Cell cycle reproduction lecture with turning point
- 1. Cell Reproduction Prokaryotes Bacteria Eukaryotes Plants & animals
- 2. Prokaryotes Lack a nucleus Have a single chromosome Reproduce by binary fission Include bacteria
- 3. Steps in Binary Fission Used by bacteria Cells increase their cell mass slightly DNA & cell components are replicated Each cell divides into 2 daughter cells
- 4. Binary Fission of Bacterial Cell
- 5. E. Coli Dividing by Binary Fission
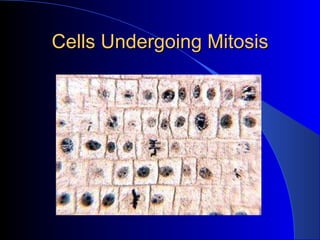
- 6. Eukaryotes Contain a nucleus & membrane bound organelles Asexually reproduce cells by mitosis
- 7. Cell Cycle Stages in growth & division G1 Phase S Phase G2 Phase M Phase Cytokinesis
- 8. G1 Phase First growth stage Cell increases in size Cell prepares to copy its DNA
- 9. Synthesis Phase Copying of all of DNA’s instructions Chromosomes duplicated
- 10. G2 Phase Time between DNA synthesis & mitosis Cell continues growing Needed proteins produced
- 11. M Phase Cell growth & protein production stop Cell’s energy used to make 2 daughter cells Called mitosis or karyokinesis (nuclear division)
- 12. Life Cycle of a Cell Mitosis is a cycle with n o beginning or end .
- 13. How do prokaryotes reproduce? Mitosis Meiosis Binary Fission Sexual Reproduction 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 14. Prokaryotes have: Mitochondria Chloroplasts Nucleus All of the above None of the above 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 15. Eukaryotes reproduce asexxually by: Mitosis Meiosis Binary Fission Binary Fusion 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 16. What happens in the G1 phase of the cell cycle? Cell growth Cell division Chromsome duplication DNA synthesis 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 17. What happens in the G2 phase of the cell cycle? DNA synthesis Cell division Chromsome duplication Protein Production 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 18. What happens in the M phase of the cell cycle? DNA synthesis Cell growth Chromsome duplication Makes 2 new cells 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 19. Interphase – Resting Stage (Not Really) Cells carrying on normal activities Chromosomes aren’t visible Cell metabolism is occurring Occurs before mitosis
- 20. Interphase
- 21. Stages of Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
- 23. Steps in Prophase DNA coils tightly & becomes visible as chromosomes Nuclear membrane disappears Nuceolus disappears Centrioles migrate to poles Spindle begins to form
- 24. Prophase
- 27. Steps in Metaphase Spindle fibers from centrioles attach to each chromosome Cell preparing to separate its chromosomes Cell aligns its chromosomes in the middle of the cell
- 28. Metaphase
- 29. Steps in Anaphase Cell chromosomes are separated Spindle fibers shorten so chromosomes pulled to ends of cell
- 30. Mitotic Spindle
- 31. Anaphase
- 32. Steps in Telophase Separation of chromosomes completed Cell Plate forms (plants) Cleavage furrow forms(animals) Nucleus & nucleolus reform Chromosomes uncoil
- 33. Telophase Plant Animal
- 34. Cytokinesis Occurs after chromosomes separate Forms two, identical daughter cells
- 35. Cytokinesis Cell Plate Forming in Plant Cells
- 36. Which of the following describes interphase? Chromosomes line up in the middle Chromosomes aren’t visible Chromosomes are pulled apart Chromosomes cross over 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 37. The nucleus reforms in: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 38. Chromosomes become visible in: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 39. Centrioles migrate to the poles in: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 40. Chromosomes separate in: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 41. Spindle fibers attach to chromsomes in: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 42. The nuclear membrane disappears in: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 43. The formation of 2 new identical daughter cells Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 44. Chromosomes line up in the middle in: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 45. Enter question text... Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
- 46. Cell plates form in plants during: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
Editor's Notes
- What happens in animal cells? Clevage furrow