Big data (word file)
- 1. DATA NETWORK AND SECURITY Trends, Applications & Security Shahbaz Ahmad Anjam BSITF15MM020 BSIT (5th ) UOS (Mianwali
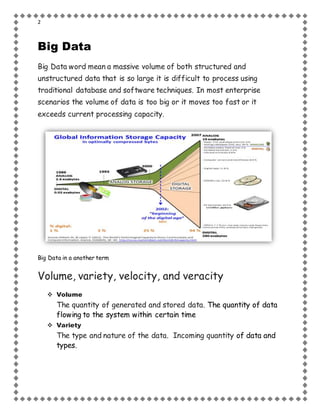
- 2. 2 Big Data Big Data word mean a massive volume of both structured and unstructured data that is so large it is difficult to process using traditional database and software techniques. In most enterprise scenarios the volume of data is too big or it moves too fast or it exceeds current processing capacity. Big Data in a another term Volume, variety, velocity, and veracity Volume The quantity of generated and stored data. The quantity of data flowing to the system within certain time Variety The type and nature of the data. Incoming quantity of data and types.
- 3. 3 Velocity The speed at which the data is generated and processed to meet the demands and challenges that lie in the path of growth and development. Veracity The data quality of captured data can vary greatly, affecting the accurate analysis. Big Sources of Big Data Some data sources that generate huge data volumes in just 60 seconds. More than 60 blog and 1500 blog posts are done. More than 70 domains are registered. More than 600 new videos are uploaded on you tube. More than 40 questions asked on yahoo are answered and 100 + questions answered on answers.com More than 1300 iPhone applications are downloaded every minute. 694445 searches are made on Google every minute. About 320 accounts are created on Twitter and more than 98000 tweets are made every minute. Trends Big Data trends shift rapidly, but experts expect machine learning, predictive analytics, IoT and edge computing to have a big impact on big data projects in the years ahead. Researchers at Forrester have "found that, in 2016, almost 40 percent of firms are implementing and expanding big data technology adoption. Another 30 percent are planning to adopt big data in the next 12 months." Similarly, the Big Data Executive Survey 2016 from New Vantage Partners found that 62.5 percent of
- 4. 4 firms now have at least one big data project in production, and only 5.4 percent of organizations have no big data initiatives planned or underway. 2015 Trends More Sensor Driven Data This would be sensor-to-sensor data being collected, collated and analyzed through purely sensor based collection. This can be done in multiple ways from the way that objects are interacting with another object, to the settings that people are using on particular devices. Non-Data Scientists Automated platforms that can allow employees who may not have as much skill with data as others, to collect, analyze and make decisions based on this data. This could be anything from simple to use interfaces with more complex backends or simpler tasks that could create business results. In-Memory Databases Databases allow companies the freedom to access, analyze and take actions based on data much quicker than regular databases. This in turn means that either decisions can be made quicker as data can be analyzed faster or more informed as more data can be analyzed in the same amount of time.
- 5. 5 2016 Trends The NoSQL NoSQL technologies, commonly associated with unstructured data, have seen significant adoption over the last 12 months.Going forward, the shift to NoSQL databases as a leading piece of the enterprise IT landscape becomes clear as the benefits of schema-less database concepts become more pronounced. Hadoop Hadoop is an open source software framwork used for distributed storage and processing of dataset of big data using Map reduce programing model. The Hadoop includes four modules: Hadoop Common (utilities), Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), Hadoop YARN (scheduler) and Hadoop MapReduce (parallel processing). IoT IoT has been touted for smart homes, wearables, smart cities, smart grids, industrial internet, connected vehicles, connected health, smart retail, agriculture, and a host of other scenarios. The Internet of Things (IoT) is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to- computer interaction.
- 6. 6 Cloud Storage Cloud storage enables applications to upload data to a network of remote, connected servers. Applications can then maintain that data and access it from anywhere. Applications access data using a web- based API that works with client applications. Storage is available in four main types: Personal storage: Services that enable individuals to store data and sync it across multiple devices. Public storage: A cloud storage provider that fully manages data for an enterprise offsite. Private storage: The cloud storage provider works on premises at an organization’s data center. Hybrid storage: A mix of public and private cloud storage. . 2017 Big Data Trends Artificial Intelligence is most common trend of 2017 Neural networks A neural network is a system of hardware and/or software patterned after the operation of neurons in the human brain. Neural networks -- also called artificial neural networks --Neural networks can analyze the flow of incoming data and highlight the patterns or abnormalities according to preconfigured parameters. This helps greatly automate the analysis and provides powerful tools for finding valuable information in the flow of unstructured data. Deep learning custom tools Is a machine learning technique, which relies on learning data representations, unlike task-specific machine learning algorithms. it
- 7. 7 definitely excels in analyzing unstructured data according to pre- configured parameters and statistics, providing a great degree of precision in evaluating the incoming data. Machine Learning Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on allowing computers to learn new things without being explicitly programmed. In other words, it analyzes existing big data stores to come to conclusions which change how the application behaves. Data monetization Predictive and prescriptive analytics are the approaches that help organizations minimize expenses and earn money using their Big Data tools. Selling the results of analytics as a service, disseminating and structuring the data for customers can also become a profitable market. Is the act of generating measurable economic benefits from available data sources. Typically these benefits accrue as revenue or expense savings, but may also include market share or corporate market value gains. R language and Jupiter notebooks Data scientists have a number of option to analyze data using statistical methods. One of the most convenient and powerful methods is to use the free R programming language. R is one of the best ways to create reproducible, high-quality analysis, since unlike a spreadsheet, R scripts can be audited and re-run easily. The R language and its package repositories provide a wide range of statistical techniques, data manipulation and plotting, to the point that if a technique exists, it is probably implemented in an R package. R is almost as strong in its support for machine learning, although it may not be the first choice for deep neural networks,
- 8. 8 which require higher-performance computing than R currently delivers. Self-Service As the cost of hiring big experts rises, many organizations are likely to be looking for tools that allow regular business professionals to meet their own big data analytics needs. IDC has previously predicted "Visual data discovery tools will be growing 2.5 times faster than rest of the business intelligence (BI) market.Several vendors have already launched big data analytics tools with "self- service" capabilities, and experts expect that trend to continue into 2018 and beyond.
- 9. 9 Applications of Big Data 1. Banking and Securities In this industry include: securities fraud early warning, tick analytics, card fraud detection, archival of audit trails, enterprise credit risk reporting, trade visibility, customer data transformation, social analytics for trading, IT operations analytics, and IT policy compliance analytics, among others.
- 10. 10 2. Media and Entertainment Big data is changing the media and entertainment industry, giving users and viewers a much more personalized and enriched experience. Big data is used for increasing revenues, understanding real-time customer sentiment, increasing marketing effectiveness and ratings and viewership. 3. Healthcare Big data is used for analyzing data in the electronic medical record (EMR) system with the goal of reducing costs and improving patient care. This Data includes the unstructured data from physician notes, pathology reports etc. Big Data and healthcare analytics have the power to predict, prevent & cure diseases.. 4. Energy and Utilities In utility companies the use of big data also allows for better asset and workforce management which is useful for recognizing errors and correcting them as soon as possible before complete failure is experienced. 5. Manufacturing Increasing demand for natural resources including oil, agricultural products, minerals, gas, metals, and so on has led to an increase in the volume, complexity, and velocity of data that is a challenge to handle.
- 11. 11 6. Education In a different use case of the use of big data in education, it is also used to measure teacher’s effectiveness to ensure a good experience for both students and teachers. Teacher’s performance can be fine-tuned and measured against student numbers, subject matter, student demographics, student aspirations, behavioral classification and several other variables 7. Transportation Governments use of big data: traffic control, route planning, intelligent transport systems, congestion management (by predicting traffic conditions) Private sector use of big data in transport: revenue management, technological enhancements, logistics and for competitive advantage (by consolidating shipments and optimizing freight movement) Individual use of big data includes: route planning to save on fuel and time, for travel arrangements in tourism etc. 8. Insurance Big data has been used in the industry to provide customer insights for transparent and simpler products, by analyzing and predicting customer behavior through data derived from social media, GPS-enabled devices and CCTV footage. The big data also allows for better customer retention from insurance companies
- 12. 12 Big Data Security Security Issues Comes due to:- There are limited levels of protection in majority of distributed systems’ computations. Security solutions are not being able to tackle the demand with several non-relational databases constantly evolving. There is lack of appropriate security processes for the transfer of automated data. System updates, audits, patches are not always carried out. Information coming in should be constantly validated, to ensure its credibility and accuracy, but that is not the case for most systems Attack on systems that contain sensitive and personal information of the customers can put the customers at risk. Certain organizations do not deploy any kind of access controls to differentiate between the confidentiality levels of data within the organization. Monitoring and tracking of systems is difficult with the current scale of Big Data application. Cyber Security Threats are Rising.
- 13. 13 How to secure the Big data Detection of frauds and replacement of SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems Optimization of sales and marketing campaigns through business intelligence as there is an abundance of data and analytics available. Real-Time Security Monitoring Endpoint Input Validation and Filtering Secure Storage and Transaction Logging. Granular Access Control. Encrypted Data-Centric Security. Best Security Practices for Non-Relational Data Stores. Application Software Security Account Monitoring and Control
- 14. 14 End