Business model
- 2. Outline 1. What isaBusinessModel? 2. Whydocompaniesneedit? 3. Howcanyoumakeone? 4. Let’smakeone 5. Different typesof BusinessModel
- 3. ● The search to define what Business Model is goes back to 1994. ● Peter Drucker published his theory of businesses in an HBR article describing what should a business do and don’t. ● In the middle of the 2002 dot com crisis, Joan Magretta built on Drucker’s business definition to exclaim that business models are “at heart, stories. Stories that explain how enterprises work. A good business model answers Peter Drucker’s age-old questions: ‘Who is the customer? And what does the customer value?” ● It can be described through 9 building blocks: Customer Segments, Value Propositions, Channels, Customer Relationships, Revenue Streams, Key Resources, Key Activities, Key Partnerships & Cost Structure.
- 4. You may call it a framework or just a set of points about key areas of your business. What is important to know is - It describes how an organisation creates, delivers and captures value. What’ s Value??
- 5. How can you make one??? Or Howdoesit looklike?
- 6. ● A Template having 9 blocks to see the business model of the company in just 1 page. Business Model Canvas
- 7. ● A Template having 9 blocks to see the business model of the company in just 1 page. Business Model Canvas 05 Key Partners 06 Key Activities 02 Value Proposition 04 Customer Relationships 01 Customer Segments 07 Key Resources 03 Channels 08 Cost Structures 09 Revenue Streams
- 8. 05 Key Partners Which external supporters are essential to the model? The people and organisations that take some of the responsibility off your shoulders. 06 Key Activities The processes and tasks that must be completed in order for our customers to be served. 02 Value Proposition What value shall you deliver to them? 04 Customer Relationships How will they interact with your business ? 01 Customer Segments Who are your Customers? 07 Key Resources People, places, machines, patents and intangible assets that are used every week. 03 Channels Where will you find your Customers? 08 Cost Structures How much we spend, how frequently we spend it, and whether it changes as sales go up and down. 09 Revenue Streams The prices each type of customer typically pays, as well as how frequently they come back.
- 9. Step 1: Customer Segments and Value Propositions Customer is the kings and we do really believe that. We will try to answer hee who we are serving and what are we serving? Step 2: Channels and Customer Relationships Now that we have a clear picture of who we’re serving and how we’ll delight them, we get to design three things: how we acquire them, how we keep them, and how we interact with them. Step 3: Key Resources, Key Activities and Key Partners These three boxes describe how the business will work “behind the scenes” – all of the operational components that make the Value Propositions a reality. We want to list all of the vital ingredients, important processes and invaluable allies that enable our business to exist. Step 4: Cost Structure and Revenue Streams The bottom line of the canvas represents the bottom line of your business: Money in, money out, hopefully some money left over. We want to understand the ways in which money moves through the business. That means understanding the quantities (how our costs/prices are set) and frequencies (how often we get repeat customers/bills). 1. Desirability 3. Viability 2. Feasibility
- 10. KP Sellers Or Manufacturers Logistic partners, Inventory Partners, Aws KA Website management, Operations like inventory management, delivery, after sales support. AAAERR VP Time saving Discoverability Pricing Door-step delivery Post purchase services CR Membership Self served Customer care Delivery executives CS Youths Anyone who uses Internet Middle n High income class Youngsters Working Professionals advertisers KR Data, employees C App Google ads TV ads Tie ups with other channels COSTS IT ops, marketing, outsourcing costs, employee, costs, R Commission per sale, Ad business. Let’s make one! for AmazonECommerce Business
- 12. Different typesof Businessmodels Based on - 1. Pricing 2. Stakeholders 3. As many parameters as you want
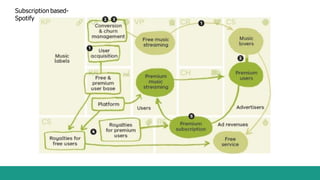
- 13. Based on Pricing 1. Advertising - The goal is to generate revenues by selling advertising space. Slightly more complex as the company first need to invest in order to create a large audience before it can attract advertisers. 2. Freemium - 3. Subscription - The company receives revenues from its subscribers at regular intervals. The Drawback with it is that it often takes several months to recover the subscriber acquisition costs leading to a lower cash generation at the beginning of the cycle. 4. Commission based - 5. Accessory Based - The company offers 2 versions of its product. A free version with a limited set of features which goals are either to raise awareness about the product or to create a network effect. And a paid version, comprising more features, from which it can generate enough margin to cover the cost of the free users. The company acts as an intermediary between the seller and the buyer and takes a cut of every sell it helps generate. Such kind of businesses are called Multi sided markets/ Platform or Aggregators. The company offers one product for free or at a price close to its production cost and generates a profit on the sale of accessories.
- 14. Ad based Business Models - Say Google
- 16. Freemium Bizz Model - Flickr
- 17. Questions?