Business Planning for Social Enterprise Cambodia April 2015
- 1. Business Planning for Social Enterprise A Presentation for Social Enterprise Cambodia Conference 4 April 2015 William P. Kittredge, PhD President, Cervelet Consulting
- 2. Why Have a Business Plan? Value lies in the process of researching and thinking about your business in a systematic way The act and learning process of making a business plan may make you a better entrepreneur Allows you to avoid big mistakes by developing a game plan1 1 http://www.inc.com/articles/201107/5-reasons-why-you-need-a-business-plan.html
- 3. Why Have a Business Plan? One survey study shows that startup companies who completed business plans were almost twice as likely to effectively expand their businesses or acquire capital compared to those who didn’t.2 2 http://smallbiztrends.com/2010/06/business-plan-success-twice-as-likely.html
- 7. Products and Services What factors will give your product or services competitive advantage or disadvantage? What are the pricing, fee, or leasing structures of your products or services?
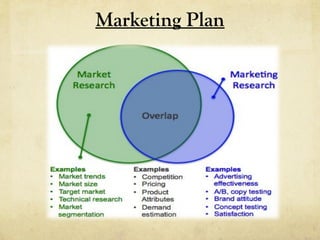
- 10. Marketing Plan Market Research Why? Make sure your business is on track How? Public information & gathering your own data Economics: What is the total size of your market? What are its growth potential and opportunities? What barriers to entry do face? Product For each product or service What are the most important features and why? What will the product do for the customer?
- 11. Marketing Plan Customers: Who are your target customers (businesses or consumers)? What are their characteristics (demographics)? Competition What products and companies will compete with you? How will your Competitive Analysis look?
- 12. Marketing Plan
- 13. Marketing Plan Niche How does your company fit into the world? Strategy Promotion: How will you get the word out to customers? Promotional Budget: How much will it cost to get the items needed for promotion? Location: Is your location important to costumers? Is it convenient? Distribution Channels: How will you sell your products/services?
- 14. Marketing Plan: Sales Forecast Spreadsheet Attaches numbers to your plan Based on historical sales, marketing strategies, market research, industry data Two forecasts: “best guess” and “worst case”
- 16. Operational Plan
- 18. Management and Organization Who will manage the business on a day to day basis? What experience does that person bring to the business? What special and distinctive competencies? What is the plan if this person is lost in incapacitated?
- 19. Management and Organization Identify and list professional and advisory support – Board of directors – Management advisory board – Attorney – Accountant – Insurance agent – Banker – Consultant(s) – Mentors and key advisors
- 21. Personal Financial Statement Shows assets and liabilities held outside the business and personal net worth.
- 23. Startup Expenses and Capitalization • Estimate expenses. Where you need sufficient capital? • Your startup business may cost more than you anticipate • Add “padding” to the budget • Add separate “contingencies” to account for the unexpected • Explain your research, sources, amounts, and terms of proposed loans. • Explain how much each investor contributes and what percent of ownership each will have.
- 24. Startup Expenses and Capitalization Spreadsheet
- 26. Financial Plan • 12-month profit and loss projection What it will take to make a profit and be successful? • 3- year profit and loss projection Optional projection if company wants to forecast longer term • Projected cash flow Plan how much you need before startup for preliminary expenses, operating expenses, and reserves
- 27. Financial Plan Profit and Loss Projections
- 28. Financial Plan • Opening day balance sheet what assets the company holds, what its liabilities are • Break-even analysis predicts sales volume at a given price required to recover total costs
- 29. Financial Plan
- 30. Financial Plan Break-Even Point Q = Fixed Cost / (Unit Price - Variable Unit Cost)
- 32. Appendices • Include details, studies, graphs and charts in your business plan, for example: • Brochures and advertising materials • Industry and market research studies • Blueprints and plans • Maps and photos of location • List of equipment owned and to be purchased • Copies of leases and contracts • Letters of support • List of assets available for a loan
- 34. Refining the Plan For Raising Capital Bankers: Amount of loan, how the funds will be used, what will it accomplish, requested payment terms Investors: Funds needed for short term and long term, how the funds will be used, estimated return on investment, exit strategy for investors, financial reporting
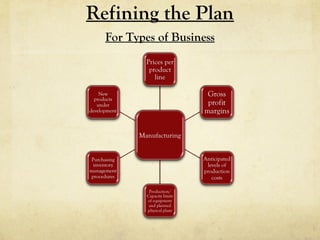
- 35. Refining the Plan For Types of Business
- 36. Refining the Plan For Types of Business
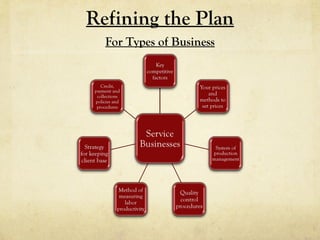
- 37. Refining the Plan For Types of Business
- 38. Refining the Plan For Types of Business
- 39. Cervelet Management & Strategy Consultants, LLC Www.cerveletconsulting.com We have developed some expertise assisting social enterprises in Cambodia and Thailand. If you have further questions or would like to inquire about our business planning or social investor recruiting services, please contact us via our webpage or through Facebook.
Editor's Notes
- Opening day balance sheet what assets the company holds, what its liabilities are Assets – Liabilities= owner’s equity Startup expenses and capitalization spreadsheet Break-even analysis predicts sales volume at a given price required to recover total costs
- Planned production levels •Anticipated levels of direct production costs and indirect (overhead) costs—how do these compare to industry averages (if available)? •Prices per product line •Gross profit margin, overall and for each product line •Production/capacity limits of planned physical plant •Production/capacity limits of equipment •Purchasing and inventory management procedures •New products under development or anticipated to come online after startup