Business agility
- 1. Agile 101 What is Business Agility? Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 2. Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 3. An Idea! Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 4. An Idea... Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 5. An Idea... ...you’ve been paid for! Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 6. What is Business Agility? generating validation that the developing getting paid the idea idea is a good one the idea for that idea Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 7. What is Business Agility? generating validation that the developing getting paid the idea idea is a good one the idea for that idea BUSINESS AGILITY = OPTIMIZE THIS PROCESS! Wednesday, June 15, 2011
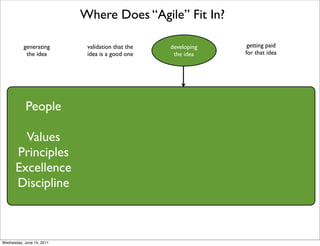
- 8. Where Does “Agile” Fit In? generating validation that the developing getting paid the idea idea is a good one the idea for that idea Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 9. Where Does “Agile” Fit In? generating validation that the developing getting paid the idea idea is a good one the idea for that idea People Values Principles Excellence Discipline Wednesday, June 15, 2011
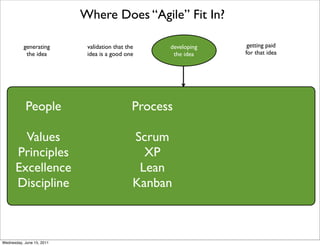
- 10. Where Does “Agile” Fit In? generating validation that the developing getting paid the idea idea is a good one the idea for that idea People Process Values Scrum Principles XP Excellence Lean Discipline Kanban Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 11. Where Does “Agile” Fit In? generating validation that the developing getting paid the idea idea is a good one the idea for that idea People Process Technical Values Scrum TDD Principles XP Pair Programming Excellence Lean Refactoring Discipline Kanban Test Automation Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 12. Where Does “Agile” Fit In? generating validation that the developing getting paid the idea idea is a good one the idea for that idea People Process Technical Values Scrum TDD Principles XP Pair Programming Excellence Lean Refactoring Discipline Kanban Test Automation not enough! Wednesday, June 15, 2011
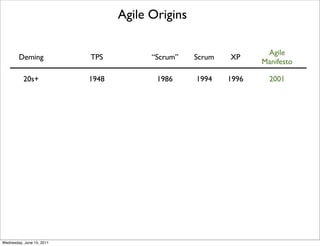
- 13. Agile Origins Agile Deming TPS “Scrum” Scrum XP Manifesto 20s+ 1948 1986 1994 1996 2001 Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 14. Agile Origins Agile Deming TPS “Scrum” Scrum XP Manifesto 20s+ 1948 1986 1994 1996 2001 Individuals and Interactions over Processes and Tools Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 15. Agile Origins Agile Deming TPS “Scrum” Scrum XP Manifesto 20s+ 1948 1986 1994 1996 2001 Individuals and Interactions over Processes and Tools Working Software over Comprehensive Documentation Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 16. Agile Origins Agile Deming TPS “Scrum” Scrum XP Manifesto 20s+ 1948 1986 1994 1996 2001 Individuals and Interactions over Processes and Tools Working Software over Comprehensive Documentation Customer Collaboration over Contract Negotiation Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 17. Agile Origins Agile Deming TPS “Scrum” Scrum XP Manifesto 20s+ 1948 1986 1994 1996 2001 Individuals and Interactions over Processes and Tools Working Software over Comprehensive Documentation Customer Collaboration over Contract Negotiation Responding to Change over Following a Plan Wednesday, June 15, 2011
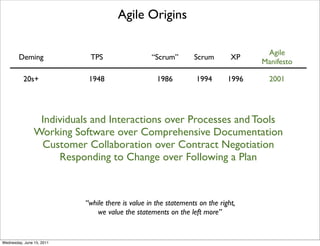
- 18. Agile Origins Agile Deming TPS “Scrum” Scrum XP Manifesto 20s+ 1948 1986 1994 1996 2001 Individuals and Interactions over Processes and Tools Working Software over Comprehensive Documentation Customer Collaboration over Contract Negotiation Responding to Change over Following a Plan “while there is value in the statements on the right, we value the statements on the left more” Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 19. What’s the Difference? Analysis Design Build Test Release 6 month traditional or “waterfall” project Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 20. What’s the Difference? Analysis Design Build Test Release 6 month traditional or “waterfall” project A A A A D D D release D Future B B and B Sprints B feedback! T T T T Sprint 2 Sprint 4 Sprint 1 Sprint 3 (2 months) (1 month) 6 month Agile project using Scrum/XP or Iterative process (2 Week Sprints) Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 21. What’s the Difference? Analysis Design Build Test Release 6 month traditional or “waterfall” project A A A A Benefits: - release working software earlier D D - validate your idea is worth D release D money earlier - get the software in the hands of Future B B and B Sprints real users earlier - no phases or handoffs, use cross- B feedback! functional teams - do ‘just enough’ planning to get T T T T started Sprint 2 Sprint 4 Sprint 1 Sprint 3 (2 months) (1 month) 6 month Agile project using Scrum/XP or Iterative process (2 Week Sprints) Wednesday, June 15, 2011
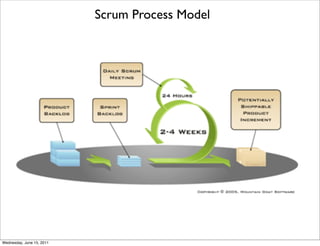
- 22. Scrum Process Model Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 23. How Are Companies Getting Agile? Scrum - simple, open and pour Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 24. How Are Companies Getting Agile? Scrum - simple, open and pour XP Practices - need more skill & precision Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 25. How Are Companies Getting Agile? Scrum - simple, open and pour XP Practices - need more skill & precision Lean/Kanban - need the basics first Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 26. Why Adopt Agile?* Top 3 Reasons for Adopting Agile: 37% cite faster time to market as the reason 36% cite enhancing ability to manage priorities 27% cite increased productivity Bottom 3 Reasons: 10% Reduce Cost/Improve Morale 8% Improve Engineering Discipline 5% Manage Distributed Teams * Version One 2010 Agile Survey (5th Year) Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 27. Why Agile Adoption is Failing* Top 3 Reasons for Failure 51% cite in-ability to change Org Culture 40% General Resistance to Change/Lack of Agile Skills 34% Management Support Bottom 3 Reasons: 16% Perceived Time to Transition 13% Budget Constraints 12% None * Version One 2010 Agile Survey (5th Year) 11 Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 28. Agile War Stories Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 29. 1 – Start-Up in Turmoil Situation •CTO Fired, New CEO, CTO, Director of Dev •$24M VC money invested •Six year old company •Mature product Objective for Agile Implementation •Unclear problem definition •Unclear objectives •Belief that the process would save the day Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 30. 1 – Start-Up in Turmoil Actions •Implemented Agile (XP) •No Agile consultants •No training •No software to support the process •Executive support (sort of) •One set of story cards held by the director Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 31. 1 – Start-Up in Turmoil Results •Weak management buy-in •Weak team buy-in •XP abandoned within four months •Returned to previous chaotic approach (entropy) Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 32. 1 – Start-Up in Turmoil Analysis •Depended on heroics of individuals •Project(s) succeeded – neither because of, or in spite of agile •Agile is not the cure for cultural, management and organizational problems •Management buy-in critical •Don’t blame the developers Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 33. 2 – Start-Up in Turmoil Situation •Very early stage (pre-commercialization) •CTO fired •Weak, ineffective, geographically dispersed team •Project very much behind, and off target •Huge pressures to deliver before the money ran out Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 34. 2 – Start-Up in Turmoil Objectives •Unclear objectives other than “get it done as quickly as possible” •Unclear definition of the problems •Belief that the process would fix the problems and make development quicker Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 35. 2 – Start-Up in Turmoil Action •Implemented Agile (Scrum) in a very lightweight fashion •Brand new team (A players) •No Agile consultants •No training •No software to support the process •Executive support (sort of) •Daily Scrum calls Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 36. 2 – Start-Up in Turmoil Results •Maintained the very lightweight Agile process •Achieved all project results •Management used the notion of Agile as an excuse for chaotic injections of new and changing requirements into the flow •Management did not respect the process and used inappropriate comparisons/ metrics Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 37. 2 – Start-Up in Turmoil Analysis •Project(s) succeeded because of heroics – not because of, or in spite of agile •Agile is not a cure for a weak team, poor management, poor planning and lack of clear objectives Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 38. 3. Established Small Company Situation •Scrum already in place •Recent corporate split into two separate entities (reshaping of business) •Went through 75% downsizing - Outgoing Dev Manager •Software tools already in place (Rally Dev) •Established products but Small customer base •Losing market share because of out-dated products and more competition •Process had become rigid, not driven by the development team •Overbearing CEO who constantly interfered and overruled team decisions Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 39. 3. Established Small Company Objectives •Belief that the process would fix the problems and make development faster •CEO a process wonk (Hidden Agenda) – Process was the objective, not a tool, but did not fully support Agile Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 40. 3. Established Small Company Action •Implemented Agile (Scrum) in a very light fashion because of team reductions •Some training •Executive support (sort of) •Daily Scrums •Sprints •Retrospectives Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 41. 3. Established Small Company Results –Ruthless adherence to the schedule by CEO (Process was the stick) –Process became the mechanism for control and the excuse for interference –CEO overruled almost every team decision –Met all development objectives –CEO abandoned the project and implemented his vision. That project was more than a year late Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 42. 3. Established Small Company Analysis •Process (Agile) is not to be used as a stick •To be effective, Agile must involve the team in decisions Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 43. 4. Start-Up (Two Years Old) Situation •Good people in the organization but revolving door •Overbearing CEO who constantly interfered and overruled team decisions •Recent launch of first product •Excellent development team •No process •CEO’s idea du jour •Constant pivots and reorganization of priorities by CEO •25 products and projects and only five developers Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 44. 4. Start-Up (Two Years Old) Objectives •Make the team faster •Demonstrate to potential investors that there was an effective process •Shield development team from CEO (team) •Establish priorities (team) •Team autonomy (team) •Huge pressures to produce as quickly as possible •Belief that the process would fix the problems and make development faster Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 45. 4. Start-Up (Two Years Old) Action •Implemented Agile (Scrum) •Got training for the entire team •Story cards •Story boards around the office (high visibility) •Daily Scrums •Sprints •Retrospectives Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 46. 4. Start-Up (Two Years Old) Results •Overall – very successful •Significant and very public buy-in from CEO •Significant team buy-in •Visibility of the process helped CEO understand why he couldn’t have everything all at once •Able to contain the CEO •Targets were defined, negotiated and achieved •Team much happier and more effective •Process adopted across the company Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 47. 4. Start-Up (Two Years Old) Analysis •Agile can be very successful •Openness of the process was important •Public buy-in of CEO was critical Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 48. Agile War Story Summary • Will not fix a broken organization • Agile is not a big stick for control of a team • Executive support is essential • Team must benefit • Process must be transparent • Process must be inclusive • Software tools are not needed – menu cards work fine • Get training Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 49. Where Can You Start? Understand: - the reasons you want to use Agile. What’s your business goal? - your culture, organization structure and the people in your organization. - it’s hard, you will need to learn a lot! - “metrics” are the wrong thing to start with! - you cannot ‘measure’ Agile success in any other term other than business outcomes. Educate: - find local Agile User Groups/Events (XP Toronto, Agile Toronto Tour) - read some books (Succeeding with Agile by Mike Cohn, Implementing Lean Software Development by Mary/Tom Poppendieck - get training (certification is less important than learning something!) - hire a consultant Reflect: - figure out what to measure, measure it and adjust - do retrospectives across all Organizational levels - is the Agile implementation strategy you picked working? 33 Wednesday, June 15, 2011
- 50. Thank You! • Michael Lant, CTO @ ENC Security Systems ( www.michaellant.com) • Jason Little, Product Owner/Agile Coach @ Q4 Web Systems ( www.agilecoach.ca ) • look for a blog post on SiliconHalton.com! 34 Wednesday, June 15, 2011