Chapter 1
- 1. Er. Nawaraj Bhandari Topic 1 Overview Computer Architecture
- 2. Outline of the Syllabus Computer Evolution and Performance Computer Interconnection Structures Internal Memory External Memory Input/output Operating Systems Support Computer Arithmetic Instruction Sets
- 3. Outline of the Syllabus CPU Structure and Function Reduced Instruction Set Computers Parallel Processing
- 4. Architecture In computer engineering, computer architecture is a set of rules and methods that describe the functionality, organization, and implementation of computer systems Architecture is those attributes visible to the programmer Instruction set, number of bits used for data representation, I/O mechanisms, addressing techniques. *Organization is how features are implemented .Eg. Control signals, interfaces, memory technology
- 5. Architecture All Intel x86 family share the same basic architecture The IBM System/370 family share the same basic architecture This gives code compatibility Organization differs between different versions
- 6. Structure & Function Structure is the way in which components relate to each other Function is the operation of individual components as part of the structure
- 7. Function All computer functions are: Data processing Data storage Data movement Control
- 8. ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania Trajectory tables for weapons Started 1943 Finished 1946 Too late for war effort Used until 1955
- 9. ENIAC - details Decimal (not binary) 20 accumulators of 10 digits Programmed manually by switches 18,000 vacuum tubes 30 tons 15,000 square feet 140 kW power consumption 5,000 additions per second
- 10. von Neumann/Turing Stored Program concept Main memory storing programs and data ALU operating on binary data Control unit interpreting instructions from memory and executing Input and output equipment operated by control unit Princeton Institute for Advanced Studies IAS Completed 1952
- 11. Structure of von Neumann machine
- 12. Transistors Replaced vacuum tubes Smaller Cheaper Less heat dissipation Solid State device Made from Silicon (Sand) Invented 1947 at Bell Labs William Shockley et al.
- 13. Transistor Based Computers Second generation machines NCR & RCA produced small transistor machines IBM 7000 DEC - 1957 Produced PDP-1
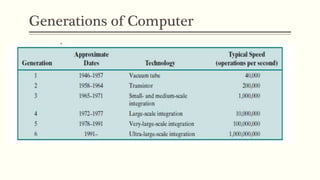
- 15. Generations of Computer Vacuum tube - 1946-1957 Transistor - 1958-1964 Small scale integration - 1965 on Up to 100 devices on a chip Medium scale integration - to 1971 100-3,000 devices on a chip Large scale integration - 1971-1977 3,000 - 100,000 devices on a chip Very large scale integration - 1978 -1991 100,000 - 100,000,000 devices on a chip Ultra large scale integration – 1991 - Over 100,000,000 devices on a chip
- 16. x86 Evolution (1) 8080 The world’s first general-purpose microprocessor. This was an 8-bit machine, with an 8-bit data path to memory. The 8080 was used in the first personal computer, the Altair. 8086 – 5MHz – 29,000 transistors much more powerful 16 bit instruction cache, pre fetch few instructions 8088 (8 bit external bus) used in first IBM PC
- 17. x86 Evolution (2) 80286 16 Mbyte memory addressable up from 1Mb 80386 32 bit Support for multitasking 80486 sophisticated powerful cache and instruction pipelining built in maths co-processor
- 18. x86 Evolution (3) Pentium Superscalar Multiple instructions executed in parallel Pentium Pro Increased superscalar organization Aggressive register renaming branch prediction data flow analysis Pentium II graphics, video & audio processing Pentium III Additional floating point instructions for 3D graphics
- 19. x86 Evolution (4) Pentium 4 Further floating point and multimedia enhancements Core First x86 with dual core Core 2 64 bit architecture Core 2 Quad – 3GHz – 820 million transistors Four processors on chip
- 20. x86 Evolution (4) x86 architecture dominant outside embedded systems Organization and technology changed dramatically Instruction set architecture evolved with backwards compatibility ~1 instruction per month added 500 instructions available
- 21. ANY QUESTIONS?