Basic DBMS ppt
- 1. Presented by : Rajendra Dangwal Branch : C.S. (III) Presented to : Mr. Yogesh Jain
- 2. DATABASE : A collection of data is referred to as database. e.g. 1. record of students stored in files 2. information stored over internet DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM: It is basically a computer based record keeping system (program). e.g. MySQL Microsoft Access FileMaker FoxPro
- 3. Purpose of database : 1. It reduces DATA REDUNDANCY to a large extent. 2. It controls DATA INCONSISTENCY. 3. It facilitate SHARING of data. 4. It ensures DATA SECURITY. Name D.O.B Fees Name D.O.B Fees Harsh 23/01/1993 Not paid Harsh 23/01/1993 Paid Amar 04/11/1994 Paid Amar 04/11/1994 Paid Devendra 14/06/1992 Not paid Devendra 14/06/1992 Paid Harsh 23/01/1993 Not paid Harsh 23/01/1993 Not paid Data Redundancy Data Inconsistency
- 4. Various levels of database implementation (concept of abstraction) 1.INTERNAL LEVEL (PHYSICAL LEVEL): It describes how data are actually stored on the storage medium. It is closest to database programmer. Lowest level of database abstraction. 2. CONCEPTUAL LEVEL: It describes what data are actually stored in database. It is closest to the database manager. It is an intermediate level of database abstraction. •EXTERNAL LEVEL (VIEW LEVEL): It describes the way in which the data are viewed by individual user. It is the level closest to the users.
- 5. Three levels of data abstraction Account holder External level User View 1 Database handler View 2 View 3 Conceptual level Physical level (DBMS Programmer) View 1 AC_Name Amount Conceptual AC_No AC_Name Type Amount Internal Stored-acc. Account # Name Type Amount Manager View 2 AC_No AC_Name Type Amount numeric(15) character(20) character(10) numeric(15) length=60 type=bytes(15) offset=0 type=bytes(20) offset=15 type=bytes(10) offset=35 type=bytes(15) offset=45
- 6. DATA MODELS 1.Relational Data Model Table : Items Item # Itemname Price I1 Cake 50.00 I2 Bread 9.00 I3 Biscuits I4 Snacks Table : Shipments Supp# Item# QtySupplie d 6.00 S1 I2 20 16.00 S1 I3 25 S1 I4 10 S2 I1 5 S2 I3 10 Table : Suppliers Supp# Supp-name S1 Britannia S2 New Bakers 1. RELATIONAL DATA MODEL: In relational data model, the data is stored in the form of tables (i.e. rows ad columns). These tables are called relations. The user of the relational database system may insert new tuples, delete tuples, and modify tuples.
- 7. 2. Network Data Model S1 20 I2 Bread 9.00 Britannia 10 25 I3 Biscui ts 6.00 I4 Snacks 16.00 2. NETWORK DATA MODEL: The network data model differs from the relational model. In this model data is represented by connection of records and relationships among data are represented by links. Records are organized as graphs.
- 8. 3. Hierarchical Data Model S1 I2 I3 I4 Britannia Bread 9.00 Biscuits 6.00 20 Snacks 16.00 25 10 3. HIERARCHICAL DATA MODEL: Data is represented by collection of records and relationships among data by links, similar to the network model. Records are organized as trees rather than graphs. Represents relationship among its records through parent child relationships.
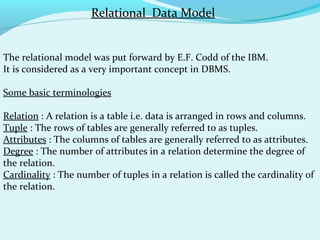
- 9. Relational Data Model The relational model was put forward by E.F. Codd of the IBM. It is considered as a very important concept in DBMS. Some basic terminologies Relation : A relation is a table i.e. data is arranged in rows and columns. Tuple : The rows of tables are generally referred to as tuples. Attributes : The columns of tables are generally referred to as attributes. Degree : The number of attributes in a relation determine the degree of the relation. Cardinality : The number of tuples in a relation is called the cardinality of the relation.
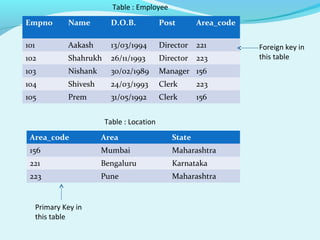
- 10. Views A view is a (virtual) table that does not really exist in its own right but is instead derived from one or more underlying base tables. It is an excellent way to give people access to some but not all information (data abstraction). Database Keys are used to establish and identify relations between tables. Primary key: It is a set of one or more attributes that can uniquely identify the tuples within the relation. Candidate key : All attribute combinations inside a relation that can serve as a primary key are candidate keys. Alternate key: A candidate key that is not the primary key is called the alternate key. Foreign key : A foreign key is a non key attribute whose value is derived from the primary key of another table.
- 11. Table : Employee Empno Name D.O.B. Post Area_code 101 Aakash 13/03/1994 Director 221 102 Shahrukh 26/11/1993 Director 223 103 Nishank 30/02/1989 Manager 156 104 Shivesh 24/03/1993 Clerk 223 105 Prem 31/05/1992 Clerk 156 Table : Location Area_code Area State 156 Mumbai Maharashtra 221 Bengaluru Karnataka 223 Pune Maharashtra Primary Key in this table Foreign key in this table