Ch6 mfg pro.sel. & design
- 1. 1 Manufacturing Process Selection and Design
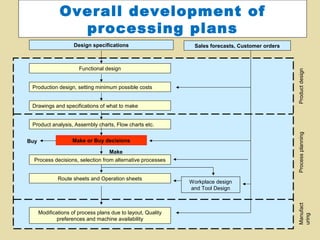
- 2. Overall development of processing plans Design specifications 2 Sales forecasts, Customer orders Product design Functional design Production design, setting minimum possible costs Drawings and specifications of what to make Make or Buy decisions Make Process decisions, selection from alternative processes Route sheets and Operation sheets Modifications of process plans due to layout, Quality preferences and machine availability Workplace design and Tool Design Manufact uring Buy Process planning Product analysis, Assembly charts, Flow charts etc.
- 3. Product-Flow Characteristics Types of Product Flow – Line Flow – Batch Flow – Project Flow Characteristics of Flows 4-3 4-3
- 4. Line Flow cut drill bend Task or work station Product flow paint
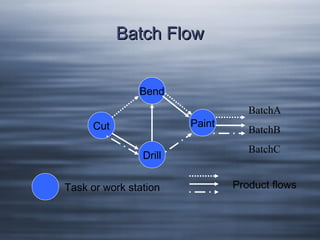
- 5. Batch Flow Bend Paint Cut Drill Task or work station BatchA BatchB BatchC Product flows
- 6. Classification by Type of Customer Order Make to Stock (MTS) Make to Order (MTO) Assemble to Order (ATO)
- 7. Process Selection Decisions Process characteristics matrix Factors affecting process choice
- 8. Factors Affecting Process Choice Market conditions and competition Capital requirements Labor supply and cost State of technology
- 9. 9 Schematic Layout of a Product focused Production System Raw Material 1 Components (procured) Components (made) 2 Assemblies 3 Sub Assemblies 2 Sub Assemblies 4 Finished Product Assemblies 3 Procured Sub Assemblies 3 1 - Component manufacturing Section 2 – Sub Assembling Section 3 – Assembling Section
- 10. 10 How to make a car : The production process in a Modern Car Plant includes lots of checks on quality and Extensive Treatment to Prevent Corrosion
- 11. 11 Process Manufacturing System- A Layout in a Cement Plant Limestone Crusher Hopper 1 Feeder 1 Iron One Hopper 2 Feeder 2 Clay Hopper 3 Feeder 3 Gympsum Blending Silo Firing Kiln Hopper 4 Feeder Dispatch Silo Raw Mill Hopper 5 Cement Mill Feeder
- 12. 12 Process Focused Production – A Schematic Layout Receiving raw materials storage Job A Foundry Welding and soldering Lathe section : : Job B : Painting and packaging : : : Quality control : : : : : :
- 13. 13 Types of Processes Conversion (ex. Iron to steel) Fabrication (ex. Cloth to clothes) Assembly (ex. Parts to components) Testing (ex. For quality of products)
- 14. 14 Process Flow Structures Job shop (Ex. Tailoring Shop ) Batch shop (Ex. Garment Manufacturer / Pharmaceutical Products) Assembly Line (ex. Automobile manufacturer) Continuous Flow (ex. Petroleum Products manufacturer)
- 15. Product-Process Strategy Strategy must consider not only the product or service, but also how to produce it. As many industries move through their product life cycles, they also move through a process life cycle. e.g. the traditional bread bakery vs. the modern automated bakery.
- 16. Product Life Cycle Stages Low volume-low standardization, one of a kind Multiple products, low volume Few major products, higher volume High volume-high standardization, commodity product
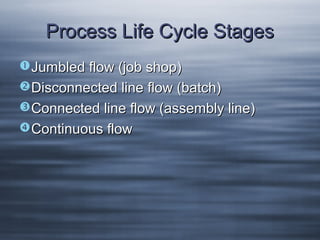
- 17. Process Life Cycle Stages Jumbled flow (job shop) Disconnected line flow (batch) Connected line flow (assembly line) Continuous flow
- 18. 18 I. Job Shop II. Batch III. Assembly Line IV. Continuous Flow Few High Low Multiple Major Volume, Volume, Products, Products, High One of a Low Higher StandardKind Volume Volume ization Commercial Printer French Restaurant Flexibility (High) Unit Cost (High) These are These are the major the major stages of stages of product product and and process process life cycles life cycles Heavy Equipment Automobile Assembly Burger King Sugar Refinery Flexibility (Low) Unit Cost (Low)
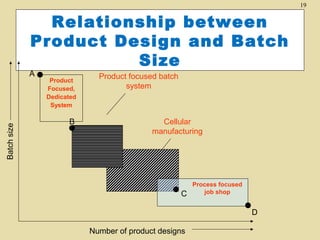
- 19. 19 Relationship between Product Design and Batch Size Batch size A Product Focused, Dedicated System B Product focused batch system Cellular manufacturing C Process focused job shop D Number of product designs
- 20. Manufacturing Process Flow Design A process flow design can be defined as a mapping of the specific processes that raw materials, parts, and subassemblies follow as they move through a plant The most common tools to conduct a process flow design include assembly drawings, assembly charts, and operation and route sheets 20
- 21. Example: Assembly Chart (Gozinto) 4 5 6 7 From Exhibit 5.14 From Exhibit 5.14 Lockring Spacer, detent spring SA-2 Rivets (2) A-2 Spring-detent A-5 Component/Assy Operation Inspection 21
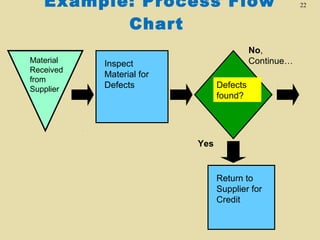
- 22. Example: Process Flow Chart Material Received from Supplier No, Continue… Inspect Material for Defects Defects found? Yes Return to Supplier for Credit 22
- 23. 23 Question Bowl What is the break-even in demand for a new process that costs Rs25,000 to install, will generate a service product that customers are willing to pay Rs500 per unit for, and whose labor and material costs for each unit is Rs100? a. 400 units b. 250 units c. 100 units d. 62.5 units e. None of the above Answer: d. 62.5 units (25,000/(500100)=62.5)
- 24. 24 Question Bowl Which of the following is an example of a Continuous Flow type of process flow structure? a. Fast food b. Grocery c. Hospitals d. Chemical company e. None of the above Answer: d. Chemical company
- 25. 25 Question Bowl Which type of process is by changing of raw materials into some specific form (such as sheet metal into a car fender)? a. Conversion b. Fabrication c. Assembly d. Testing e. None of the above Answer: b. Fabrication