Biomaterials
- 1. biomaterialsBy:Amparo Ortega YagoCristina Ballesteros FerrerLaura Martínez AlonsoVíctor del Moral RondaAbigail DombrowskySuescun
- 2. Index:DefinitionWhy are they so particular?KindsThemostusedbiomaterialsSomeexamples
- 3. Definition:Biomaterials are all the inert materials used for producing a pharmacological object that is going to be introduced in a living organism. An artificial tendon
- 4. Why are they so particular?All the biomaterials are specially studied because are important for our health, and the body could react against them. Biomaterials have to support in the body natural conditions: temperature, Ph, corrosive fluids… and they can not never to oxidize.
- 5. KINDSIntern layout: All the biomaterials placed in the intern body.External layout: All the biomaterial placed in the exterior of the body.
- 7. KINDSInert biocompatible: are accepted for the body and can stay in the body for long periods of time. Used for permanent implants.Reabsorble biocompatible: Designed for being reabsorbed and substituted for the natural tissue.Biocompatible bioactive: them react strongly with the natural tissue, forming a strong link.
- 8. THE MOST USED BIOMATERIALSThe polymers, such as the nylon, the silicone or the Teflon. They are elastic an easy to fabric them. On the other hand, they are easy to demote. The new materials, as the nanocomposits, that are really difficult to sintetise.A silicone prosthesis
- 9. THE MOSt USED BIOMATERIALSThe ceramic materials, as the aluminum oxide. They have a great biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, but they are not elastic at all, and are fragile. Some materials like steel 316, 316 with a less contest of carbon, titanium alloys. They have great resistance, but they are not very biocompatible.
- 10. PACEMAKER A pacemaker is a medical device witch uses electrical impulses delivered by electrodes contacting the heart musclesWhen the pacemaker fails to sense a heartbeat within a normal beat to beat period, it will stimulate the ventricle of heart with a short low voltage pulse. This sensing and stimulating activity continues on a beat by beat basis.
- 11. PACEMAKER
- 12. pacemakerPacemakersconsist of a pager-sizedhousingdevicethatcontains a battery and theelectroniccircuitrythatrunsthedevice, alongwithoneortwolongthinelectricalwiresthattravelfromthepacemakerhousingdevicetotheheart, it'simplantedbelowtheskin in theshoulderarea.
- 13. PACEMAKER MATERIALSThematerialsusedtoconstructpacemakersmustbepharnacologicallyinert, nontoxic, sterilizable, and abletofunction in theenvironmentalconditions of thebody.Thecasingismade of titaniumor a titaniumalloy. The lead isalsomade of a metal alloy, butitisinsulatedby a polymersuch as polyurethane. Onlythe metal tip of the lead isexposed. Thecircuitryisusuallymade of modifiedsiliconsemiconductors.
- 14. PACEMAKER
- 15. Contact lens A contactlensis a correctivelens placed onthe cornea of theeyeIt'sdesignedtoimprovevisionbecausesomepeoplehave a mismatchbetweentherefractivepower of theeye and thelength of theeye, leadingto a refraction error. A contactlensneutralizesthismismatch and allowsforcorrectfocusing of light ontothe retina.
- 16. CONTACT LENS
- 17. Contact lensContactlenses are made of pliablehydrophilicplasticscalledhydrogels. Hydrogelsabsorbsignificantamounts of watertokeepthelensessoft and supple.New softcontactlensescalledsiliconehydrogellensesincludesiliconewithinthehydrogel material toincreasetheoxygentransmissibility of thelenses.
- 18. KneeImplants
- 19. OperationThis piece replaces the joint (sometimes also the ligaments), it allowing the movement of the knee and the mobility of the leg.
- 20. Features It is intended to assist in joint mobility of the knee, but this may have negative side effects to the person like urinary incontinence among others.
- 21. MaterialsThe materials used are plastic and metal, as they help in the performance of the prosthesis. You can also join the prosthesis with bone using cement to the knee, to improve efficiency.
- 22. KidneyImplants
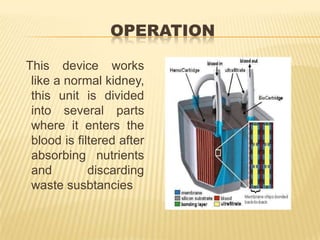
- 23. OperationThisdeviceworkslike a normal kidney, thisunitisdividedintoseveralpartswhereitentersthebloodisfilteredafterabsorbingnutrients and discardingwastesusbtancies
- 24. Features Due to this piece people don’t have to worry about the problems of making a kidney implant because this device is designed to prevent rejection and to do the function like a normal kidney.
- 25. MaterialsThere are many kinds of kidney, and the materials are varied for example it can be of silicone, plastic, etc.
- 26. Artificial heartArtificial hearts are a mechanicaldevice, They are typically used in order to bridge the time to heart transplantation, or to permanently replace the heart in case transplantation is impossible.
- 27. Artificial heartthe heart is conceptually simple, it’s formed by synthetic materials and power supplies. A possible consequence it could be the body rejection. These complications limited the lifespan of early human recipients to hours or days
- 28. AbioHeartIt’s the last artificial heart invented. It’s made by titanium and a special plastic in which the blood doesn’t stick. The heart has got flexible walls with silicon, a motor that moves it, and in the valve it controls the pressure.5 years are the life of this hearts.