Biw fixture
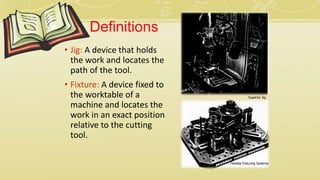
- 2. Definitions • Jig: A device that holds the work and locates the path of the tool. • Fixture: A device fixed to the worktable of a machine and locates the work in an exact position relative to the cutting tool. Superior Jig Flexible Fixturing Systems
- 3. Fixtures • More of a permanent tool that is used for assembly purposes. • Typically does not have as much flexibility as a jig. • Most likely used for high volume production. • Made of durable materials such as tool steel, iron, aluminum alloys, etc.
- 4. Other Fixture Examples • Used most commonly for welding and metal assembly work. • Typically used for products that must be very precise. • Sometimes are exposed to high temperatures and stresses
- 5. Type of Fixtures (a) Turning fixtures (b) Milling fixtures (c) Fixture for grinding (d) Fixture for broaching (e) Fixture for boring/drilling (f) Tapping fixture (g) Fixture for welding (h) Assembling fixture Standard Parts Co.
- 6. Fixture components • Fixture base • Fixture components and the workpiece are usually located on a base, which is securely fastened to the milling machine table. Standard Parts Co.
- 7. Fixture components • Clamps • Clamps counteract forces from the feed of the table and rotation of the cutter. American Drill Bushing Co.
- 8. Fixture components • Set blocks • Cutter set blocks are mounted on the fixture to properly position the milling cutter in relation to the workpiece.
- 10. • Detailed design of locators • Detailed design of clamps • Detailed design of supports • Positions of locators • Positions of clamps • Positions of supports, if any • Type of locators • Type of clamps • Type of supports • Clamping forces and sequence The following outputs are included in the fixture element design:
- 11. Fixture Design Criteria • Design specifications • Factory standards • Ease of use and safety • Economy
- 12. Body In White (BIW) Fixtures Example : Fixture For Welding
- 13. Various Aspects Of Fixture Design
- 14. BIW – Weld Fixtures Design Process/Methodology . Different Types of Welding Fixture Units. Design Inputs. Design Outputs.
- 15. Design Input Functional and Performance Requirements. Car Product. System Layout. Tool Information Sheet. Weld Study Information. Miscellaneous Information.
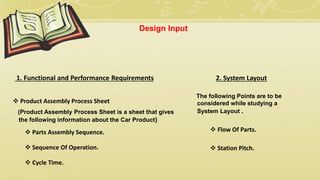
- 16. Design Input 1. Functional and Performance Requirements Product Assembly Process Sheet (Product Assembly Process Sheet is a sheet that gives the following information about the Car Product) Parts Assembly Sequence. Sequence Of Operation. Cycle Time. 2. System Layout The following Points are to be considered while studying a System Layout . Flow Of Parts. Station Pitch.
- 17. 3. Car Product The following Points are to be considered for the Car Product . GD&T Sheet. Part List. CAD Files of the car part. Design Input 4. Tool Information Sheet The Tool Information Sheet consists of the following. Tool Summary. Tool Content Sheet .
- 18. 5. Weld Study Information The Weld Study Information consists of the following. Welding Spots. Welding Guns. Design Input 6. Miscellaneous Information Customer preferences. Standard parts to be used. Informations derived from previous Designs and Development . Title Sheet Informations to be filled.
- 19. STAGE 1 Study the System Layout thoroughly. Reviewing Customer Input Data. Determine the No. of Tools required. Study the GD &T Sheet. Study the PLP position. Rough concept of tool. Design Methodology STAGE 2 Retrieve Car Part. Create Keysheet ( Final Tool / Station with all the Units ). Determine the Base Height from the Car part surface. Check for interference with adjacent units or Tools. Cut final sections and offset metal thickness .
- 20. STAGE 3 Retrieve Customer approved Standard sheets. Detail the unit according to the customer specification. Fill out Title Block Information . Create BOM . Create LAYOUT . Create all necessary Views . Fully Dimension all the Details . Design Methodology STAGE 4 Review information ,Customer input data and Key sheet. Complete check. Updating the errors. Back Check. Plot job for Check.
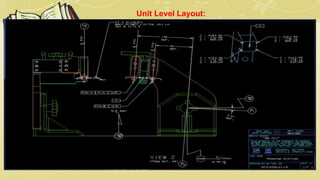
- 21. Design Output 3D Model & 2D Drawings Non Unitized Tools. Unitized Tools require 2 types of drawing sheets. 1. Key sheets. 2. Layout Sheets. 3. Part Detailing's. Tool Level detailing i.e. Key Sheet Layout Unit Level Detailing i.e. Layout & BOM Part Level Detailing
- 22. Type of Welding Fixtures Units 1) CLAMP UNIT. 2) PIN UNIT. 3) REST UNIT. 4) COMBINATION OF CLAMP & REST UNIT. 5) DUMP UNIT.
- 23. Typical Clamp Unit CYLINDICATOR SUB-PLATE RISER FLOW CONTROL CYLINDER L-BLOCK NC-BLOCK CLAMP ARM BLADE
- 24. A COMBINED LOCATING, CLAMPING AND RESTING UNIT RISER BRACKET PIN PROXIMITY SWITCH
- 25. A Typical Welding fixture-after assembly
- 26. A Typical Welding fixture-in shop floor Locating Pin Unit Clamping Unit Weld Gun Robot Welding Electrodes Car Part
- 28. Thanks
- 29. Design Example :
- 39. Unit BOM (Make Parts):
- 40. Thanks