carboxylic acids.ppt
- 1. Qualitative tests, structure and uses of different carboxylic acids By Dr. Nidhi Gupta M.M. College of Pharmacy Maharishi Markandeshwar (Deemed to be University), Mullana, Ambala, Haryana, India
- 2. The following tests can be used to identify carboxylic acids: 1. Litmus Test Carboxylic acid turns blue litmus red. The hydroxyl group in carboxylic is far more acidic than that in alcohol. The dissociation of carboxylic acid is represented as:
- 3. 2. Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate Test Carboxylic acids reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate to produce carbon dioxide gas which can be seen in the form of a brisk effervescence. 3. Ester Test Carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol in presence of conc. sulphuric acid to form ester that is identified by the presence of a fruity smell.
- 4. Tests of amides: •Reaction of NaOH: Amides are decomposed by NaOH to evolve ammonia. The gas can be tested by a moist red litmus paper which is then turned blue. •Alkaline hydrolysis of aromatic amides to aromatic acid: The soluble sodium salt of aromatic acid formed from aromatic amides upon hydrolysis is regenerated as white precipitate in acidic medium.
- 5. •Biuret Reaction for aliphatic diamide: When aliphatic diamide is heated at a temperature above its melting point, ammonia is evolved and crystalline biuret is formed. This biuret in alkaline medium gives a violet colour with a drop of copper sulphate solution.
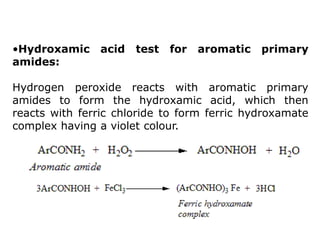
- 6. •Hydroxamic acid test for aromatic primary amides: Hydrogen peroxide reacts with aromatic primary amides to form the hydroxamic acid, which then reacts with ferric chloride to form ferric hydroxamate complex having a violet colour.
- 7. 3. Esters There is no simple test for an ester. Usually a colourless liquid with a pleasant 'odour'. Hydroxamic acid test R-CO-OR' + H2N-OH -> R-CO-NH-OH + R'-OH Esters react with hydroxylamine in the presence of sodium hydroxide to form the sodium salt of the corresponding hydroxamic acid. On acidification and addition of ferric chloride the magenta- coloured iron (III) complex of the hydroxamic acid is formed. It is always advisable to ensure that an unknown compound does not give a colour with iron (III) chloride before carrying out the hydroxamic acid test.
- 8. Structure of acetic acid
- 9. Uses of acetic acid • The largest single use of acetic acid is in the production of vinyl acetate monomer. • The major esters of acetic acid are commonly used as solvents for inks, paints and coatings. • Glacial acetic acid is an excellent polar protic solvent, as noted above. • Acetic acid injection into the tumor has been used to treat cancer
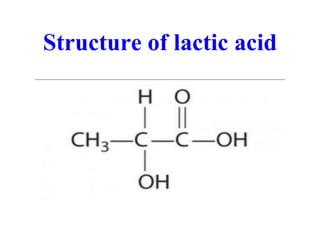
- 10. Structure of lactic acid
- 11. Uses of lactic acid • In medicine, lactate is one of the main components of lactated Ringer's solution and Hartmann's solution. • In industry, lactic acid fermentation is performed by lactic acid bacteria, which convert simple carbohydrates. • Lactic acid is used as a food preservative, curing agent, and flavoring agent.
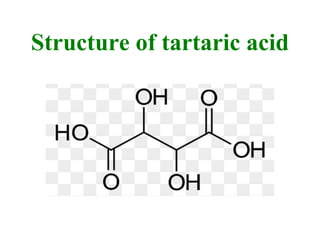
- 12. Structure of tartaric acid
- 13. Uses of tartaric acid • Tartaric acid is found in cream of tartar, which is used in cooking candies and frostings for cakes. • Tartaric acid is also found in baking powder, where it serves as the source of acid that reacts with sodium bicarbonate. • Industrial uses for tartaric acid include within the gold and silver plating process, tanning leather and making blue ink for blueprints.
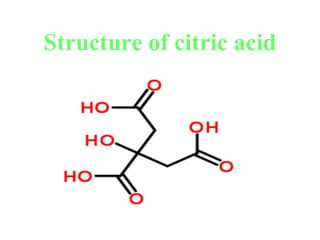
- 14. Structure of citric acid
- 15. Uses of citric acid • Citric acid is a weak organic acid found in citrus fruits. • It is a natural preservative and is also used to add an acidic (sour) taste to foods and soft drinks. • Citric acid’s chemical properties as a weak organic acid make it a powerful water softener. • Citric acid is a relatively common ingredient used in cosmetics products to balance the pH level according to Cosmetics Database.
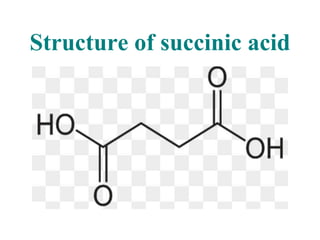
- 16. Structure of succinic acid
- 17. Uses of succinic acid • Succinic acid is a precursor to some polyesters and a component of some alkyd resins. • Succinic acid is used primarily as an acidity regulator in the food and beverage industry. • It is also available as a flavoring agent, contributing a somewhat sour and astringent component to umami taste. • As an excipient in pharmaceutical products, it is also used to control acidity or as a counter ion.
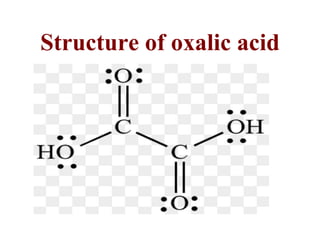
- 18. Structure of oxalic acid
- 19. Uses of oxalic acid • Oxalic acid is rubbed onto completed marble sculptures to seal the surface and introduce a shine. • Oxalic acid is used as a bleach for wood, removing black stains. • Oxalic acid is also used for the removal of rust. • Vaporized oxalic acid, or a 3.2% solution of oxalic acid in sugar syrup, is used by some beekeepers as a miticide against the parasitic varroa mite.
- 20. Structure of salicylic acid
- 21. Uses of salicylic acid • Salicylic acid causes shedding of the outer layer of skin. • Salicylic acid topical is used in the treatment of acne, dandruff, seborrhea, or psoriasis, and to remove corns, calluses, and warts. • Salicylic acid is used in the production of other pharmaceuticals, including 4-aminosalicylic acid, sandulpiride. • Salicylic acid is used as a food preservative, a bactericidal and an antiseptic.
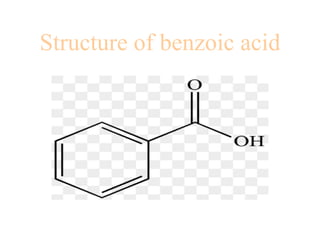
- 22. Structure of benzoic acid
- 23. Uses of benzoic acid • Benzoic acid is mainly consumed in the production of phenol by oxidative decarboxylation. • Benzoic acid is a constituent of Whitfield's ointment which is used for the treatment of fungal skin diseases such as tinea, ringworm. • In teaching laboratories, benzoic acid is a common standard for calibrating a bomb calorimeter. • Benzoic acid was used as an expectorant, analgesic.
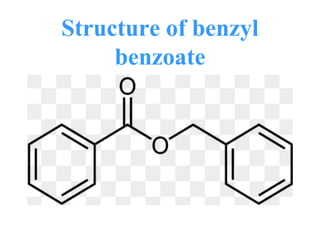
- 25. Uses of benzyl benzoate • Benzyl benzoate is an effective and inexpensive topical treatment for human scabies. • Benzyl benzoate is used as a repellent for chiggers, ticks, and mosquitoes. • It is also used as a dye carrier, solvent for cellulose derivatives, and fixative in the perfume industry.
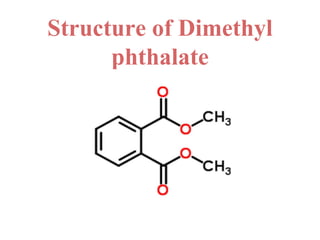
- 27. Uses of dimethyl phthalate • Dimethyl phthalate is used as an insect repellent for mosquitoes and flies. • It is also an ectoparasiticide and has many other uses, including in solid rocket propellants, and plastics. • Industry Uses • a) Finishing agents • b) Intermediates • c) Plasticizers • d) Processing aids, specific to petroleum production
- 29. Uses of methyl salicylate • This product is used to treat minor aches and pains of the muscles/joints. • It is used in high concentrations as a rubefacient and analgesic in deep heating liniments. • It is used as a bait for attracting male orchid bees for study, which apparently gather the chemical to synthesize pheromones. • It is used to clear plant or animal tissue samples of color.
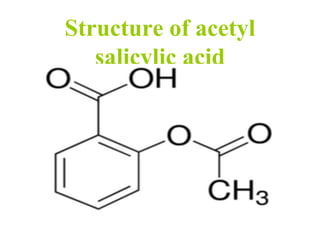
- 30. Structure of acetyl salicylic acid
- 31. Uses of acetyl salicylic acid • Aspirin is used in the treatment of a number of conditions, including fever, pain, rheumatic fever. • Aspirin is used as an anti-inflammatory agent for both acute and long-term inflammation. • Aspirin is thought to reduce the overall risk of both getting cancer and dying from cancer. • Low-dose aspirin supplementation has moderate benefits when used for prevention of pre-eclampsia.