Ch7 C++
- 1. // Functions that take no arguments #include <iostream> using namespace std; void function1(); void function2( void ); int main() { function1(); function2(); return 0; } void function1() { cout << "function1 takes no arguments" << endl; } void function2( void ) { cout << "function2 also takes no arguments" << endl; }
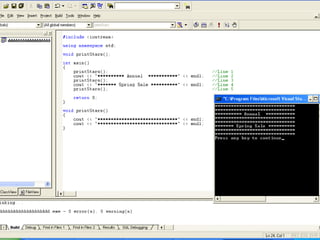
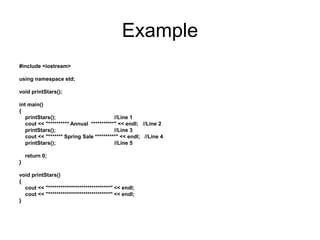
- 3. Example #include <iostream> using namespace std; void printStars(); int main() { printStars(); //Line 1 cout << "********** Annual ***********" << endl; //Line 2 printStars(); //Line 3 cout << "******* Spring Sale **********" << endl; //Line 4 printStars(); //Line 5 return 0; } void printStars() { cout << "******************************" << endl; cout << "******************************" << endl; }
- 5. solution #include<iostream> using namespace std; void square( int m ); // function prototype //it can be int square( int ); int main() { for ( int x = 1; x <= 10; x++ ) square( x ) ; //calling statement x is actual parameter cout << endl; return 0; } // Function definition void square( int y ) // Heading y is Formal Parameter { return y * y; // The return Statement }
- 6. #include<iostream> using namespace std; void square( int m ); // function prototype //it can be int square( int ); int main() { for ( int x = 1; x <= 10; x++ ) square( x ) ; //calling statement x is actual parameter cout << endl; return 0; } // Function definition void square( int y ) // Heading y is Formal Parameter { cout<< y * y<<endl; // The return Statement }
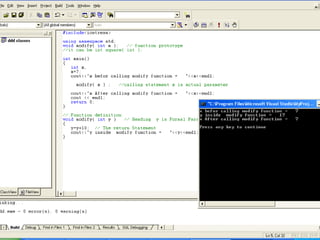
- 9. Modify (Value parameters) #include<iostream> using namespace std; void modify( int m ); // function prototype int main() { int x; x=7; cout<<"x befor calling modify function = "<<x<<endl; modify( x ) ; //calling statement x is actual parameter cout<<"x After calling modify function = "<<x<<endl; cout << endl; return 0; } // Function definition void modify( int y ) // Heading y is Formal Parameter { y=y+10; // The return Statement cout<<"y inside modify function = "<<y<<endl; }
- 11. Reference parameters #include<iostream> using namespace std; void modify( int &m ); // function prototype int main() { int x; x=7; cout<<"x befor calling modify function = "<<x<<endl; modify( x ) ; //calling statement x is actual parameter cout<<"x After calling modify function = "<<x<<endl; cout << endl; return 0; } // Function definition void modify( int &y ) // Heading y is Formal Parameter { y=y+10; // The return Statement cout<<"y inside modify function = "<<y<<endl; }
- 13. Reference // References must be initialized #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int x = 3, &y = x; // y is now an alias for x cout << "x = " << x << endl << "y = " << y << endl; y = 7; cout << "x = " << x << endl << "y = " << y << endl; return 0; }
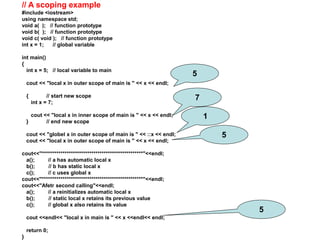
- 15. // A scoping example #include <iostream> using namespace std; void a( ); // function prototype void b( ); // function prototype void c( void ); // function prototype int x = 1; // global variable int main() { int x = 5; // local variable to main cout << "local x in outer scope of main is " << x << endl; { // start new scope int x = 7; cout << "local x in inner scope of main is " << x << endl; } // end new scope cout << "globel x in outer scope of main is " << ::x << endl; cout << "local x in outer scope of main is " << x << endl; cout<<"*************************************************"<<endl; a(); // a has automatic local x b(); // b has static local x c(); // c uses global x cout<<"*************************************************"<<endl; cout<<"Afetr second calling"<<endl; a(); // a reinitializes automatic local x b(); // static local x retains its previous value c(); // global x also retains its value cout <<endl<< "local x in main is " << x <<endl<< endl; return 0; } 5 7 1 5 5
- 16. void a( ) { int x = 25; // initialized each time a is called cout << endl << "local x in a is " << x << " after entering a" << endl; } void b( ) { static int x = 50; // Static initialization only // first time b is called. cout << endl << "local static x is " << x << " on entering b" << endl; x=x+2; } void c( void ) { cout << endl << "global x is " << x << " on entering c" << endl; x *= 10; } 25 50 in first call 10 after second call 1 25 in secon d call 52 in Second call call
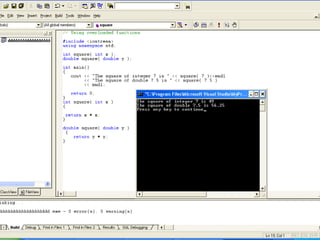
- 18. // Using overloaded functions // Using overloaded functions #include <iostream> using namespace std; int square( int x ); double square( double y ); int main() { cout << "The square of integer 7 is " << square( 7 )<<endl << "The square of double 7.5 is " << square( 7.5 ) << endl; return 0; } int square( int x ) { return x * x; } double square( double y ) { return y * y; }
- 20. // Using default arguments // Using default arguments #include <iostream> using namespace std; int boxVolume( int length = 1, int width = 1, int height = 1 ); int main() { cout << "The default box volume is: " << boxVolume() <<endl; cout<< "width 1 and height 1 is: " << boxVolume( 10 ) << endl; cout << "width 5 and height 1 is: " << boxVolume( 10, 5 ) << endl; cout << "width 5 and height 2 is: " << boxVolume( 10, 5, 2 ) << endl; return 0; } // Calculate the volume of a box int boxVolume( int length, int width, int height ) { return length * width * height; }