carbon fibre
- 2. Introduction History Future of carbon fiber Structure Types of carbon fiber Manufacturing of carbon fiber Properties Applications
- 3. A Material Consisting Of Thin, Strong Crystalline Filaments Of Carbon, Used As A Strengthening Material, Especially In Resins And Ceramics.
- 4. Currently, the United States of America uses nearly 60% of the world production of carbon fibers and the Japanese account for almost 50% of the world capacity for production. The largest producer of this fiber is Toray Industries of Japan.
- 5. Carbon Fibers Were Developed In The 1950s By Heating Strands Of Rayon Until They Carbonized. In The Early 1960s, A Process Was Developed Using Polyacrylonitrile As A Raw Material. During The 1970s, Experimental Work To Find Alternative Raw Materials Led To The Introduction Of Carbon Fibers Made From A Petroleum Pitch Derived From Oil Processing.
- 6. In 2009, Zyvex Technologies introduced carbon nanotube-reinforced polymer. Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced Polymer is several times stronger and tougher than Carbon fibre and was used in the manufacturing of air craft as a structural material.
- 7. The atomic structure of carbon fiber is similar to that of graphite, consisting of sheets of carbon atoms arranged in a regular hexagonal pattern (graphene sheets), the difference being in the way these sheets interlock.
- 9. Structural modal of carbon fiber
- 12. Pan type carbon fiber A type of the fiber produced by carbonization of PAN precursor (PAN:Polyacrylonitrile) Pitch Type Carbon Fiber: Another type of the fiber,produced by carbonization of oil/coal pitch precursor, Types
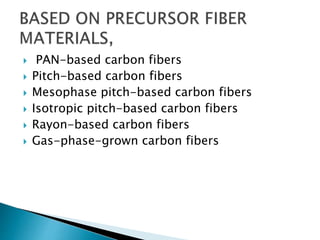
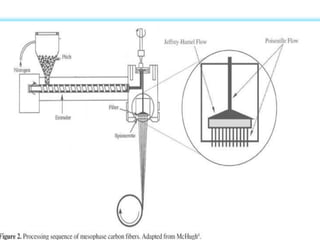
- 13. PAN-based carbon fibers Pitch-based carbon fibers Mesophase pitch-based carbon fibers Isotropic pitch-based carbon fibers Rayon-based carbon fibers Gas-phase-grown carbon fibers
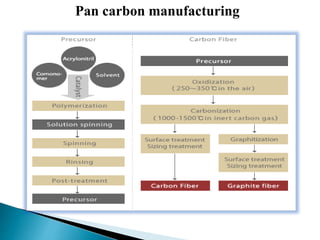
- 14. Manufacturing of carbon fiber:Manufacturing of carbon fiber:Manufacturing of carbon fiber: Manufacturing of carbon fiber
- 15. Each carbon filament is produced from a polymer such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN), rayon, or petroleum pitch, known as a precursor the precursor is first spun into filament yarns, using chemical and mechanical processes to initially align the polymer atoms in a way to enhance the final physical properties of the completed carbon fiber.
- 18. Manufacturing of carbon fiber The raw material used to make carbon fiber is called the precursor. About 90% of the carbon fibers produced are made from polyacrylonitrile (PAN). The remaining 10% are made from rayon or petroleum pitch .
- 20. Manufacturing challenges The need for more cost effective recovery and repair. Close control required to ensure consistent quality. Health and safety. Skin irritation. Breathing irritation.
- 21. Properties of carbon fibers Properties of carbon fibers High tensile strength. Low thermal expansion. Electrically and thermally conductors. Light weight and low density. Tensity : 1.8-2.4(kn/mm2) Density : 1.95 gm/cc Elongation at break: 0.5% Elasticity: Not good
- 22. Moisture Regain (MR%): 0% Ability to protest friction: Good Color: Black Lusture : Like silky Ability to protest heat : Good Effect of sunlight : no change in color Effect of bleaching : Sodiun hypochlorite slightly effect carbon fiber. Protection against flame : Excellent Protection ability against insectsn : Do not harm carbon fiber
- 23. Applications Civil Engineering Sports equipments Aerospace and Aircraft industry Acoustics Portable power Building and construction materials Fiber reinforced plastics