxiety The patients shall be provided a safe and normothermic environment in the pre-op waiting area The patient shall be transferred safely to the OR table and safety straps appropriately applied
- 9. Unsterile Team Member - Circulating Nurse Responsible for nursing care in the operating room Responsible for the organization of the workload Responsible for the maintenance of policy and procedures Responsible for signing and documentation The Circulating Nurse is the professional staff member in the operating room, representing the patient (Patient Advocate) and the hospital administration
- 10. SURGICAL POSITIONING Facilitated through the nursing process Patient’s body must remain in physiologic alignment Dependent Upon: The surgical procedure Exposure at the surgical field Surgeon’s preference and idiosyncrasies Patient’s condition Special Considerations: Geriatric patients Obese patients Malnourished patients
- 11. TYPES OF SURGERY MAJOR -- Present a real threat to life MINOR -- Present little threat to life
- 12. Surgical Nurse 1889 A level head & keen eyes, ever watchful for all that may be required, a mind not easily irritated or confused, combined with the facility of keeping out of the way & still being of the greatest help……..Thoroughness, speed, gentleness especially fit the surgical nurse. (Asepsis for the Nurse, Clemons, 1889)
- 13. SCRUB NURSE “ The nurse who is the immediate assistant to the surgeon is often called the “scrub” or “sterile” nurse. She first scrubs her hands and arms the required length of time, puts on sterile gown & gloves, and handles only sterile material.” Crawford 1945
- 17. • PLACE THE BLADE TO THE KNIFE HANDLE USING NEEDLE HOLDER, ASSEMBLE SUCTION TIP & SUCTION TUBE • BRING MAYO STAND & INSTRUMENT TABLE NEAR THE DRAPED PATIENT AFTER DRAPING IS COMPLETE • SECURE SUCTION TUBE & CAUTERY CORD WITH TOWEL CLIPS OR ALLIS • PREPARE SUTURE & NEEDLE ACCORDING TO NEED
- 18. DURING AN OPERATION • MAINTAIN THE STERILITY THROUGHOUT THE PROCEDURE • AWARENESS OF THE PATIENT’S SAFETY • ADHERES TO THE POLICY REGARDING SPONGE/INSTRUMENTS/NEEDLE COUNT • ARRANGE THE INSTRUMENTS ON THE MAYO & INSTRUMENTS TABLE
- 19. BEFORE THE INCISION • PROVIDE SPONGES/MOPS NEAR OPERATIVE SITE PRIOR TO INCISION • PASS THE FIRST KNIFE FOR THE SKIN TO THE SURGEON WITH THE BLADE FACING DOWNWARD & HEMOSTATS TO THE ASSISTANT SURGEON • HAND THE RETRACTOR TO THE ASSISTANT SURGEON • WATCH THE FIELD/PROCEDURE & ANTICIPATE THE SURGEON’S NEEDS • PASS THE INSTRUMENTS IN A DECISIVE & POSITIVE MANNER
- 20. • WATCH OUT FOR HAND SIGNALS - FOR INSTRUMENTS • KEEP USED INSTRUMENTS CLEAN BY WIPING INSTRUMENTS WITH A MOIST SPONGE • ALWAYS REMOVE THE CHARRED TISSUE FROM THE CAUTERY TIP • NOTIFY CIRCULATING NURSE IN A CLEAR MANNER IF ADDITIONAL INSTRUMENTS ARE NEEDED • KEEP SPONGES ON THE FIELD FOR USE • SAVE & CARE FOR TISSUE/SPECIMEN ACCORDING TO HOSPITAL POLICY
- 21. • REMOVE EXCESS INSTRUMENTS FROM STERILE FIELD • ADHERE & MAINTAIN STERILE TECHNIQUES & WATCH FOR ANY BREAKS
- 22. END OF OPERATION • UNDERTAKE COUNT OF SPONGES & INSTRUMENTS ALONG WITH CIRCULATING NURSE • INFORM THE SURGEON THE COUNT RESULT • REMOVE INSTRUMENTS & EQUIPMENTS • AFTER OPERATION HELP TO APPLY DRESSING • REMOVE & DISPOSE THE DRAPES (if disposable) • COVERS PATIENT BEFORE SHIFTING TO HDU
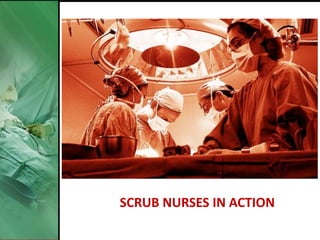
- 24. SCRUB NURSES IN ACTION
- 25. Dressing for ACTION! Appropriate attire for restricted area in preparation for scrubbing
- 26. About sterility……. • Unless you are scrubbed, gowned and gloved, do not enter the ‘sterile zone’. • For example, do not walk between two sterile areas (such as between the scrub nurse’s trolley and the draped patient), and do not touch the drapes. If you accidentally breach the sterile field, it is essential that you admit your mistake. • If your gloved finger accidentally touches something unsterile when you are scrubbed, you must immediately stop using that hand in the sterile field (unless removing the hand will cause a problem), and request a new glove from the scrub nurse, as soon as the opportunity arises. No-one should think badly of you for doing this; on the contrary, they will probably be pleased with your honesty and respect for the sterile field.
- 27. About sterility…….contd. • The degree to which a surgeon will adhere meticulously to sterility will vary according to the operation. • Clearly, meticulous asepsis is much more important when implanting a new cardiac valve, than when draining a perianal abscess
- 28. When to scrub • The scrub nurse normally scrubs well before the surgeon, to allow time to set up the sterile instruments.
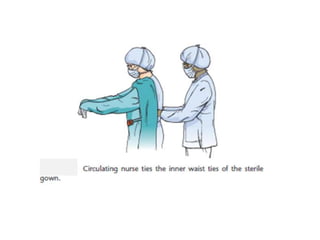
- 29. Gowning….
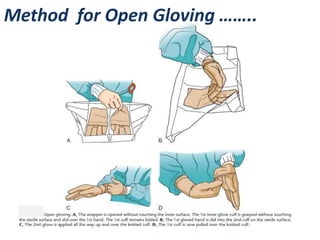
- 32. Method for Open Gloving ……..
- 33. Where to put your hands Any area lower than the level of the operating table is usually considered suspect, even if it is covered by sterile drapes. Firstly, you should keep your hands above this area Rest the hands together against the chest, as though praying but with fingers interlaced
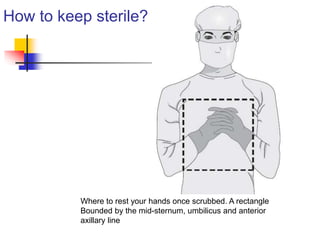
- 34. How to keep sterile? Where to rest your hands once scrubbed. A rectangle Bounded by the mid-sternum, umbilicus and anterior axillary line
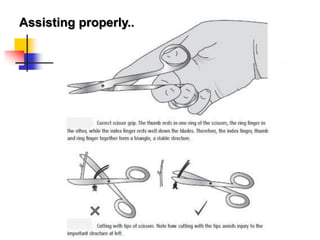
- 35. Note these…….
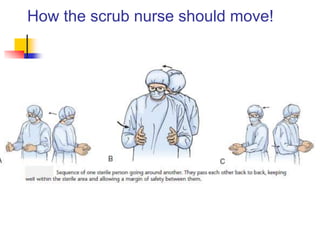
- 36. How the scrub nurse should move!
- 39. SCRUB TEAM @ WORK
- 41. Contd…
- 42. Contd…
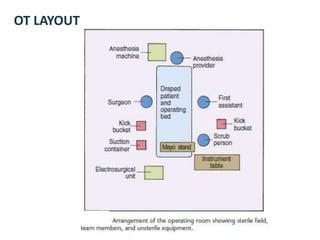
- 43. OT Layout OT LAYOUT
- 44. PRESENT DAY OPERATION THEATRE – MAJOR SURGERY
- 45. Fundamentals of Nursing Care: Concepts, Connections, & Skills ROBOTIC SURGERY Copyright © 2011 F.A. Davis Company
- 46. Fundamentals of Nursing Care: Concepts, Connections, & Skills ROBOTIC SURGERY Copyright © 2011 F.A. Davis Company
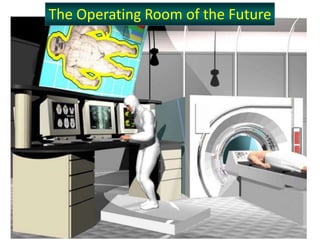
- 47. The Operating Room of the Future
- 48. The Operating Room of the Future
- 49. The Operating Room Personnel of the Future Surgeon Assistant Scrub Nurse Circulating Nurse Satava March, 2000
Editor's Notes
- Is someone is anxious, it may alter their anesthesia.
- Even turn lights down & be quiet during induction (person going under). Make sure everything is available (assist during intubation) Position: know patient history… if they have heart problems, need to make sure patient is positioned safely. Very easy to dislocate joints or break bones while someone is “under”. Every needle & sponge & supply must be counted before surgery is over!
- Must be an RN
- Robotic or Robot-assisted surgery integrates advanced computer technology with the experience of the skilled surgeons. This technology provides the surgeon with a 10x magnified, high-definition, 3D-image of the body's intricate anatomy. The surgeon uses controls in the console to manipulate special surgical instruments that are smaller, as well as more flexible and maneuverable than the human hand. The robot replicates the surgeon's hand movements, while minimizing hand tremors. The surgeon thus can operate with enhanced precision, dexterity and control even during the most complex procedures.