C dna
- 1. CDNA AND GENOMIC LIBRARIES: CONSTRUCTION AND SCREENING RE-DESIGN AND CONTRUCT BY T MICHAEL ADEDAYO
- 2. Outline • INTRODUCTION • DEFINITION OF cDNA • CONSTRUCTION AND SCREENING OF cDNA LIBRARY. • DEFINITION OF GENOMIC LIBRARY • CONSTRUCTION AND SCREENING OF GENOMIC LIBRARY. • CONCLUSION.
- 3. Introduction • A DNA library is a collection of DNA clones, gathered together as a source of DNA for sequencing, gene discovery, or gene function studies. • There are two types of DNA libraries: cDNA and Genomic
- 4. cDNA Library • A cDNA library is a set of cDNA clones prepared from the mRNAs isolated from a particular type of tissue. • The cDNA library contains only complementary DNA molecules synthesized from mRNA molecules in a cell. This molecules represents all the gene that are expressed in the cell at different stage of its development.
- 5. CONSTRUCTION cDNA libraries are constructed by synthesizing cDNA from purified cellular mRNA via oligo(dT)-cellulose chromatography. This is done to recover the poly (A) mRNA so as to anneal with the oligo(dT) chains.
- 6. Fig 1. Isolation of Eukaryotic mRNA using oligo(dT)-cellulose chromatography
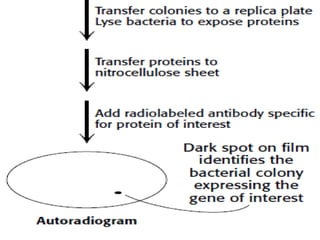
- 8. SCREENING • A probe is a piece of DNA or RNA used to detect specific nucleic acid sequences by hybridization (binding of two nucleic acid chains by base pairing). Oligonucleotide can be used as a probe. • They are radioactively labeled so that the hybridized nucleic acid can be identified by autoradiography.
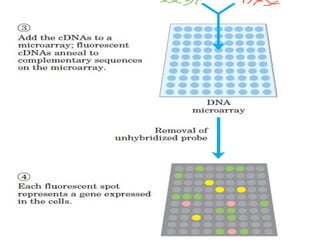
- 9. Two general approaches are available for screening libraries to identify clones carrying a gene or other DNA region of interest: (1) Detection with oligonucleotide probes that bind to the clone of interest and (2)Detection based on expression of the encoded protein
- 10. fig 3.a plasmid cDNA library for screening
- 12. FIG 4.To detect the expression of encoded protein
- 14. Genomic Library •Is the largest type of library which consist of the complete genome of a particular organism which is cleaved into thousands of fragments, and all the fragments are cloned by insertion into a cloning vector. • A collection of clones that collectively represent all the DNA sequences in the genome of a particular organism.
- 15. CONSTRUCTION The first step in preparing a genomic library is partial digestion of the DNA by restriction endonucleases, such that any given sequence will appear in fragments of a range of sizes and is represented in the library.
- 16. Construction cont. Secondly, the cloning vector, such as a BAC or YAC plasmid, is cleaved with the same restriction endonuclease and ligated to the genomic DNA fragments. Thereafter ligated DNA mixture is then used to transform bacterial or yeast cells to produce a library of cell types, each type harboring a different recombinant DNA molecule.
- 17. Construction cont. Each transformed bacterium or yeast cell grows into a colony, or “clone,” of identical cells, each cell bearing the same recombinant plasmid.
- 18. The ability to clone such large DNA fragments raise the possibility of the Genomic library, but it has been found that there is a problem as to what number of clones are required to construct a genomic library. A solution has been provided with the use of a formular: N=ln(1-P)/ln(1-a/b) which enhances the capacity of constructing a genomic library, and also ease the problem of screening.(i.e. the higher the fragments, the smaller the number of clones).
- 19. Species Genome Size(bp) Number of clones 17kb fragments 35kb fragments Escherichia coli 4.8x106 850 410 S. cerevisiae 1.4x107 2500 1200 Tomato 7.0x108 123500 59000 Man 3.0x109 529000 257000 Frog 2.3x1010 4053000 1969000
- 20. Fig 6.showing the genomic library construction
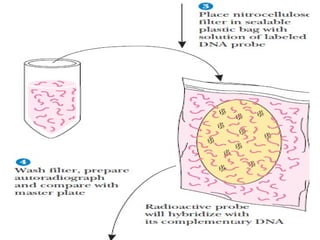
- 21. SCREENING A common method of screening is the plasmid-based genomic libraries which is to carry out a colony hybridization experiment. host bacteria containing either a plasmid based or bacteriophage-based library are plated out on a petri dish and allowed to grow overnight to form colonies
- 22. Fig 5.shows the screening process in genomic library.
- 25. CONCLUSION In conclusion, Genomic DNA segments can be organized in libraries known as genomic libraries and cDNA libraries with a wide range of designs and purposes.