BIM objects
- 1. B I M O B J E C T S
- 2. INDEX 1. What is a BIM object? 2. The sources of BIM objects 3. Our software solutions ▪ elec calc™ BIM ▪ archelios™ PV BIM BIM objects
- 3. 1. What is a BIM object? BIM objects
- 4. BIM objects A BIM object is an intelligent object as it contains*: *According to the book “Delivering value with BIM: a whole of life approach”
- 5. Information that defines the product or element BIM objects Geometric characteristic of the physical product or element Visualization data giving the object a recognizable appearance Functional data that allows the object to be positioned or to behave in a certain manner
- 6. Therefore, a BIM object is not a simple digital representation in 3D, but an intelligent object as it contains the metadata that describes: BIM objects
- 7. BIM objects what kind of object it is its classification performance values the material type expected lifetime manufacturer maintenance its behavior and also information regarding sustainability and energy efficiency
- 8. BIM objects When the object is placed in the parametric model, the eventual changes applied will be available to all the operators involved in the building project.
- 9. BIM objects Image source: akropolis network http://akropolisnetwork.altervista.org/bim-cni-la-digitalizzazione-dei-processi/
- 10. BIM objects This means that the BIM model guarantees the use of consistent information amongst the building professionals and it consequentially leads to less waste by reducing the occurrence of errors.
- 11. 2. The sources of BIM objects BIM objects
- 12. BIM objects BIM objects come from 3 types of sources: ▪ BIM software (predefined BIM objects) ▪ Online libraries of objects such as BIM&CO ▪ Users’ own libraries objects.
- 13. BIM objects Online libraries such as BIM&CO stores manufacturer’s objects, whose properties must be structured in a standardized way.
- 14. BIM objects One of BIM&CO’s distinctive features is having identified the classification of existing objects, and the software and properties required by this software.
- 15. BIM objects Once they have been referenced, this knowledge base is regrouped within a unified dictionary, thanks to which each property can be named in a standardized way and can, therefore, be exploited by any software, whatever the country.
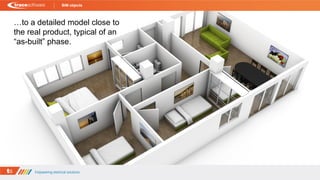
- 16. BIM objects Moving from a simplified schematic model in the initial phase…
- 17. BIM objects …to a detailed model close to the real product, typical of an “as-built” phase.
- 18. 3. Our software solution BIM objects
- 19. BIM objects The digitalization of the building industry is having an impact on both electricity and energy markets.
- 20. BIM objects We have conceived two software solutions able to leverage the benefits of BIM:
- 21. BIM objects
- 22. BIM objects
- 23. BIM objects elec calc™ BIM is the first software in the world that perfectly integrates the electrical calculation into the Open BIM process.
- 24. BIM objects With elec calc™ BIM, the user can design, calculate and size the electrical installation in the digital model in IFC 4 format, generated by any 3D architecture software (Revit, ArchiCAD, SketchUp …).
- 25. BIM objects The software can connect to the BIM&CO platform to access manufacturer data.
- 27. BIM objects archelios™ PV BIM is the Building Information Modelling (BIM) concept applied to Photovoltaics.
- 28. BIM objects Use 3D mock-ups along with physical and electrical characteristics Works with BIM&CO, the newest collaborative platform where all digital modelling players can create, publish, contribute and use BIM objects. PV modules mock-ups are stored in BIM&CO
- 29. BIM objects D O Y O U W A N T T O K N O W M O R E ?
- 30. Since 1987, Trace Software International has been committed to the development of software solutions and services dedicated to the industrial engineering, with a unique expertise in the design of electrical installations. www.trace-software.com
- 31. Trace Software France Parc Eco-Normandie 76430 Saint Romain de Colbosc France commercial@trace-software.com Trace Software Iberia Via Augusta, 48-54 08006 Barcelona – Spain sales@trace-software.com Trace Software China Shangda International Room D408, No. 3100 Hutai Road,Baoshan District Shanghai 200436, P.R.China sales@trace-software.com Trace Software Morocco 104 bis boulevard Abdelmoumen 4ème étage 20042 Casablanca – Maroc maroc@trace-software.com