Behavior Based Safety (BBS).pptx
- 1. “Behavior Based Safety (BBS)” Establishing A Safety Culture
- 2. Safety measures to be followed at work place.
- 3. Occurrence of accident • When no. of different circumstances or factors combined to create hazardous situations; accidental causes – Major & Minor • Two groups – Unsafe Act and Unsafe Condition Accident Unsafe Act Unsafe Condition • Untidy work area, Faulty equipment, Slippery floor, Inadequate lighting etc. • These results from people’s behavior – Not following safety procedures, Inappropriate use of equipment, Not wearing PPE
- 4. Unsafe Acts • It can be controlled by: Training, Establishment of safe work procedures & practices, Plant safety rules, Incentive programs etc. • However, despite these efforts UA continue to be major factor in preventing workplace accidents • UA are difficult to control as they involve human factor, they occur as a result of people’s behavior and attitudes • By adopting Behavioral approach to safety which must be used in conjunction with traditional safety control measures, UA can be effectively addressed this approach is known as BBS.
- 5. Unsafe Condition WORKING HAZARDS • Slippery Floor • Lack of fencing of rotating machines • Unguarded Machinery • Lack of Electrical Earthing • Lack of illumination on working table • Unsafe Working Platform • Environment factor causing Nuisances
- 6. Unsafe Condition WORKING PROBLEMS • Psychological Pressure due to rude boss • Lack of clear message/communication • Lack of training about Safe Working • Lack of Personal Protective Equipment • Work Pressure • Unsafe Work Equipments • Unsafe access • Lack of working facilities
- 7. Safety culture It was quite late for our industry to realize that organizational safety culture drives the at-risk behaviors resulting into rows of incidents, and now the industrial leadership is gradually understanding as how to transform reactive culture into interdependent safety culture with BBS approach
- 8. Behavioral Based Safety •Behavioural Safety aims to reduce the incidents of UA by modifying people's behavior and improving their attitude towards safety… •UA is an intentional or unintentional violation of an established safety work practice, procedure or method Two categories: a. Acts of indifference – in every situation safe work methods are known but are not followed b. Lack of knowledge – people performing jobs in which they are not trained or authorized to carryout
- 9. BBS: Introduction •BBS is a practice that ensures safe workplace for employees in an organization, across all industries •As compared to other workplace safety practices, BBS is the safety culture of the new-generation of managers •It’s employee's insurance against accidents at the workplace •The main safety objective of every organization is to bring down the number of work-related accidents to zero •Since the safety in the organization cannot be less than 100 percent, the participation of each and every employee also must be no less than 100 percent •Before BBS implementation safety procedures were like police inspection, BBS training has improved communication between safety officers and other employees and the attitude of the employees towards safety •That is what Behavior Safety is all about •BBS is a scientific approach to positively reinforce a safe work environment by modulating unsafe behavioral patterns
- 10. Literature says that… •Almost 100 percent of workplace related accidents are caused by unsafe human acts and behaviours •30% of the unsafe behaviours are noticeable at any plant at any given point in time •25-30% of safety awareness is lacking among employees which gets reflected in their unsafe behavior •Unsafe behaviors are at the core of almost all near misses, injuries, and accidental deaths, if we can control unsafe behavior at our workplace, we may not have even near-misses
- 15. To reduce accidents, managements have taken safety interventions such as: • Risk assessment, • Training, • Suggestion scheme, • Safety committee, • Auditing, • Motivational programmes (quiz, award, incentives), • SOPs, • Plant inspection, • Work permit system etc.
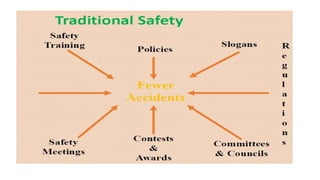
- 17. How does BBS differ from traditional Safety Behaviour Based Safety is Is proactive- discourages “at-risk” behaviours Focuses on observing workers behaviour Common behaviours that place employees at risks are noted and adjustments are made Data comes from behavioural observations Has a holistic understanding of workers behaviour Notes the environment in which behavior occurs, the behaviour itself and consequence of behaviour
- 24. Human Factors in Incidents Negligence - Failure to observe safety rules or instructions or to maintain equipment. Anger/Temper - Causes one to become irrational and to disregard common sense. Hasty Decisions - Acting before thinking can lead people to take hazardous shortcuts. Indifference - Lack of attention to the task; not alert; daydreaming. Distractions - Interruptions by others (perhaps caused by family troubles, bad news, horseplay) while someone performs normal job duties or non-routine hazardous tasks. Curiosity - Workers do something unexpected just to see what happens. Inadequate Instruction - Results in an untrained or improperly trained worker. Poor Work Habits - Cluttered workplace, floor, loose clothing, wearing jewelry.
- 25. We can reduce the number of accidents caused by “human factors”. Knowledge – By knowing and observing safety rules or instructions and maintaining equipment. Relax/Calm Down – If you find you are angry or your temper is flaring, take the time to relax, address the issue, and calm down before you proceed with the work. Think Before You Act – Take a few minutes to think of the work to be done and identify the potential hazards and what you can do to avoid or prevent an accident. Focus – Focus on the task at hand and keep you mind on your work. Minimize Interruptions - Interruptions by others may be one of the easiest to identify, but one of the most difficult to control. However, as an example we can turn off cell phones when they are not needed or cannot be answered safely. Don’t Experiment – Don’t do anything unless you know what the results will be, and it is required for the project. Proper Training/Instruction – Train and instruct your team and yourself on the proper and safe way to complete the project. If you feel uncomfortable about performing the work, ask someone with more experience for some help. Proper Work Habits – Keep you work area clean and free of hazards. Wear the proper clothing and PPE for the project.
- 26. WHY ACCIDENTS HAPPEN ????? • Y ..Y .. Y ..Y ..Y... & the Root cause is........... • CARELESSNESS • OVER CONFIDENCE • NEGLIGENCE • INCOMPETENCY • SHORTCUTS • LACK OF AWARENESS • PROCASTINATION H U M A N BEHAVIOURS
Editor's Notes
- BK Shivani, is a teacher in the Brahma Kumaris spiritual movement of India