Beckmann rearrangement
- 3. Rearrangement: When carbon skeleton of the molecule is rearranged to give a structural isomer of original molecule Migration of group from one to another atom either within same molecule or to another molecule definitions
- 5. Beckmann rearrangement: History: Ernst Beckmann Definition: “The acid catalyzed conversion of Oximes to N-substituted Amides is called Beckmann rearrangement’’
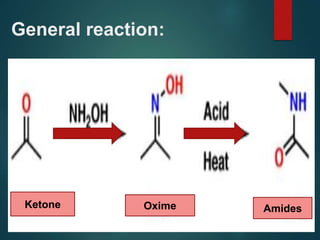
- 6. General reaction: Ketone Oxime Amides
- 9. Reactant and Product: Ph H N H N NOH NOH NOH H N O O O Ph
- 11. How to form Oxime:
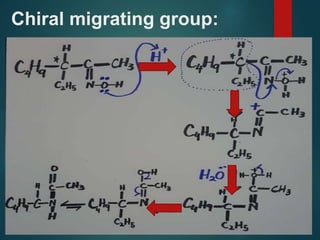
- 12. Stereoselect -ive Concerted Group ANTI to l.g migrates Retention of configurati on of M.G Stereochemistry:
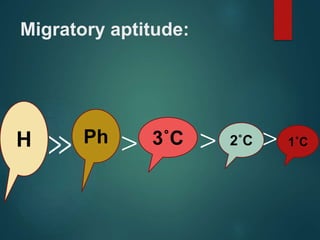
- 13. Migratory aptitude: H Ph 3˚C 2˚C 1˚C ≫ > > >
- 14. Mechanism with Acid: +H + + H2O _R H2O H + H + ←← Oxime Oxonium ion + + N-Subs Amides + + = → Tautomerize -
- 17. EWG with migrating group:
- 19. Formation of NYLON: BaseH2SO4 Mechanism N-hydroxylamines Caprolactam Nylon
- 21. s