Black hole ppt
- 2. INDEX • Introduction to Black Holes • What are Black Holes • How are Black Holes created • Types of Black Holes • Parts of Black Holes
- 3. 1.INTRODUCTION • The first time the idea was proposed in 1790 by laplace and john michell • They called it invisible star • Basic idea through newton`s first law • Einstein`s prediction in 1915 • In 1967 it was named black hole
- 4. 2.WHAT ARE BLACK HOLES? • A black hole is a great amount of matter packed in a very small area . • It is a place in space which have such gravitational field , that nothing , not even light can escape • we can`t observe it directly • It is observed by the effects on nearby matter from it • It radiate all types of radiations
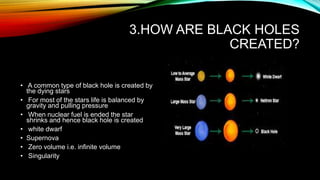
- 5. 3.HOW ARE BLACK HOLES CREATED? • A common type of black hole is created by the dying stars • For most of the stars life is balanced by gravity and pulling pressure • When nuclear fuel is ended the star shrinks and hence black hole is created • white dwarf • Supernova • Zero volume i.e. infinite volume • Singularity
- 6. 4.TYPES OF BLACK HOLES Mainly there are three types of black holes • 1: Stellar black holes • 2: Supermassive black holes • 3: Miniature black holes
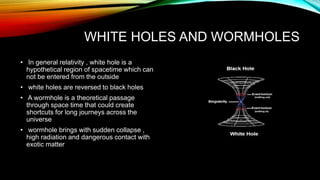
- 7. WHITE HOLES AND WORMHOLES • In general relativity , white hole is a hypothetical region of spacetime which can not be entered from the outside • white holes are reversed to black holes • A wormhole is a theoretical passage through space time that could create shortcuts for long journeys across the universe • wormhole brings with sudden collapse , high radiation and dangerous contact with exotic matter
- 8. 5.PARTS OF A BLACK HOLE The Event Horizon: This is the part of the black hole where nothing can get out. It is usually defined as a big sphere that surrounds the black hole , and which absorbs any material including light.
- 9. S The Singularity: This the part of black hole in which all the mass of the black hole has been compressed to a very small space. As a result, the singularity has almost infinite density
- 10. The Accretion Disk An accretion disk is a structure formed by diffused material in orbital motion around a massive central body. Gravitational and frictional forces increase the temperature of material that causes emission of electromagnetic radiation The Ergosphere The ergosphere is a region located outside a rotating black holes`s outer event horizon. It is theoretically possible that in this region mass and energy can be extracted The Schwarzschild radius This is the event horizon`s radius . It is the radius at which the escape velocity is equal to the velocity of light. R=2GM/C^2
- 11. CURIOUS FACTS ABOUT BLACK HOLES • They can explote • They fire intergalactic death rays • It is not their mass, it is their size what matters • Black holes disort space time • Objects appear to freeze near a black hole • Black holes eventually evaporate over time • A 1100 decibel sound would create a black hole with a diameter larger than the observable universe
- 12. HAWKING RADIATION • Hawking radiation is blackbody radiation that is predicted to be released by black holes , due to quantum effects near the event horizon . • Hawking radiation reduces the mass and energy of black holes and is therefore also known as black hole evaporation Because of this, black holes that do not gain mass through other means are expected to shrink and ultimately vanish.
- 13. REFERANCES • https://www.nasa.gov/audience/forstudents/k-4/stories/.../what-is-a-black-hole- k4.html • https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black_hole • https://www.space.com › Science & Astronomy